多线程
1 两种方式创建多线程
1.1 第一种
-
定义线程类实现Runnable接口
-
Thread myThread = new Thread(target)target为Runnable接口类型 -
Runnable中只有一个方法——
public void run();用来定义线程运行体 -
使用Runnable接口可以为多个线程提供共享的数据
-
在实现Runnable接口类的run方法定义中可以使用Thread的静态方法——
public static Thread currentThread()获取当前线程的引用
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Runner r = new Runner();
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start(); //线程启动
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Main Thread:------" + i);
}
}
}
class Runner implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Runner :" + i);
}
}
}
1.2 第二种
-
可以定义一个Thread的子类并重写其run方法
class MyThread extends Thread{ public void run() {}} -
然后生成该类的对象
MyThread my Thread = new MyThread()
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Runner r = new Runner();
r.start();
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Main Thread:------" + i);
}
}
}
class Runner extends Thread {
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Runner :" + i);
}
}
}
执行效果:Main 线程和Runner线程交叉 并行运行。
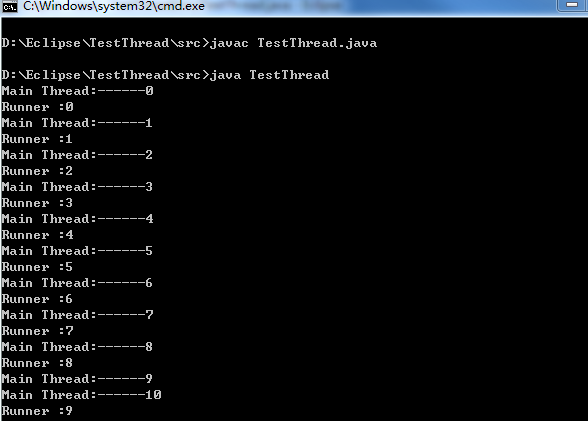
注:以extends继承方式创建线程,Runner不能再继承其他类。而以Runnable接口方式创建线程,可以继续继承其他类,不受约束。通常情况,使用接口方式创建线程。
2 t.start()线程启动和r.run()方法调用的区别
2.1 start()启动
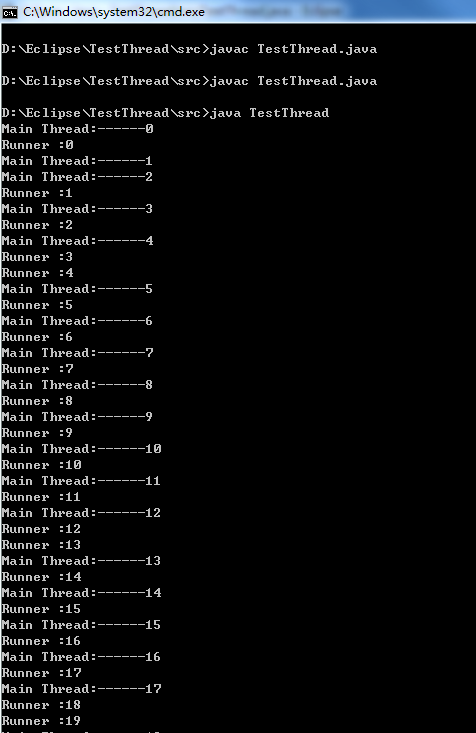
start()启动Runner线程 两个线程并行执行
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Runner r = new Runner();
r.start(); //线程启动
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Main Thread:------" + i);
}
}
}
class Runner extends Thread {
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) {
System.out.println("Runner :" + i);
}
}
}
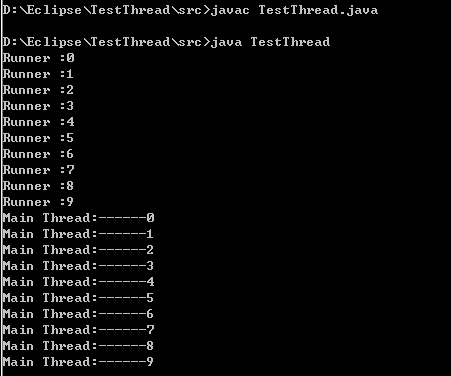
2.2 run()
run()方法调用,Runner线程运行结束后Main线程才开始运行
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Runner r = new Runner();
r.run(); //方法调用
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println("Main Thread:------" + i);
}
}
}
class Runner extends Thread {
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println("Runner :" + i);
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号