vue-router 工作原理
简述
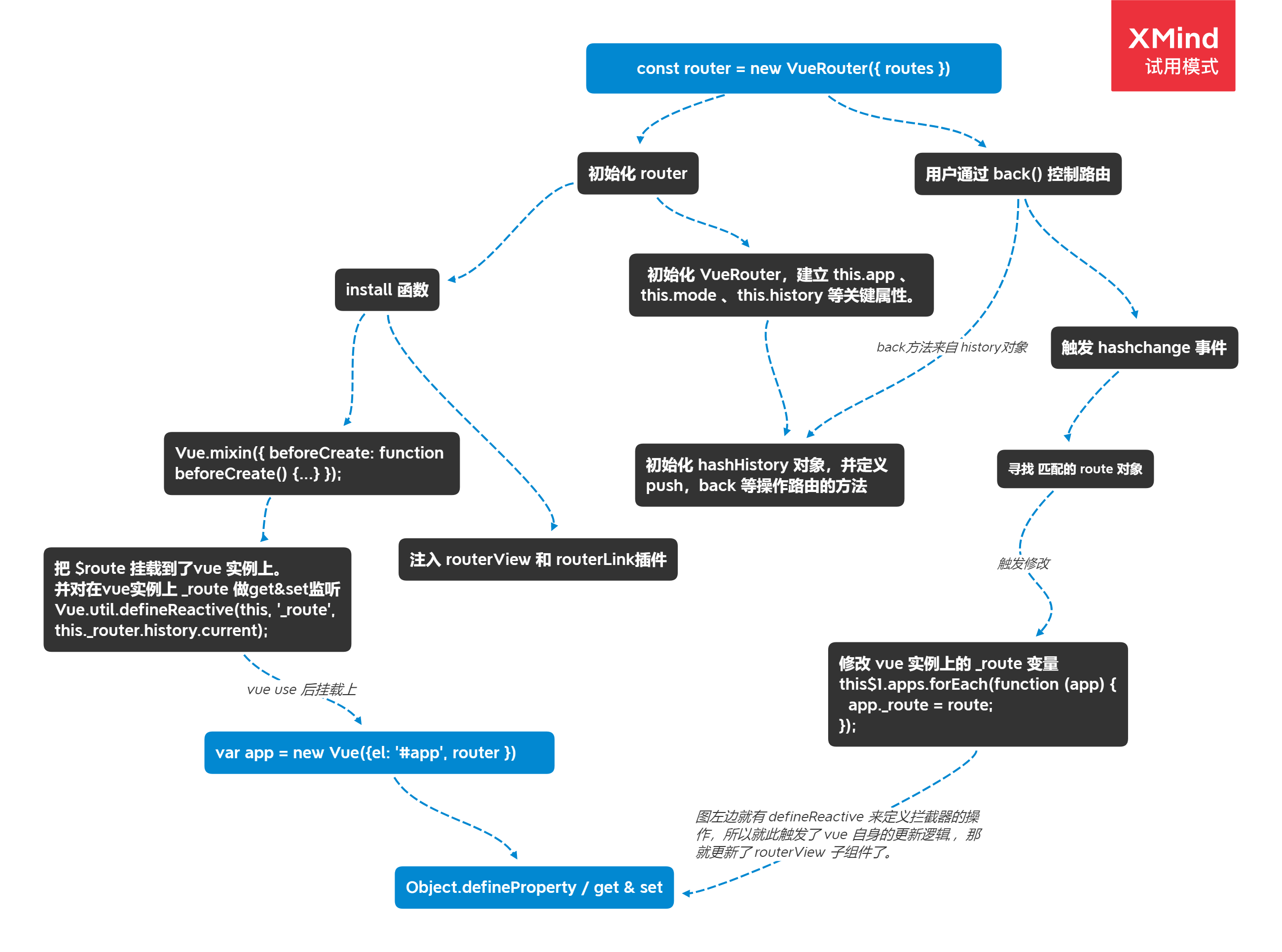
hashchange
-->
match route
-->
set vm._route
-->
<router-view> render()
-->
render matched component
监听hashchange方法
window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => {
// this.transitionTo(...)
})
进行地址匹配,得到对应当前地址的 route。
将其设置到对应的 vm._route 上。侵入vue监听_route变量而触发更新流程
最后是router-view组件调用render函数渲染匹配到的route
测试代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>vue test</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1>Hello App!</h1>
<button @click="goBack">click me and go back</button>
<button @click="goIndex">click me and go to index</button>
<p>
<router-link to="/foo">Go to Foo</router-link>
</p>
<p>
<router-link to="/bar">Go to Bar</router-link>
</p>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<!-- Vue.js v2.6.11 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue-router/3.1.3/vue-router.js"></script>
<script>
const Foo = { template: '<div>render foo</div>' }
const Bar = { template: '<div>render bar</div>' }
const routes = [
{ path: '/foo', component: Foo },
{ path: '/bar', component: Bar }
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes // (缩写) 相当于 routes: routes
})
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
methods: {
goBack() {
this.$router.back();
},
goIndex() {
this.$router.push('/');
}
}
})
console.log(app);
// var event = new CustomEvent('test', { 'detail': 5 }); window.dispatchEvent(event);
</script>
</body>
</html>
怎么注入进的 vue
一个 install 函数,把 $route 挂载到了 Vue.prototype 上,保证 Vue 的所有组件实例,都是取同一份 router。并且在里面注册了 RouterView 和 RouterLink 组件
function install(Vue) {
// ...
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate: function beforeCreate() {
// ...
this._routerRoot = this;
this._router = this.$options.router;
this._router.init(this);
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current);
// ...
},
destroyed: function destroyed() {
// ...
}
});
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$router', {
get: function get() { return this._routerRoot._router }
});
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$route', {
get: function get() { return this._routerRoot._route }
});
Vue.component('RouterView', View);
Vue.component('RouterLink', Link);
// ...
}
VueRouter.install = install;
最后进入了 vue 的初始化逻辑里 initUse 函数里去触发插件的 install 函数执行。
router 是个什么结构
详见 function VueRouter (options),下面代码中需要注意三点:
- app 将会挂上 vue 实例对象
- mode 代表用户配置的路由模式,默认是 hash,也就是使用 url 上的 hash 部分作为路由路径的判定。
- history 将会挂载上用户曾经的访问的记录数组。
var VueRouter = function VueRouter (options) {
this.app = null;
this.apps = [];
this.options = options;
this.beforeHooks = [];
this.resolveHooks = [];
this.afterHooks = [];
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this);
var mode = options.mode || 'hash';
// ...
this.mode = mode;
switch (mode) {
case 'history':
this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base);
break
case 'hash':
this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback);
break
case 'abstract':
this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base);
break
default:
{
assert(false, ("invalid mode: " + mode));
}
}
};
RouterView 组件长什么样
看下文代码,总结一下关键的步骤:
最关键的一步 var component = cache[name] = matched.components[name]; 获取到具体是那个组件,这里的 component 其实是
{
template: "<div>render bar</div>"
_Ctor: {0: ƒ}
__proto__: Object
}
然后最后面就是调用 h(component, data, children) 完成渲染,h其实是 Vue 实例的 $createElement 函数,它会具体解析此 template 成为视图渲染。
var View = {
name: 'RouterView',
functional: true,
props: {
name: {
type: String,
default: 'default'
}
},
render: function render (_, ref) {
var props = ref.props;
var children = ref.children;
var parent = ref.parent;
var data = ref.data;
// used by devtools to display a router-view badge
data.routerView = true;
// directly use parent context's createElement() function
// so that components rendered by router-view can resolve named slots
var h = parent.$createElement;
var name = props.name;
var route = parent.$route;
var cache = parent._routerViewCache || (parent._routerViewCache = {});
// ...
var component = cache[name] = matched.components[name];
// ...
return h(component, data, children)
}
};
RouterLink 呢?
很精妙,此组件的 props 默认把 tag 设置为 a,并且代码中还支持 slotScope 插槽。
最后一样 h(this.tag, data, this.$slots.default) 去渲染,所以此组件渲染后的标签才会默认是 a 标签呀。。
var Link = {
name: 'RouterLink',
props: {
to: {
type: toTypes,
required: true
},
tag: {
type: String,
default: 'a'
},
exact: Boolean,
append: Boolean,
replace: Boolean,
activeClass: String,
exactActiveClass: String,
event: {
type: eventTypes,
default: 'click'
}
},
render: function render(h) {
var router = this.$router;
var current = this.$route;
var ref = router.resolve(
this.to,
current,
this.append
);
// ...
var href = ref.href;
// ...
var data = { class: classes };
var scopedSlot =
!this.$scopedSlots.$hasNormal &&
this.$scopedSlots.default
// ...
if (scopedSlot) {
if (scopedSlot.length === 1) {
return scopedSlot[0]
} else if (scopedSlot.length > 1 || !scopedSlot.length) {
// ...
return scopedSlot.length === 0 ? h() : h('span', {}, scopedSlot)
}
}
if (this.tag === 'a') {
data.on = on;
data.attrs = { href: href };
} else {
// ...
}
return h(this.tag, data, this.$slots.default)
}
};
路由控制是怎么做的
本质上就是改变了 hash
hashchange 的事件监听触发,接着去触发 HashHistory 实例里的 updateRoute 函数,updateRoute 函数里触发回调去更新 route 对象,route 对象更新就走入了 vue 自身的 set 触发广播通知被观察者了。
VueRouter.prototype.back = function back () {
this.go(-1);
};
VueRouter.prototype.go = function go (n) {
this.history.go(n);
};
HashHistory.prototype.go = function go (n) {
window.history.go(n);
};
// ...
window.addEventListener(
supportsPushState ? 'popstate' : 'hashchange',
function () {
var current = this$1.current;
// ...
this$1.transitionTo(getHash(), function (route) {
if (supportsScroll) {
handleScroll(this$1.router, route, current, true);
}
if (!supportsPushState) {
replaceHash(route.fullPath);
}
});
}
);
// ...
History.prototype.transitionTo = function transitionTo(
location,
onComplete,
onAbort
) {
var this$1 = this;
var route = this.router.match(location, this.current);
this.confirmTransition(
route,
function () {
this$1.updateRoute(route);
// ...
},
function (err) {
// ...
}
);
};
// ...
History.prototype.updateRoute = function updateRoute(route) {
var prev = this.current;
this.current = route;
// 这里的 cb 就是下面一段的 history.listen
this.cb && this.cb(route);
this.router.afterHooks.forEach(function (hook) {
hook && hook(route, prev);
});
};
// ...
history.listen(function (route) {
this$1.apps.forEach(function (app) {
// 改变 app._route 就会进入 vue 实例自身的 get/set 拦截器中,然后自己触发更新。
// 因为上文 install 函数里做了属性劫持 Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current);
app._route = route;
});
});
钩子是怎么做的
this.beforeHooks 是个数组,registerHook 函数做的就只是往前面的数组里添加进入这个方法。
VueRouter.prototype.beforeEach = function beforeEach(fn) {
return registerHook(this.beforeHooks, fn)
};
VueRouter.prototype.beforeResolve = function beforeResolve(fn) {
return registerHook(this.resolveHooks, fn)
};
VueRouter.prototype.afterEach = function afterEach(fn) {
return registerHook(this.afterHooks, fn)
};
beforeHooks 在每次触发更新前的队列里调用
resolveHooks 执行是在下文的 runQueue 里,也就是是在触发更新前,但比 beforeHooks 晚,主要用于异步组件
afterHooks 的触发,是在 updateRoute 函数后,也就是开始触发 vue 的更新逻辑时,但并不一定视图已经更新完毕,因为 vue 自身也有不少的队列操作,不会立即更新。
// beforeHooks
var queue = [].concat(
// in-component leave guards
extractLeaveGuards(deactivated),
// global before hooks
this.router.beforeHooks,
// in-component update hooks
extractUpdateHooks(updated),
// in-config enter guards
activated.map(function (m) { return m.beforeEnter; }),
// async components
resolveAsyncComponents(activated)
);
runQueue(queue, iterator, function () {
// ...
}
// resolveHooks
runQueue(queue, iterator, function () {
// ...
// wait until async components are resolved before
// extracting in-component enter guards
var enterGuards = extractEnterGuards(activated, postEnterCbs, isValid);
var queue = enterGuards.concat(this$1.router.resolveHooks);
runQueue(queue, iterator, function () {
//...
onComplete(route);
//...
});
});
// afterHooks
History.prototype.updateRoute = function updateRoute(route) {
var prev = this.current;
this.current = route;
this.cb && this.cb(route);
this.router.afterHooks.forEach(function (hook) {
hook && hook(route, prev);
});
};
history 是怎么做的
hash 模式的路由是采用的 hash change 函数来做监听,并且操作浏览器 hash 做标识,
而 history 模式采用的 popstate event 来记住路由的状态,而 window.history.state 里的 key 只是用时间来生成的一个缓存。
HTML5History.prototype.push = function push (location, onComplete, onAbort) {
var this$1 = this;
var ref = this;
var fromRoute = ref.current;
this.transitionTo(location, function (route) {
pushState(cleanPath(this$1.base + route.fullPath));
handleScroll(this$1.router, route, fromRoute, false);
onComplete && onComplete(route);
}, onAbort);
};
function pushState (url, replace) {
saveScrollPosition();
// try...catch the pushState call to get around Safari
// DOM Exception 18 where it limits to 100 pushState calls
var history = window.history;
try {
if (replace) {
history.replaceState({ key: getStateKey() }, '', url);
} else {
history.pushState({ key: setStateKey(genStateKey()) }, '', url);
}
} catch (e) {
window.location[replace ? 'replace' : 'assign'](url);
}
}
function genStateKey () {
return Time.now().toFixed(3)
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号