Django学习小记2-用户登录实例
首先回顾上节的Django三个基础函数:
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse #返回字符串 from django.shortcuts import render #给他一个数据,再给他一个模板 来渲染后返给用户 from django.shortcuts import redirect #跳转到某个地址
因为request中包含用户请求相关的所有信息(对象),所以可以通过
request.method来看请求的方法【GET\POST】
题外话:GET是以URL的形式传递数据,不安全。
print(request.method)
所以基于此,就可以作为判断,提取用户post提交的表单数据:
if request.method == "GET": return render(request,'login.html') else: #用户POST提交的数据 u = request.POST.get('user') p = request.POST.get('pwd') if u == 'admin' and p == 'admin': #登录成功跳转 return redirect('http://www.baidu.com') else: #登录失败 return render(request,'login.html')
login.html配置:
<form method="POST" action="/login/">
这时候我们发现确实实现的登陆控制,但是没有登陆失败提示啊~!!!
这就用到 {{ msg}}
这个是在html中容载特殊字符的,若没有给他传值,django就不显示。
login.html中: ... <input type="submit" value="登录"/><br> {{ msg }} --------------------- urls.py中: ... else: #登录失败 return render(request,'login.html',{'msg':'用户名或密码错误!'})
其实这个{{ msg}} 就是模板引擎中的特殊标记
除了字符串外,还支持列表和字典、循环、if.else等的特殊标记取值
return render(request,'index.html',{...})
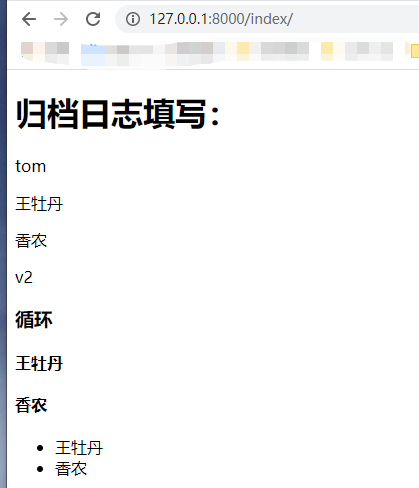
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>日志文档填写</title> </head> <body> <h1>归档日志填写:</h1> <p>{{ name }}</p> <p>{{ users.0 }}</p> <p>{{ users.1 }}</p> <p>{{ user_dict.k2 }}</p> <h3>循环</h3> {% for item in users %} <h4>{{ item }}</h4> {% endfor %} <ul> {% for item in users %} <li>{{ item }}</li> {% endfor %} </ul> </body> </html>
附加补充:
{% if a == b %}
..
{% else %}
..
{% endif %}
urls.py的配置:
def index(request): return render( request, 'index.html', { 'name':'tom', 'users':['王牡丹','香农'], 'user_dict':{'k1':'v1','k2':'v2'}, } ) urlpatterns = [ #path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('login/',login), path('index/',index), ]
注意:
- 特殊标记可以为列表和字典,用 · 来索引取值;
- 特殊标记作为循环时,可以连同标签一块循环,也可以单独循环。
使用场景举例:
接上面index.html:
模板源进行渲染可以加列表加表格增删操作之
... <ul> {% for row in user_dict %} <li>{{ row.id }}--{{row.name}}--{{ row.email }}</li> {% endfor %} </ul> <table border="1"> {% for row in user_dict %} <tr> <td>{{ row.id }}</td> <td>{{ row.name }}</td> <td>{{ row.email }}</td> <td> <a>编辑</a>|<a href="/del/?nid={{ row.id }}">删除</a> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table>
相当于对列表元素进行循环,每一项又是一个字典,所以可以用哪个row.id ...
接上面urls.py 修改为:
... def index(request): return render( request, 'index.html', { 'user_dict':[ {'id':'1','name':'shannon','email':'112334@134.com'}, {'id': '2', 'name': 'yunz', 'email': '11233d4@134.com'}, {'id': '3', 'name': 'tom', 'email': '11233d4@134.com'}, ] } )
执行:

一定注意索引用 · 获取

【网络铅笔头,扫一扫~】
附录1:实验登陆 login.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>登录 </title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/common.css" /> </head> <body style="background-color:PowderBlue;"> <h1>用户登录入口</h1> <form method="POST" action="/login/"> 用户名:<br> <input type="text" name="user" required autofocus placeholder="username"><br> 密码:<br> <input type="password" name="pwd" maxlength="12" placeholder="password"><br><br> <input type="submit" value="登录"/><br> {{ msg }} </form> </body> </html>
附录2:实验urls.py
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse,render,redirect def login(request): ''' 处理用户请求并返回内容 :param request:用户请求相关的所有信息(对象) :return: ''' #return HttpResponse('<input type="text" />') if request.method == "GET": return render(request,'login.html') else: #用户POST提交的数据 u = request.POST.get('user') p = request.POST.get('pwd') if u == 'admin' and p == 'admin': #登录成功跳转 #return redirect('http://www.baidu.com') return redirect('/index/') else: #登录失败 return render(request,'login.html',{'msg':'用户名或密码错误!请重新输入'}) def index(request): return render(request,'index.html') urlpatterns = [ #path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('login/',login), path('index/',index), ]
为美好的生活奋斗!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号