3.JAVA语言基础部分—Class类与反射
什么是Java反射机制?
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法;这种动态获取的以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为Java的反射机制。
反射机制提供了哪些功能?
-
在运行时判定任意一个对象所属的类
-
在运行时构造任意一个类的对象;
-
在运行时判定任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法;
-
在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法;
-
生成动态代理;
Java反射机制类:
java.lang.Class; //类 java.lang.reflect.Constructor;//构造方法 java.lang.reflect.Field; //类的成员变量 java.lang.reflect.Method;//类的方法 java.lang.reflect.Modifier;//访问权限
Java反射机制实现:
1.)class对象的获取
//第一种方式 通过对象getClass方法
Person person = new Person();
Class<?> class1 = person.getClass();
//第二种方式 通过类的class属性
class1 = Person.class;
try {
//第三种方式 通过Class类的静态方法——forName()来实现
class1 = Class.forName("com.whoislcj.reflectdemo.Person");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
2.)获取class对象的摘要信息
boolean isPrimitive = class1.isPrimitive();//判断是否是基础类型(boolean、char、byte、short、int、long、float、double) boolean isArray = class1.isArray();//判断是否是集合类 boolean isAnnotation = class1.isAnnotation();//判断是否是注解类 boolean isInterface = class1.isInterface();//判断是否是接口类 boolean isEnum = class1.isEnum();//判断是否是枚举类 boolean isAnonymousClass = class1.isAnonymousClass();//判断是否是匿名内部类 boolean isAnnotationPresent = class1.isAnnotationPresent(Deprecated.class);//判断是否被某个注解类修饰 String className = class1.getName();//获取class名字 包含包名路径 Package aPackage = class1.getPackage();//获取class的包信息 String simpleName = class1.getSimpleName();//获取class类名 int modifiers = class1.getModifiers();//获取class访问权限 Class<?>[] declaredClasses = class1.getDeclaredClasses();//内部类 Class<?> declaringClass = class1.getDeclaringClass();//外部类
3.)获取class对象的属性、方法、构造函数等
Field[] allFields = class1.getDeclaredFields();//获取class对象的所有属性
Field[] publicFields = class1.getFields();//获取class对象的public属性
try {
Field ageField = class1.getDeclaredField("age");//获取class指定属性
Field desField = class1.getField("des");//获取class指定的public属性
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Method[] methods = class1.getDeclaredMethods();//获取class对象的所有声明方法
Method[] allMethods = class1.getMethods();//获取class对象的所有方法 包括父类的方法
Class parentClass = class1.getSuperclass();//获取class对象的父类
Class<?>[] interfaceClasses = class1.getInterfaces();//获取class对象的所有接口
Constructor<?>[] allConstructors = class1.getDeclaredConstructors();//获取class对象的所有声明构造函数
Constructor<?>[] publicConstructors = class1.getConstructors();//获取class对象public构造函数
try {
Constructor<?> constructor = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(new Class[]{String.class});//获取指定声明构造函数
Constructor publicConstructor = class1.getConstructor(new Class[]{});//获取指定声明的public构造函数
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Annotation[] annotations = class1.getAnnotations();//获取class对象的所有注解
Annotation annotation = class1.getAnnotation(Deprecated.class);//获取class对象指定注解
Type genericSuperclass = class1.getGenericSuperclass();//获取class对象的直接超类的 Type
Type[] interfaceTypes = class1.getGenericInterfaces();//获取class对象的所有接口的type集合
4.)class对象动态生成
//第一种方式 Class对象调用newInstance()方法生成
Object obj = class1.newInstance();
//第二种方式 对象获得对应的Constructor对象,再通过该Constructor对象的newInstance()方法生成
Constructor<?> constructor = class1.getDeclaredConstructor(new Class[]{String.class});//获取指定声明构造函数
obj = constructor.newInstance(new Object[]{"lcj"});5.)动态调用函数
try {
// 生成新的对象:用newInstance()方法
Object obj = class1.newInstance();
//判断该对象是否是Person的子类
boolean isInstanceOf = obj instanceof Person;
//首先需要获得与该方法对应的Method对象
Method method = class1.getDeclaredMethod("setAge", new Class[]{int.class});
//调用指定的函数并传递参数
method.invoke(obj, 28);
method = class1.getDeclaredMethod("getAge");
Object result = method.invoke(obj, new Class[]{});
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
6.)通过反射机制获取泛型类型
例如下面这种结构
//People类
public class People<T> {}
//Person类继承People类
public class Person<T> extends People<String> implements PersonInterface<Integer> {}
//PersonInterface接口
public interface PersonInterface<T> {}获取泛型类型
Person<String> person = new Person<>(); //第一种方式 通过对象getClass方法 Class<?> class1 = person.getClass(); Type genericSuperclass = class1.getGenericSuperclass();//获取class对象的直接超类的 Type Type[] interfaceTypes = class1.getGenericInterfaces();//获取class对象的所有接口的Type集合 getComponentType(genericSuperclass); getComponentType(interfaceTypes[0]);
getComponentType具体实现
private Class<?> getComponentType(Type type) {
Class<?> componentType = null;
if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {
//getActualTypeArguments()返回表示此类型实际类型参数的 Type 对象的数组。
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType) type).getActualTypeArguments();
if (actualTypeArguments != null && actualTypeArguments.length > 0) {
componentType = (Class<?>) actualTypeArguments[0];
}
} else if (type instanceof GenericArrayType) {
// 表示一种元素类型是参数化类型或者类型变量的数组类型
componentType = (Class<?>) ((GenericArrayType) type).getGenericComponentType();
} else {
componentType = (Class<?>) type;
}
return componentType;
}
6.)通过反射机制获取注解信息
这里重点以获取Method的注解信息为例
try {
//首先需要获得与该方法对应的Method对象
Method method = class1.getDeclaredMethod("jumpToGoodsDetail", new Class[]{String.class, String.class});
Annotation[] annotations1 = method.getAnnotations();//获取所有的方法注解信息
Annotation annotation1 = method.getAnnotation(RouterUri.class);//获取指定的注解信息
TypeVariable[] typeVariables1 = method.getTypeParameters();
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotationsArray = method.getParameterAnnotations();//拿到所有参数注解信息
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();//获取所有参数class类型
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();//获取所有参数的type类型
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();//获取方法的返回类型
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();//获取方法的访问权限
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
反射机制的应用场景:
- 逆向代码 ,例如反编译
- 与注解相结合的框架 例如Retrofit
- 单纯的反射机制应用框架 例如EventBus 2.x
- 动态生成类框架 例如Gson
反射机制的优缺点:
优点:
运行期类型的判断,动态类加载,动态代理使用反射。
缺点:
性能是一个问题,反射相当于一系列解释操作,通知jvm要做的事情,性能比直接的java代码要慢很多。
以上转自https://www.cnblogs.com/whoislcj/p/6038511.html
annotaion注释
定义annotaion的写法
例1,定义用于构造方法的annotation
/**
* 定义一个用于构造方法的annotation ,使用@interface定义
*/
//@Target指定适用于的地方,可以为多个
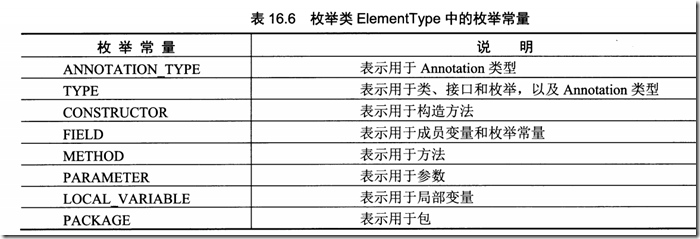
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR)
//指定在运行时加载annotation到jvm中
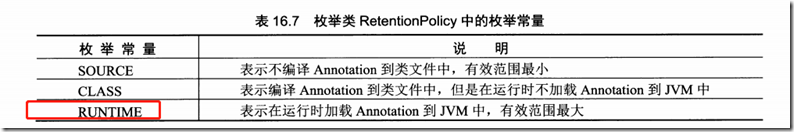
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Constructor_Annotation {
String descn();//定义一个成员
String value2() default "默认字符串";//定义一个具有默认值的成员
Class type() default Void.class;
}
例2,定义用于字段、方法、方法参数的注释
//可以同时指定适用多种类型
@Target({ ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion {
String desc();
Class type() default Void.class;
}
在使用类中调用annotation
public class Example01 {
//字段的注释
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion(desc="变量i",type=int.class)
int i;
//调用用于构造方法的annotation
@Constructor_Annotation(descn="初始化构造方法",value2="test",type=Example01.class)
public Example01() {
}
//用于参数
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion(desc="say方法",type=String.class)
public String say(
//此写法用方法里面的参数
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion(desc="方法参数name",type=String.class)
String name) {
return name;
}
}
通过反射获得类的注释内容
public static void main(String[] args) {
Example01 example01 = new Example01();
//反射得到Class
Class cls = example01.getClass();
//获取所有构造方法
Constructor[] ccs=cls.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor c:ccs) {
//判断是否有指定类型的注释
if(c.isAnnotationPresent(Constructor_Annotation.class)) {
//获得指定的annotation
Constructor_Annotation ca=(Constructor_Annotation)c.getAnnotation(Constructor_Annotation.class);
print(ca.descn());
}
}
//下面为获取字段annotaion,如上面方法一致
Field[] fields=cls.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion.class)) {
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion fmpa=(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion)field.getAnnotation(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion.class);
print(fmpa.desc());
}
}
//下面获取方法参数的annotation
//原理一样,通过反射获取方法,再逐个方法获取所有参数
Method[] methods=cls.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
Parameter[] parameters=method.getParameters();
for (Parameter para : parameters) {
if(para.isAnnotationPresent(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion.class)) {
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion fmpa=(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion)para.getAnnotation(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotaion.class);
print(fmpa.desc());
}
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号