红黑树插入操作原理及java实现
红黑树是一种二叉平衡查找树,每个结点上有一个存储位来表示结点的颜色,可以是RED或BLACK。红黑树具有以下性质:
(1) 每个结点是红色或是黑色
(2) 根结点是黑色的
(3) 如果一个结点是红色的,则它的两个儿子都是黑色的
(4) 对于每个结点,从该结点到其子孙结点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑结点
通过红黑树的性质,可以保证所有基于红黑树的实现都能保证操作的运行时间为对数级别(范围查找除外。它所需的额外时间和返回的键的数量成正比)。
Java的TreeMap就是通过红黑树实现的。
红黑树的操作如果不画图很容易搞糊涂,下面通过图示来说明红黑树的插入操作。
插入一个红色的节点到红黑树中之后,会有6种情况:图示中N表示插入的节点,P表示父节点,U表示叔叔节点,G表示祖父节点,X表示当前操作节点
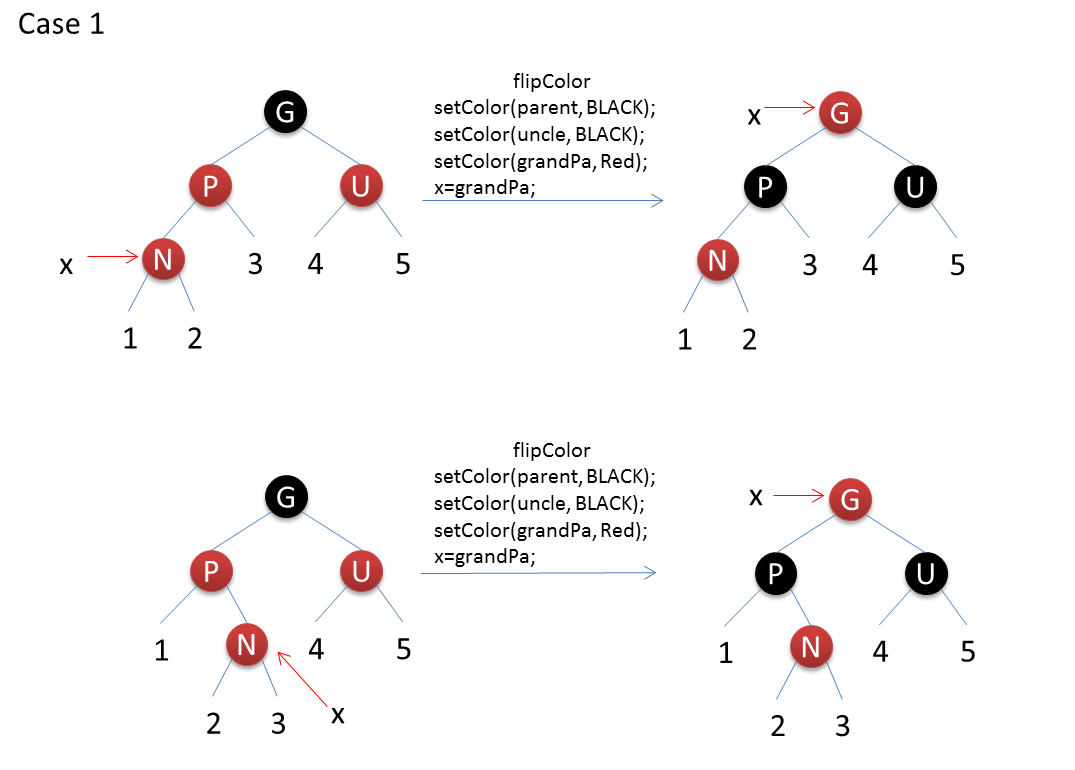



代码如下:
1 public class RedBlackBST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> { 2 private Node root; 3 private static final boolean RED = true; 4 private static final boolean BLACK = false; 5 private class Node{ 6 private Key key; //键 7 private Value val; //值 8 private Node left, right, parent; //左右子树和父节点 9 private boolean color; //由其父节点指向它的链接的颜色 10 11 public Node(Key key, Value val,Node parent, boolean color){ 12 this.key = key; 13 this.val = val; 14 this.color = color; 15 } 16 } 17 18 public Value get(Key key){ 19 Node x = root; 20 while(x!=null){ 21 int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key); 22 if(cmp < 0 ) x = x.left; 23 else if(cmp > 0) x = x.right; 24 else return x.val; 25 } 26 return null; 27 } 28 29 public void put(Key key, Value val){ 30 if(root==null) { //如果是根节点,就将节点新建为黑色 31 root = new Node(key,val,null,BLACK); 32 return; 33 } 34 //寻找合适的插入位置 35 Node parent = null; 36 Node cur = root; 37 while(cur!=null) { 38 parent = cur; 39 if(key.compareTo(cur.key)>0) cur=cur.right; 40 else cur = cur.left; 41 } 42 Node n = new Node(key,val,parent,RED); //普通的新建节点为红色 43 //将新节点插入parent下 44 if(key.compareTo(parent.key) > 0) parent.right = n; 45 else parent.left = n; 46 //插入新节点后要调整树中部分节点的颜色和属性来保证红黑树的特征不被破坏 47 fixAfterInsertion(n); 48 } 49 private Node parentOf(Node x) { 50 return (x==null ? null : x.parent); 51 } 52 private boolean colorOf(Node x) { 53 return (x==null ? BLACK : x.color); 54 } 55 private Node leftOf(Node x) { 56 return (x==null ? null : x.left); 57 } 58 private Node rightOf(Node x) { 59 return(x==null ? null : x.right); 60 } 61 private void setColor(Node x, boolean color) { 62 if(x!=null) 63 x.color = color; 64 } 65 66 private void fixAfterInsertion(Node x) { 67 while(x!=null && colorOf(parentOf(x)) == RED) { 68 Node grandPa = parentOf(parentOf(x)); 69 Node parent = parentOf(x); 70 if(parent == leftOf(grandPa)) {//case 1 || case2 || case3 71 Node uncle = rightOf(grandPa); 72 if(colorOf(uncle) == RED) {//case1, uncle is red 73 setColor(parent,BLACK); //父节点置黑 74 setColor(uncle, BLACK); //叔叔节点置黑 75 setColor(grandPa,RED); //祖父节点置红 76 x = grandPa; //因为祖父节点由黑转红,故要重新调整父节点及其祖先的红黑属性 77 }else {//case2 || case3,uncle is black 78 if(x==rightOf(parent)) { //case2 79 x = parent; 80 rotateLeft(x); 81 } 82 //case3 83 setColor(parent,BLACK); 84 setColor(grandPa, RED); 85 rotateRight(grandPa); 86 } 87 88 }else {//case4 || case 5 || case6 89 Node uncle = leftOf(grandPa); 90 if(colorOf(uncle) == RED) { //case4 || case5 || case6 91 setColor(parent,BLACK); 92 setColor(uncle, BLACK); 93 setColor(grandPa,RED); 94 x = grandPa; 95 }else{ //case5 || case6, uncle is black 96 if(x==leftOf(parent)) { //case5 97 x = parent; 98 rotateRight(x); 99 } 100 //case6 101 setColor(parent,BLACK); 102 setColor(grandPa, RED); 103 rotateLeft(grandPa); 104 } 105 } 106 } 107 } 108 private void rotateLeft(Node x) { 109 if(x==null) return; 110 Node y = x.right; 111 x.right = y.left; 112 if(y.left!=null) 113 y.left.parent = x; 114 y.left = x; 115 y.parent = x.parent; 116 if(x.parent == null) { 117 root = y; 118 } 119 else if(x.parent.left == x) { 120 x.parent.left = y; 121 }else { 122 x.parent.right = y; 123 } 124 x.parent = y; 125 } 126 private void rotateRight(Node x) { 127 if(x==null) return; 128 Node y = x.left; 129 x.left = y.right; 130 if(y.right != null) 131 y.right.parent = x; 132 y.right = x; 133 y.parent = x.parent; 134 if(x.parent == null) { 135 root = y; 136 }else if(x.parent.left==x) { 137 x.parent.left = y; 138 }else { 139 x.parent.right=y; 140 } 141 x.parent = y; 142 } 143 144 }
上面的rotateLeft和rotateRight有必要画个图示:

本文版权归evasean所有,转载请标明出处
http://www.cnblogs.com/evasean/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号