java API
提示:
注意在使用基本数据类型 (四项八类 字符、整型、浮点、布尔)的时候可以直接传入参数。其他的需要new对象进行传入(匿名或者声明)
equals方法:
我们经常遇到过两个对象的比较,判断2个对象是否相等的情况,在python中,因为不是强类型语言,在比较基本数据类型的时候,我们一般用== 在比较对象的时候,根据对象的属性判断对象是否相等。
在java中也是,在比较对象的时候根据对象的属性值来判断,在java中,所有java类的超类是object(Class Object is the root of the class hierarchy. Every class has Object as a superclass. All objects, including arrays, implement the methods of this class.),object本身为我们提供了一些方法,为子类可以对object的方法进行重写。
equals方法:
object中equal方法,只是比较2个对象的内存地址是否相等(内部用==比较),如下:
1 package com.test; 2 3 public class Equal_Demo { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 equal p1=new equal("tom"); 6 equal p2=new equal("tom"); 7 if(p1.equals(p2)){ 8 System.out.printf("相等"); 9 }else { 10 System.out.printf("不相等"); 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 class equal{ 15 private String name; 16 public equal(String name){ 17 this.name=name; 18 } 19 public void show(){ 20 System.out.printf("ok"); 21 } 22 }
输出:

object类实现:
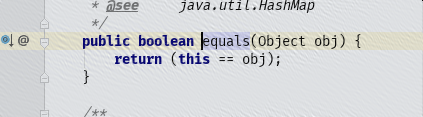
内部实际上使用==来比较2个对象内存地址是否相等。这个并不是我们想要的,因为有时候我们对2个对象的属性值相等即可。比如上面的我们认为对象的name属性相等的话,就认为这2个对象相等。
我们重写equals方法。
1 package com.test; 2 3 public class Equal_Demo { 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 equal p1=new equal("tom"); 6 equal p2=new equal("tom"); 7 if(p1.equals(p2)){ 8 System.out.printf("相等"); 9 }else { 10 System.out.printf("不相等"); 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 class equal{ 15 private String name; 16 public equal(String name){ 17 this.name=name; 18 } 19 public void show(){ 20 System.out.printf("ok"); 21 } 22 public boolean equals(Object obj){ 23 if(obj==this){//this 是当前被调用对象。如果对象的内存地址相等的话,必然相等。 24 return true; 25 } 26 if(obj instanceof equal){ 27 equal p=(equal) obj;//因为obj是Object 对象所以并不包含子类的字段,所以需要向下转型。 28 if(this.name==p.name){//判断字段的相等性. 29 return true; 30 }else { 31 return false; 32 } 33 }else { 34 return false; 35 } 36 } 37 }
注意:
在方法中当前调用对象为this引用。
字段是当前类的属性,如上例子,object为父类所以无法调用子类的字段,如果想调用的话,需要类型转换。
二:在Object中,也toString方法。Returns a string representation of the object. 默认返回对象的内存地址。
1 package test01; 2 3 public class Tostring { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 Check_Prin p1=new Check_Prin("tom","22"); 6 System.out.printf(p1.toString()); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class Check_Prin{ 11 private String age; 12 private String name; 13 public Check_Prin(String name,String age){ 14 this.name=name; 15 this.age=age; 16 } 17 public void show(){ 18 System.out.printf("PK"); 19 } 20 }
输出结果:
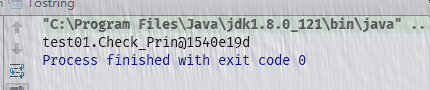
输出是对象的内存地址。所以我们需要重写Object的tostring方法。一般当我们System的输出打印对象的时候,会调用对象的tostring方法。如果对象的类没有重写这个方法,会调用父类的toString方法。
类似python 中的内置方法__str__方法。在输出字符串的时候,我们更像要得到的是对象的属性信息。如下:
1 package test01; 2 3 public class Tostring { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 Check_Prin p1=new Check_Prin("tom","22"); 6 System.out.printf(p1.toString()); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class Check_Prin{ 11 private String age; 12 private String name; 13 public Check_Prin(String name,String age){ 14 this.name=name; 15 this.age=age; 16 } 17 public void show(){ 18 System.out.printf("PK"); 19 } 20 public String toString(){ 21 return this.name+" "+this.age; 22 } 23 }
效果:

三:String类。
String类是public final class String extends Object implements Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence 是不可被继承类。字符串类一旦被创建之后,不可以被更改。(Strings are constant; their values cannot be changed after they are created. String buffers support mutable strings.)
赋值不需要new。
1 String str = "abc";
初始化字符串:
1 String() 2 String(byte[] bytes) 3 String(byte[] bytes, Charset charset) 4 String(byte[] ascii, int hibyte)
代码:
1 public class String_Test { 2 public static void main(String ...args){ 3 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 4 s.Pri(); 5 } 6 } 7 8 class In_Str{ 9 private String s_a= new String(); 10 byte[] s_b=new byte[]{1,2,3,4}; 11 byte[] s_c={1,3,4,5}; 12 String S_d=new String(s_b); 13 char[] ch_s=new char[]{'a','b','c'}; 14 String ch_str=new String(ch_s); 15 public void Pri(){ 16 System.out.printf(this.S_d); 17 String s_g=new String(new byte[]{1,2,3,4}); 18 System.out.printf(s_g); 19 System.out.printf(ch_str); 20 } 21 }
之前学习python的时候,我们常用的String方法比如说 分片、切割、获取索引等等。
类似分片:
substring方法:
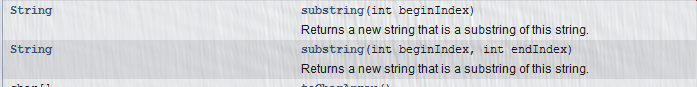
返回值为String类型,参数为int 为字符串的切割起始,可以是单个参数也可以是2个参数,一个默认为到最后。和python切片一样。
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 Sub s=new Sub(); 6 s.sub(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 11 class Sub{ 12 String sub="owner"; 13 public void sub(){ 14 System.out.printf(sub.substring(1)+"\n"); 15 System.out.printf(sub.substring(1,2)); 16 17 18 } 19 }
以什么字符串开头和结尾,返回值为布尔类型:
bool startWith(String) bool endWith(String)
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 private String s_a= new String(); 12 byte[] s_b=new byte[]{1,2,3,4}; 13 byte[] s_c={1,3,4,5}; 14 String S_d=new String(s_b); 15 char[] ch_s=new char[]{'a','b','c'}; 16 String ch_str=new String(ch_s); 17 public void Pri(){ 18 if(ch_str.startsWith("a")){ 19 System.out.printf("ok"); 20 }else if (ch_str.endsWith("f")){ 21 System.out.printf("not end f\n"); 22 }; 23 } 24 }
判断字符串是否包含以及所在字符串的索引:
bool contains(String str) int str.indexof(substr) 判断包含,则返回相应的索引,不包含的返回-1,返回是第一次匹配的索引。
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 char[] ch_s=new char[]{'a','b','c','d','f'}; 12 String ch_str=new String(ch_s); 13 public void Pri(){ 14 if(ch_str.contains("ab")){ 15 System.out.printf("contains\n"); 16 int ind=ch_str.indexOf("ab"); 17 int ind1=ch_str.indexOf("dd"); 18 System.out.printf(ind+"\n"); 19 System.out.print(ind1); 20 } 21 } 22 }
存在就返回相应的索引,否则返回-1。

获取字符串和字节数组:char[] toCharArray(string) byte[] getBytes()
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 char[] ch_s=new char[]{'a','b','c','d','f'}; 12 String ch_str=new String(ch_s); 13 public void Pri(){ 14 char[] s_ch=ch_str.toCharArray(); 15 byte[] s_ch_1=ch_str.getBytes(); 16 for(char i:s_ch){ 17 System.out.print(i+"\n"); 18 } 19 System.out.print(s_ch_1); 20 } 21 }
判断两个字符串是否相等,因为String类中已经重写对应的equals方法,所以判断2个字符串对象是否相等使用equeals()以及忽略大小写比较2个字符串是否一样。equalsIgnoreCase()


1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 char[] ch_s=new char[]{'a','b','c','d','f'}; 12 char[] ch_s_1=new char[]{'A','b','c','D','f'}; 13 String ch_str=new String(ch_s); 14 String ch_str_2=new String(ch_s); 15 String ch_str_1=new String(ch_s_1); 16 public void Pri(){ 17 if(ch_str.equalsIgnoreCase(ch_str_1)){ 18 System.out.printf("相等!"); 19 } 20 if(ch_str.equals(ch_str_2)){ 21 System.out.printf("相等!"); 22 } 23 } 24 }
判断字符串是否为空:bool isEmpty()
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 String ch_str=new String(); 12 public void Pri(){ 13 if(this.ch_str.isEmpty()){ 14 System.out.printf("is empty"); 15 } 16 } 17 }
获取指定位置的字符: char charAt(int index) 去掉字符串的首尾的空格和回车 str.trim()
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 String str=new String("chi ckck \n"); 12 public void Pri(){ 13 System.out.print(str.trim()+'\n'); 14 System.out.print(str.charAt(2)); 15 } 16 }
字符串的大小写转换:toUpperCase(str) toLowerCase()
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 String str=new String("cHi ckck \n"); 12 public void Pri(){ 13 System.out.printf(str.toUpperCase());//大写转换。 14 System.out.printf(str.toLowerCase());//小写转换. 15 } 16 }
将给定新旧的字符转换成新的字符 replace(old char,new char)
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 String str=new String("cHi ckck \n"); 12 public void Pri(){ 13 System.out.printf(str.replace('H','p')); 14 } 15 }
将给定的旧的字符串转换成新的字符串 replace(old str,new str)
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 String str=new String("cHi ckck \n"); 12 public void Pri(){ 13 System.out.printf(str.replace("Hi","koo")); 14 } 15 }
字符串的切割:String[] str.split()切割字符串 返回字符串数组。
1 package test02; 2 3 public class String_Test { 4 public static void main(String ...args){ 5 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 6 s.Pri(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 class In_Str{ 11 String str=new String("cHi ckck \n"); 12 public void Pri(){ 13 String[] new_str=str.split("i"); 14 for(String i:new_str){ 15 System.out.print(i+'\n'); 16 } 17 } 18 }
练习:
题目一:获取指定字符串中,大写字母、小写字母、数字的个数。
1 package test02; 2 3 4 import java.util.ArrayList; 5 6 public class String_Test { 7 public static void main(String ...args){ 8 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 9 s.Pri(); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class In_Str{ 14 String str=new String("cHi1T2ckc2k"); 15 char[] ch_n=str.toCharArray(); 16 private int upcount=0; 17 private int lowcount=0; 18 private int numcount=0; 19 public void Pri(){ 20 for (char i:ch_n){ 21 if('A'<i && i<'Z'){ 22 this.upcount+=1; 23 } 24 if('a'<i&& i<'z'){ 25 this.lowcount+=1; 26 } 27 if('1'<i && i<'9'){ 28 this.numcount+=1; 29 } 30 31 32 } 33 34 System.out.print(lowcount+"\n"); 35 System.out.print(upcount+"\n"); 36 System.out.print(numcount+"\n"); 37 38 } 39 }
注意:+加号在字符串中是连接的作用,在字符中意思求和!!!!
可以直接用字符来直接比较大小!!!
&&和&区别:&&是 前一个表达式为false,则不执行右边的表达式。而&为无论左边表达式是否为false都执行右边。相同点是:只有所有表达式为正确才true。同理||和|
题目二:将字符串中,第一个字母转换成大写,其他字母转换成小写,并打印改变后的字符串。
1 package test02; 2 3 4 import java.util.ArrayList; 5 6 public class String_Test { 7 public static void main(String ...args){ 8 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 9 s.Pri(); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class In_Str{ 14 String str=new String("cHi1T2ckc2k"); 15 char[] ch_n=str.toCharArray(); 16 public void Pri(){ 17 String start =str.substring(0,1); 18 String end=str.substring(1); 19 String new_start=start.toUpperCase(); 20 String new_end=end.toLowerCase(); 21 String new_str=new_start+new_end; 22 System.out.print(new_str); 23 24 }
题目三:查询大字符串中,出现指定小字符串的次数。如“hellojava,nihaojava,javazhenbang”中查询出现“java”的次数。
1 package test02; 2 3 4 import java.util.ArrayList; 5 6 public class String_Test { 7 public static void main(String ...args){ 8 In_Str s=new In_Str(); 9 s.Pri(); 10 } 11 } 12 13 class In_Str{ 14 String str=new String("hellojava,nihaojava,javazhenbang"); 15 int re_count=0; 16 public void Pri(){ 17 int st_index=0; 18 while (st_index!= -1) { 19 if (str.indexOf("java") != -1) { 20 re_count += 1; 21 st_index = str.indexOf("java"); 22 str = str.substring(st_index + 1); 23 }else { 24 st_index=-1; 25 } 26 } 27 System.out.print(re_count); 28 29 } 30 }
三:StringBuffer 字符串可变缓冲区。有append、insert、replace、reverse等方法,注意操作之后也是StringBuffer 需要用toString来获取对应字符串。
StringBuilder类,比StringBuilder 处理速度更快,建议使用这个类。
1 package test03; 2 3 public class Str_Bu { 4 public static void main(String...args){ 5 S_B s_b=new S_B("winner"); 6 s_b.ch_str(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 11 class S_B{ 12 private String str; 13 public S_B(String str){ 14 this.str=str; 15 } 16 public void ch_str(){ 17 StringBuffer st_bu=new StringBuffer(str); 18 st_bu.append("ok");//尾部追加。 19 st_bu.insert(2,"ko");//指定位置添加字符串。 20 System.out.printf(st_bu.toString()+'\n'); 21 st_bu.delete(1,111); 22 System.out.printf(st_bu.toString()); 23 st_bu.replace(1,3333,"ooop"); 24 System.out.printf(st_bu.toString()+"\n"); 25 st_bu.reverse(); 26 System.out.printf(st_bu.toString()); 27 } 28 }
输出:
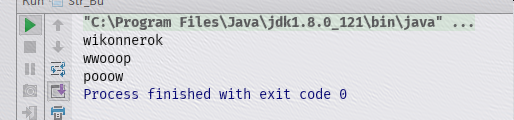
练习:
l 从指定位置开始,到末尾结束,截取该字符串缓冲区,返回新字符串
1 package test03; 2 3 public class Str_Bu { 4 public static void main(String...args){ 5 S_B s_b=new S_B("winner"); 6 s_b.ch_str(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 11 class S_B{ 12 private String str; 13 public S_B(String str){ 14 this.str=str; 15 } 16 public void ch_str(){ 17 StringBuffer st_bu=new StringBuffer(str); 18 String st_new=st_bu.substring(3); 19 System.out.printf(st_new); 20 } 21 }
在原有字符串缓冲区内容基础上,删除指定位置上的字符
1 package test03; 2 3 public class Str_Bu { 4 public static void main(String...args){ 5 S_B s_b=new S_B("winner"); 6 s_b.ch_str(); 7 } 8 } 9 10 11 class S_B{ 12 private String str; 13 public S_B(String str){ 14 this.str=str; 15 } 16 public void ch_str(){ 17 StringBuffer st_bu=new StringBuffer(str); 18 st_bu.deleteCharAt(2); 19 System.out.printf(st_bu.toString()); 20 } 21 }
方法的链式调用:即一个方法的返回是一个对象,我们可 以基于这个对象继续调用对象,这种形式叫做方法的调用,比如:st_bu是StringBuffer对象。
1 st_bu.deleteCharAt(2).append("ok").append("oooo");
练习:int[] arr = {34,12,89,68};将一个int[]中元素转成字符串 格式 [34,12,89,68]
1 package test03; 2 3 import org.omg.Messaging.SYNC_WITH_TRANSPORT; 4 5 import java.lang.reflect.Array; 6 7 public class Str_Bu { 8 public static void main(String...args){ 9 int[] in_ar={34,12,89,68}; 10 S_B s_b=new S_B(in_ar); 11 s_b.ch_str(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 16 class S_B{ 17 private int[] in; 18 public S_B(int[] in){ 19 this.in=in; 20 } 21 public void ch_str(){ 22 StringBuffer in_bu=new StringBuffer(); 23 for(int i=0;i<this.in.length;i++){ 24 if(i==0){ 25 in_bu.append("["); 26 in_bu.append(Array.get(this.in,i)); 27 }else if (i==this.in.length-1){ 28 in_bu.append(Array.get(this.in,i)); 29 in_bu.append("]"); 30 }else{ 31 in_bu.append(Array.get(this.in,i)); 32 } 33 34 }; 35 System.out.printf(in_bu.toString()); 36 } 37 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号