Ray Tracing: The Rest of Your Life
3. One Dimensional MC Integration
- 蒙特卡洛积分[1]
一般表达式如下:
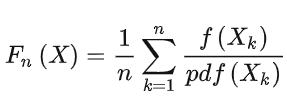
这样做的原因是保持期望值,做到无偏差。
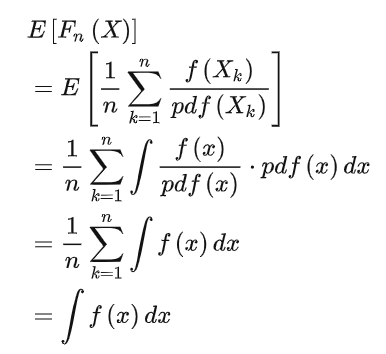
- 重要性采样 importance sampling:一般采样的概率分布与目标函数的概率分布一致。
5. Light Scattering
- Albedo
当光子打在材料上,会有一定概率被吸收,也可能被反射出去,那么某种波长的光子被反射的概率是反射率Albedo。对于RGB形式的表示,三色是有不同的反射率,相应的白色光打到表面上会有不同颜色的光反射出去。 - scattering
从某个方向入射的光,其入射方向与法线方向越是接近则能量越是集中,即radience越大。一般的,使用夹角余弦来做变换。这个便是漫反射材质的分布函数,scattering。总的来看,对于漫反射材质而言,假设其反射是各向同性的,那么其反射就是各个方向入射光color(drection)的irradiance经过转换scattering(direction)到radiance,然后通过各色反射率albedo得到。可见,scattering是积分的重点。
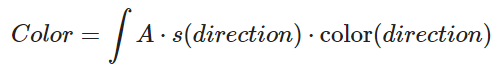
- The Scattering PDF
基于蒙特卡洛方法,得到一次采样的积分表达式。此处的p(direction)是采样的概率密度函数。
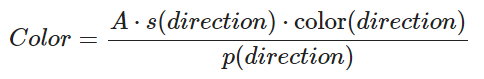
已知scattering(direction)是正比于
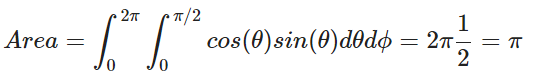
考虑到概率密度函数积分为1,取概率密度函数为
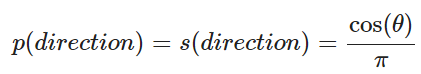
这样一来,一次采样的结果就是一次线性变换,也正是之前没有正式引入蒙特卡洛时的采样方法。
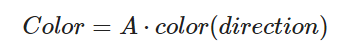
6. Importance Sampling Materials
- 修改material类,首先在scatter函数中加入了pdf参数,用于同albedo、scattered一同得到;此外,加入了scattering_pdf函数,用于返回scatter的概率密度函数。
class material {
public:
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, color& albedo, ray& scattered, double& pdf
) const {
return false;
}
virtual double scattering_pdf(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, const ray& scattered
) const {
return 0;
}
virtual color emitted(double u, double v, const point3& p) const {
return color(0,0,0);
}
};
- 修改lambertian类。在scatter函数中计算了pdf,此处是cos分布的采样方式;在scattering_pdf中同样计算了pdf,也是cos分布。
class lambertian : public material {
public:
lambertian(const color& a) : albedo(make_shared<solid_color>(a)) {}
lambertian(shared_ptr<texture> a) : albedo(a) {}
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, color& alb, ray& scattered, double& pdf
) const override {
auto scatter_direction = rec.normal + random_unit_vector();
// Catch degenerate scatter direction
if (scatter_direction.near_zero())
scatter_direction = rec.normal;
scattered = ray(rec.p, unit_vector(scatter_direction), r_in.time());
alb = albedo->value(rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
pdf = dot(rec.normal, scattered.direction()) / pi;
return true;
}
double scattering_pdf(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, const ray& scattered
) const {
auto cosine = dot(rec.normal, unit_vector(scattered.direction()));
return cosine < 0 ? 0 : cosine/pi;
}
public:
shared_ptr<texture> albedo;
};
- 修改ray_color函数,同样的加入了pdf参数,此外,在返回值中显示的将scattering_pdf与pdf加入了进去。
color ray_color(const ray& r, const color& background, const hittable& world, int depth) {
hit_record rec;
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered.
if (depth <= 0)
return color(0,0,0);
// If the ray hits nothing, return the background color.
if (!world.hit(r, 0.001, infinity, rec))
return background;
ray scattered;
color emitted = rec.mat_ptr->emitted(rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
double pdf;
color albedo;
if (!rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, albedo, scattered, pdf))
return emitted;
return emitted
+ albedo * rec.mat_ptr->scattering_pdf(r, rec, scattered)
* ray_color(scattered, background, world, depth-1) / pdf;
}
- 到目前为止,将蒙特卡洛显式的表达出来了,但是效果应该是没有太大区别的,因为之前便是该方法的隐式表达。
7. Generating Random Directions
- 我们可以生成均匀分布的随机数,但是我们期待可以通过均匀分布随机数得到特殊分布的随机数。具体的方法是:首先表示出概率密度函数,然后得到概率分布函数,因为概率分布函数是[0,1]随机分布的,所以表示出由概率分布函数到目标分布参数的逆表达式,便相当于可以由均匀分布得到特殊分布的随机数生成方式。
- 对于球面上均匀分布:
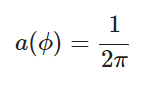
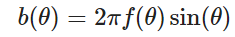
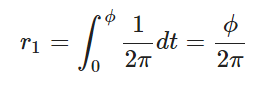
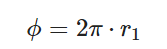
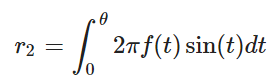
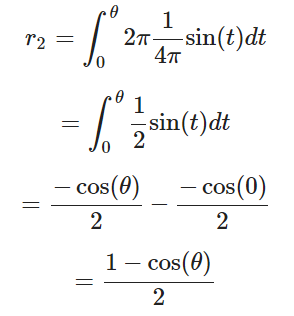
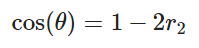
即
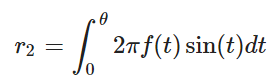
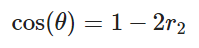
相应的,可以得到xyz坐标为:
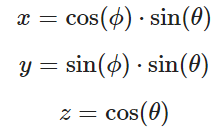

- 相应的半球面随机数为:
inline vec3 random_cosine_direction() {
auto r1 = random_double();
auto r2 = random_double();
auto z = sqrt(1-r2);
auto phi = 2*pi*r1;
auto x = cos(phi)*sqrt(r2);
auto y = sin(phi)*sqrt(r2);
return vec3(x, y, z);
}
8. Orthonormal Bases
- 之前的随机生成的半球面矢量是xyz坐标的,为了能够对任意切面法向量方向做随机生成,需要根据法向量生成一个正交坐标系。在onb.h中定义onb类,其主要内容是一个vec3数组,用于保存uvw三个方向的基矢量。build_from_w可以基于法向矢量生成以其为w方向的onb,这是通过随机给予一个参考单位矢量进行两次叉积运算得到,为了避免随机矢量与w平行,通过判断w的x坐标来生成(1,0,0)或(0,1,0)。此外,local函数可以利用一个点矢量作为该坐标系下的坐标来获得世界坐标系下的坐标。
#ifndef ONB_H
#define ONB_H
#include "rtweekend.h"
class onb {
public:
onb() {}
inline vec3 operator[](int i) const { return axis[i]; }
vec3 u() const { return axis[0]; }
vec3 v() const { return axis[1]; }
vec3 w() const { return axis[2]; }
vec3 local(double a, double b, double c) const {
return a*u() + b*v() + c*w();
}
vec3 local(const vec3& a) const {
return a.x()*u() + a.y()*v() + a.z()*w();
}
void build_from_w(const vec3&);
public:
vec3 axis[3];
};
void onb::build_from_w(const vec3& n) {
axis[2] = unit_vector(n);
vec3 a = (fabs(w().x()) > 0.9) ? vec3(0,1,0) : vec3(1,0,0);
axis[1] = unit_vector(cross(w(), a));
axis[0] = cross(w(), v());
}
#endif
- 相应的,修改scatter中生成随机矢量的部分。通过hit_record中记录的法向矢量,来创建unb。然后将random_cosine_direction生成的随机矢量转换到unb坐标系中。
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, color& alb, ray& scattered, double& pdf
) const override {
onb uvw;
uvw.build_from_w(rec.normal);
auto direction = uvw.local(random_cosine_direction());
scattered = ray(rec.p, unit_vector(direction), r_in.time());
alb = albedo->value(rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
pdf = dot(uvw.w(), scattered.direction()) / pi;
return true;
}
- 到目前为止,修改了随机矢量生成方式,即采样方式。但是效果仍然不会有明显变化。
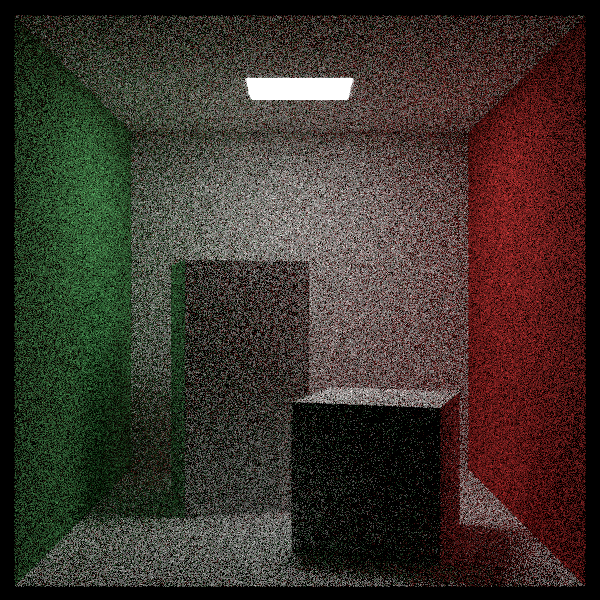
9. Sampling Lights Directly
- 噪声很严重,这是因为难以命中光源。
- 采样光源。直接对光源做采样,作为reflection equation中的直接光照部分,至于间接光照仍然采取反射采样。
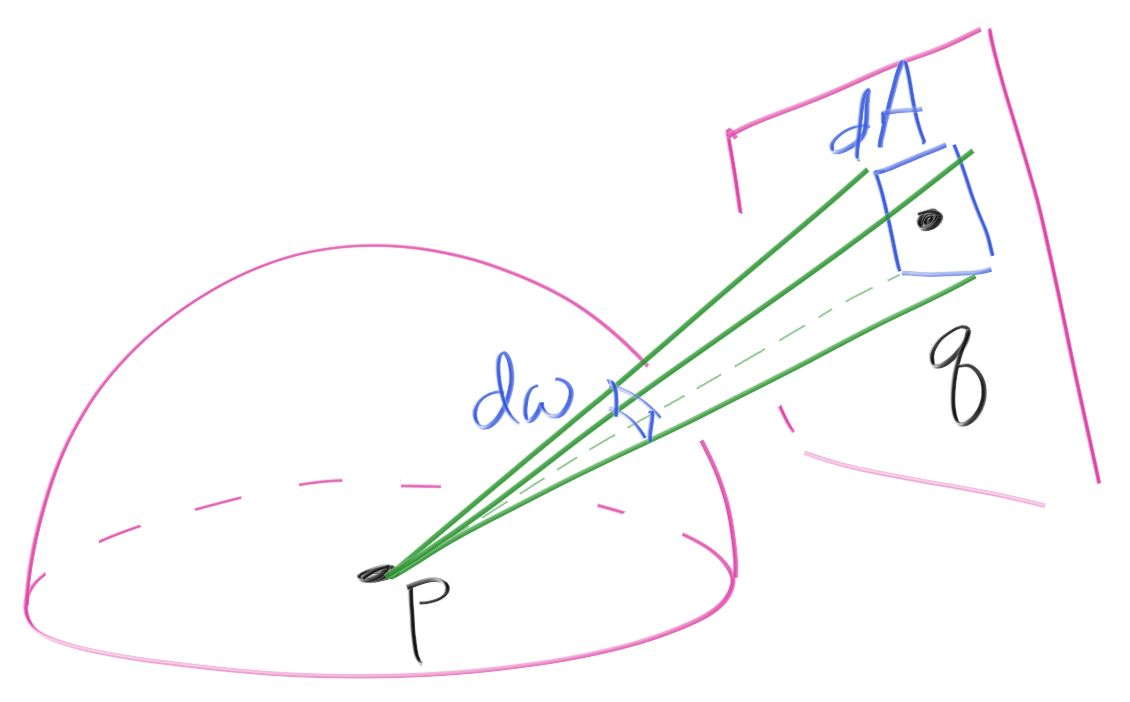
将光源的单位面积转换为反射点的单位立体角为:
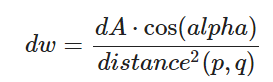
相应的到:
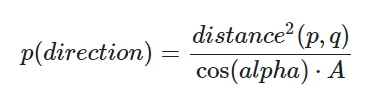
- 修改ray_color,只使用光源采样的直接光照,还有自发光。一个需要注意的地方是,这里给出了两个与光源的相交判断,一个是背后相交,另一个是平行光线。其中,后者也是与pdf计算有关,为了避免除以零值。
color ray_color(const ray& r, const color& background, const hittable& world, int depth) {
hit_record rec;
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered.
if (depth <= 0)
return color(0,0,0);
// If the ray hits nothing, return the background color.
if (!world.hit(r, 0.001, infinity, rec))
return background;
ray scattered;
color attenuation;
color emitted = rec.mat_ptr->emitted(rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
double pdf;
color albedo;
if (!rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, albedo, scattered, pdf))
return emitted;
auto on_light = point3(random_double(213,343), 554, random_double(227,332));
auto to_light = on_light - rec.p;
auto distance_squared = to_light.length_squared();
to_light = unit_vector(to_light);
if (dot(to_light, rec.normal) < 0)
return emitted;
double light_area = (343-213)*(332-227);
auto light_cosine = fabs(to_light.y());
if (light_cosine < 0.000001)
return emitted;
pdf = distance_squared / (light_cosine * light_area);
scattered = ray(rec.p, to_light, r.time());
return emitted
+ albedo * rec.mat_ptr->scattering_pdf(r, rec, scattered)
* ray_color(scattered, background, world, depth-1) / pdf;
}
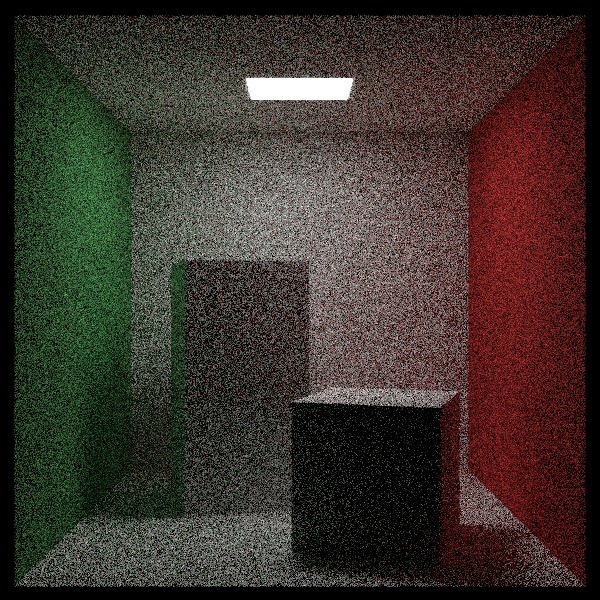
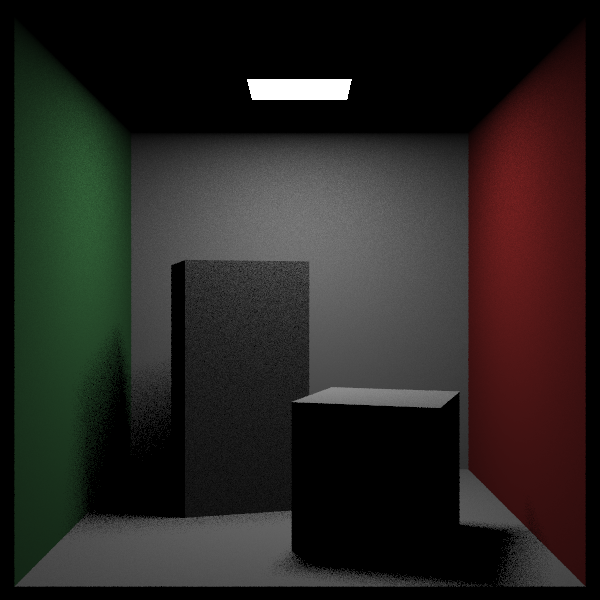
效果如下,很快,帅!但是没有间接光照。
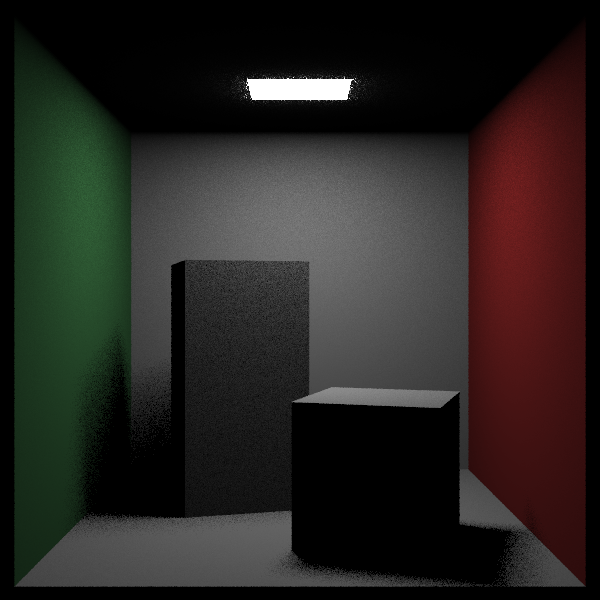
- 可以看见,在光源附近有噪声,这是背后发光造成的。除此之外,可以看到在影子的边缘也存在噪声。这些都是因为处于光源采样的边界位置,是用少量的采样次数就会造成噪声。下面将光源改为单向光源,只向外法线方向发光。当然,这并不是在解决噪声问题。因为aarect类的外法线方向是hit函数内部设置了的,为了方便修改光源的外法线,定义了flip_face翻转类,其只有一个作用,就是在hit函数中对hit_record类的front_face标记取反。
virtual color emitted(const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, double u, double v,
const point3& p) const override {
if (rec.front_face)
return emit->value(u, v, p);
else
return color(0,0,0);
}
class flip_face : public hittable {
public:
flip_face(shared_ptr<hittable> p) : ptr(p) {}
virtual bool hit(
const ray& r, double t_min, double t_max, hit_record& rec) const override {
if (!ptr->hit(r, t_min, t_max, rec))
return false;
rec.front_face = !rec.front_face;
return true;
}
virtual bool bounding_box(double time0, double time1, aabb& output_box) const override {
return ptr->bounding_box(time0, time1, output_box);
}
public:
shared_ptr<hittable> ptr;
};
画个图:
hittable_list cornell_box() {
hittable_list objects;
auto red = make_shared<lambertian>(color(.65, .05, .05));
auto white = make_shared<lambertian>(color(.73, .73, .73));
auto green = make_shared<lambertian>(color(.12, .45, .15));
auto light = make_shared<diffuse_light>(color(15, 15, 15));
objects.add(make_shared<yz_rect>(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, green));
objects.add(make_shared<yz_rect>(0, 555, 0, 555, 0, red));
objects.add(make_shared<flip_face>(make_shared<xz_rect>(213, 343, 227, 332, 554, light)));
objects.add(make_shared<xz_rect>(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, white));
objects.add(make_shared<xz_rect>(0, 555, 0, 555, 0, white));
objects.add(make_shared<xy_rect>(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, white));
...
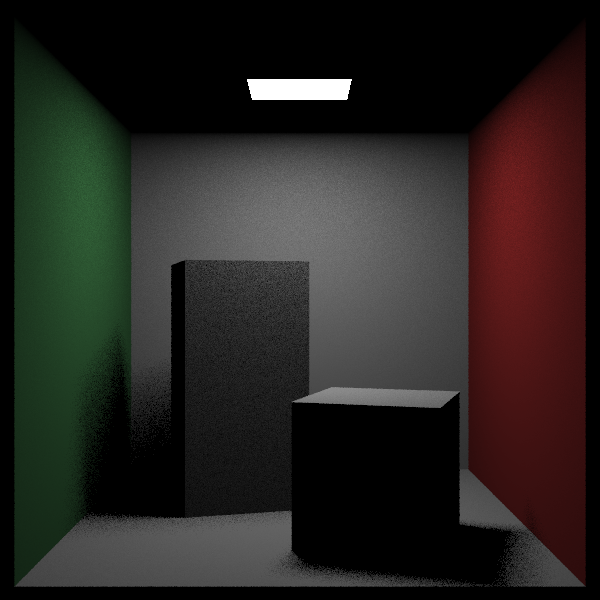
10. Mixture Densities
- 在上面将反射采样集成在material中,而光源采样直接在ray_color中实现,有必要将他们统一起来。
- 显然的,各种采样方式有两个方面最为重要,一个是按照某种分布随机生成光线矢量,另一个是得到该光线矢量在这个分布中的pdf值。基于此,在pdf.h中定义了pdf抽象类。其中两个纯虚函数value与generate分别提供了查询某个矢量的pdf值与生成随机矢量的功能。
#ifndef PDF_H
#define PDF_H
class pdf {
public:
virtual ~pdf() {}
virtual double value(const vec3& direction) const = 0;
virtual vec3 generate() const = 0;
};
#endif
- 基于此定义了cosine_pdf类,这个是之前定义在漫反射材质中的随即方式。cosine_pdf的主要内容是根据法向矢量生成一个onb,然后使用random_cosine_direction生成一个半球面矢量,并用onb做坐标变换,最终得到随机方向矢量。并在value复现了pdf计算。
inline vec3 random_cosine_direction() {
auto r1 = random_double();
auto r2 = random_double();
auto z = sqrt(1-r2);
auto phi = 2*pi*r1;
auto x = cos(phi)*sqrt(r2);
auto y = sin(phi)*sqrt(r2);
return vec3(x, y, z);
}
class cosine_pdf : public pdf {
public:
cosine_pdf(const vec3& w) { uvw.build_from_w(w); }
virtual double value(const vec3& direction) const override {
auto cosine = dot(unit_vector(direction), uvw.w());
return (cosine <= 0) ? 0 : cosine/pi;
}
virtual vec3 generate() const override {
return uvw.local(random_cosine_direction());
}
public:
onb uvw;
};
画个图。可见这里在scatter之后,使用cosine_pdf重新计算了pdf与scattered。
color ray_color(const ray& r, const color& background, const hittable& world, int depth) {
hit_record rec;
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered.
if (depth <= 0)
return color(0,0,0);
// If the ray hits nothing, return the background color.
if (!world.hit(r, 0.001, infinity, rec))
return background;
ray scattered;
color attenuation;
color emitted = rec.mat_ptr->emitted(r, rec, rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
double pdf_val;
color albedo;
if (!rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, albedo, scattered, pdf_val))
return emitted;
cosine_pdf p(rec.normal);
scattered = ray(rec.p, p.generate(), r.time());
pdf_val = p.value(scattered.direction());
return emitted
+ albedo * rec.mat_ptr->scattering_pdf(r, rec, scattered)
* ray_color(scattered, background, world, depth-1) / pdf_val;
}

- 光源采样。在pdf.h中定义了hittable_pdf,用于对hittable类采样,相应的便可以用于光源采样。因为不同的hittable的空间结构不同,所以其随机生成方式不同,因此将hittable_pdf的value与generate交给hittable实现,而hittable_pdf只作为对外接口,并且保持了基本的反射点o与hittable。因此,在hittable中需要增加pdf_value与random两个虚函数。相应的,在xz_rect类中实现这两个函数,基本上是将上面集成在ray_color中的部分迁移过来。
class hittable_pdf : public pdf {
public:
hittable_pdf(shared_ptr<hittable> p, const point3& origin) : ptr(p), o(origin) {}
virtual double value(const vec3& direction) const override {
return ptr->pdf_value(o, direction);
}
virtual vec3 generate() const override {
return ptr->random(o);
}
public:
point3 o;
shared_ptr<hittable> ptr;
};
class hittable {
public:
virtual bool hit(const ray& r, double t_min, double t_max, hit_record& rec) const = 0;
virtual bool bounding_box(double time0, double time1, aabb& output_box) const = 0;
virtual double pdf_value(const point3& o, const vec3& v) const {
return 0.0;
}
virtual vec3 random(const vec3& o) const {
return vec3(1, 0, 0);
}
};
class xz_rect : public hittable {
public:
...
virtual double pdf_value(const point3& origin, const vec3& v) const override {
hit_record rec;
if (!this->hit(ray(origin, v), 0.001, infinity, rec))
return 0;
auto area = (x1-x0)*(z1-z0);
auto distance_squared = rec.t * rec.t * v.length_squared();
auto cosine = fabs(dot(v, rec.normal) / v.length());
return distance_squared / (cosine * area);
}
virtual vec3 random(const point3& origin) const override {
auto random_point = point3(random_double(x0,x1), k, random_double(z0,z1));
return random_point - origin;
}
画个图。
color ray_color(
const ray& r, const color& background, const hittable& world,
shared_ptr<hittable>& lights, int depth
) {
...
ray scattered;
color attenuation;
color emitted = rec.mat_ptr->emitted(r, rec, rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
double pdf_val;
color albedo;
if (!rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, albedo, scattered, pdf_val))
return emitted;
hittable_pdf light_pdf(lights, rec.p);
scattered = ray(rec.p, light_pdf.generate(), r.time());
pdf_val = light_pdf.value(scattered.direction());
return emitted
+ albedo * rec.mat_ptr->scattering_pdf(r, rec, scattered)
* ray_color(scattered, background, world, lights, depth-1) / pdf_val;
}
...
int main() {
...
// World
auto world = cornell_box();
shared_ptr<hittable> lights =
make_shared<xz_rect>(213, 343, 227, 332, 554, shared_ptr<material>());
...
for (int j = image_height-1; j >= 0; --j) {
std::cerr << "\rScanlines remaining: " << j << ' ' << std::flush;
for (int i = 0; i < image_width; ++i) {
...
pixel_color += ray_color(r, background, world, lights, max_depth);
...
- mixture pdf。实现mixture_pdf类。
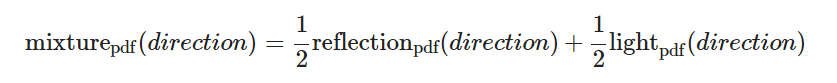

class mixture_pdf : public pdf {
public:
mixture_pdf(shared_ptr<pdf> p0, shared_ptr<pdf> p1) {
p[0] = p0;
p[1] = p1;
}
virtual double value(const vec3& direction) const override {
return 0.5 * p[0]->value(direction) + 0.5 *p[1]->value(direction);
}
virtual vec3 generate() const override {
if (random_double() < 0.5)
return p[0]->generate();
else
return p[1]->generate();
}
public:
shared_ptr<pdf> p[2];
};

- 可以看出来,这个要比单独一种采样方式的效果好多了。这是因为光源采样保证了提供人眼最敏感的亮度信息的直接光照部分,而反射采样又补充了间接光照。同时间接光照部分也会使用光源采样,这样就算是间接光照也要比只是用反射采样更容易寻到光源,更加抗噪声。
12. Cleaning Up PDF Management
- 目前已经实现了漫反射材质的蒙特卡洛路径积分,但是对于其他材质如镜面、介质等等光追方式并不相同,因此有必要统一各种材质scatter的对外方式。material的scatter函数是在不同材质之间存在最大争议的地方,之前通过pdf类取代了漫反射材质的scatter中pdf与scattered部分,但是这个流程对于其他材质并不友好。因此,仍然保持scatter相对于pdf的主体地位,将漫反射材质所需的albedo与pdf作为scatter的输出值,然后在漫反射材质的情况下进行计算。相应的,将其他材质的计算过程所需信息也集成在scatter计算中。由之前可知,对于其他材质,scatter的主要作用是计算得到attenuation与scattered。因此将他们组成scatter_record结构体,同时加入标志is_specular来作为后续计算的分支标记。相应的,修改scatter的参数,改为scatter_record。
struct scatter_record {
ray specular_ray;
bool is_specular;
color attenuation;
shared_ptr<pdf> pdf_ptr;
};
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, scatter_record& srec
) const {
return false;
}
- 漫反射材质
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, scatter_record& srec
) const override {
srec.is_specular = false;
srec.attenuation = albedo->value(rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
srec.pdf_ptr = make_shared<cosine_pdf>(rec.normal);
return true;
}
- 修改ray_color函数
color ray_color(
const ray& r,
const color& background,
const hittable& world,
shared_ptr<hittable>& lights,
int depth
) {
hit_record rec;
// If we've exceeded the ray bounce limit, no more light is gathered.
if (depth <= 0)
return color(0,0,0);
// If the ray hits nothing, return the background color.
if (!world.hit(r, 0.001, infinity, rec))
return background;
scatter_record srec;
color emitted = rec.mat_ptr->emitted(r, rec, rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
if (!rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, srec))
return emitted;
auto light_ptr = make_shared<hittable_pdf>(lights, rec.p);
mixture_pdf p(light_ptr, srec.pdf_ptr);
ray scattered = ray(rec.p, p.generate(), r.time());
auto pdf_val = p.value(scattered.direction());
return emitted
+ srec.attenuation * rec.mat_ptr->scattering_pdf(r, rec, scattered)
* ray_color(scattered, background, world, lights, depth-1) / pdf_val;
}
- metal
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, scatter_record& srec
) const override {
vec3 reflected = reflect(unit_vector(r_in.direction()), rec.normal);
srec.specular_ray = ray(rec.p, reflected+fuzz*random_in_unit_sphere());
srec.attenuation = albedo;
srec.is_specular = true;
srec.pdf_ptr = 0;
return true;
}
dielectric
virtual bool scatter(
const ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, scatter_record& srec
) const override {
srec.is_specular = true;
srec.pdf_ptr = nullptr;
srec.attenuation = color(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
double refraction_ratio = rec.front_face ? (1.0/ir) : ir;
...
srec.specular_ray = ray(rec.p, direction, r_in.time());
return true;
}
- 修改ray_color,加入分支。
color ray_color(
const ray& r,
const color& background,
const hittable& world,
shared_ptr<hittable>& lights,
int depth
) {
...
scatter_record srec;
color emitted = rec.mat_ptr->emitted(r, rec, rec.u, rec.v, rec.p);
if (!rec.mat_ptr->scatter(r, rec, srec))
return emitted;
if (srec.is_specular) {
return srec.attenuation
* ray_color(srec.specular_ray, background, world, lights, depth-1);
}
...
}
-
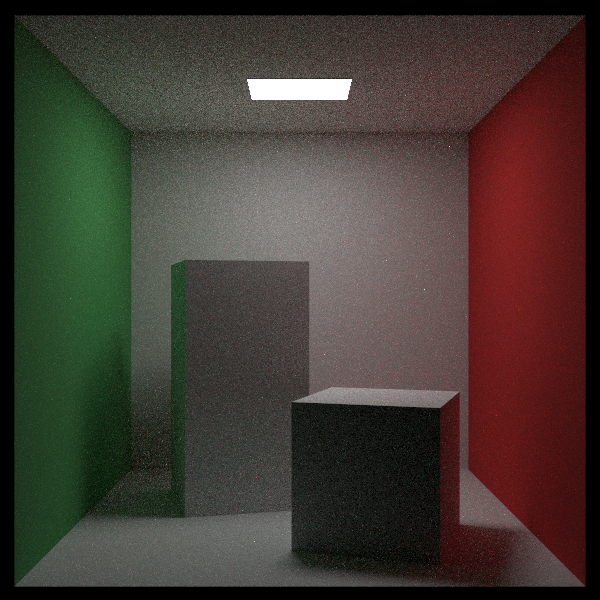
加入sphere的采样。类似于对平面做面元均匀采样,对于球体采取的是对立体角做均匀采样。参考之前对半球面做均匀采样的做法,有
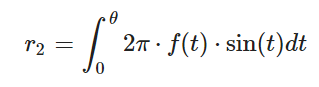
因为是均匀采样,有:
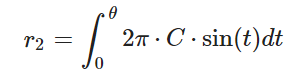
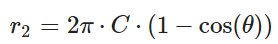
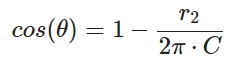
考虑到,半球面采样与对远处球面做采样的总立体角不同,设置边界条件:
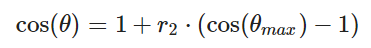
得到:
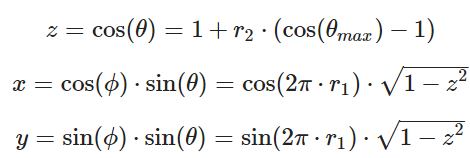
同时可知:
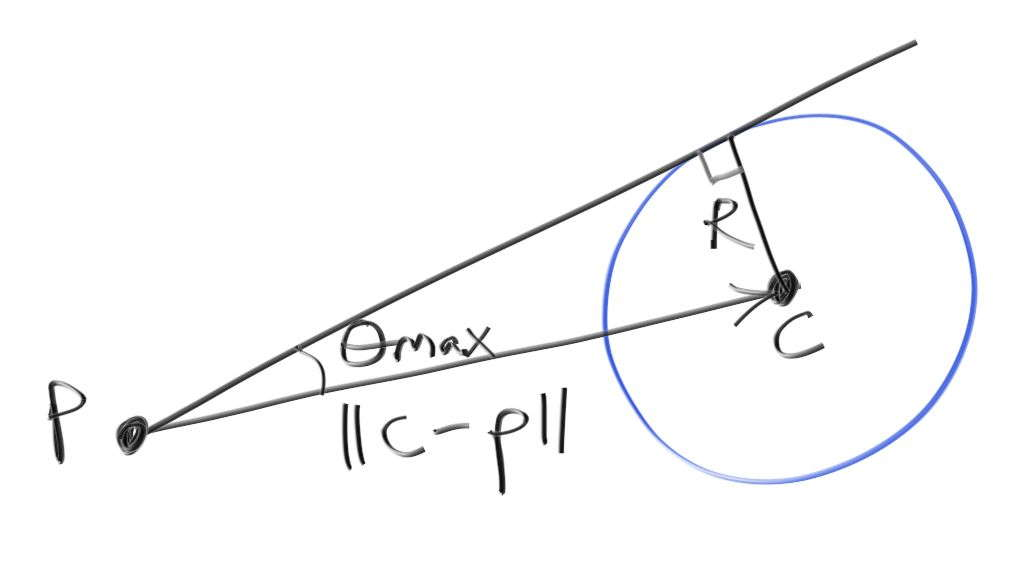
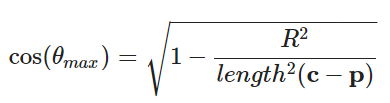
对于均匀采样的总立体角,有如下。相应的,其倒数就是pdf。

-
修改sphere
double sphere::pdf_value(const point3& o, const vec3& v) const {
hit_record rec;
if (!this->hit(ray(o, v), 0.001, infinity, rec))
return 0;
auto cos_theta_max = sqrt(1 - radius*radius/(center-o).length_squared());
auto solid_angle = 2*pi*(1-cos_theta_max);
return 1 / solid_angle;
}
vec3 sphere::random(const point3& o) const {
vec3 direction = center - o;
auto distance_squared = direction.length_squared();
onb uvw;
uvw.build_from_w(direction);
return uvw.local(random_to_sphere(radius, distance_squared));
}
- 相应的函数为
inline vec3 random_to_sphere(double radius, double distance_squared) {
auto r1 = random_double();
auto r2 = random_double();
auto z = 1 + r2*(sqrt(1-radius*radius/distance_squared) - 1);
auto phi = 2*pi*r1;
auto x = cos(phi)*sqrt(1-z*z);
auto y = sin(phi)*sqrt(1-z*z);
return vec3(x, y, z);
}
- 为hittable类加入采样。
double hittable_list::pdf_value(const point3& o, const vec3& v) const {
auto weight = 1.0/objects.size();
auto sum = 0.0;
for (const auto& object : objects)
sum += weight * object->pdf_value(o, v);
return sum;
}
vec3 hittable_list::random(const vec3& o) const {
auto int_size = static_cast<int>(objects.size());
return objects[random_int(0, int_size-1)]->random(o);
}
- 消除nan
void write_color(std::ostream &out, color pixel_color, int samples_per_pixel) {
auto r = pixel_color.x();
auto g = pixel_color.y();
auto b = pixel_color.z();
// Replace NaN components with zero. See explanation in Ray Tracing: The Rest of Your Life.
if (r != r) r = 0.0;
if (g != g) g = 0.0;
if (b != b) b = 0.0;
// Divide the color by the number of samples and gamma-correct for gamma=2.0.
auto scale = 1.0 / samples_per_pixel;
r = sqrt(scale * r);
g = sqrt(scale * g);
b = sqrt(scale * b);
// Write the translated [0,255] value of each color component.
out << static_cast<int>(256 * clamp(r, 0.0, 0.999)) << ' '
<< static_cast<int>(256 * clamp(g, 0.0, 0.999)) << ' '
<< static_cast<int>(256 * clamp(b, 0.0, 0.999)) << '\n';
}
画个图:
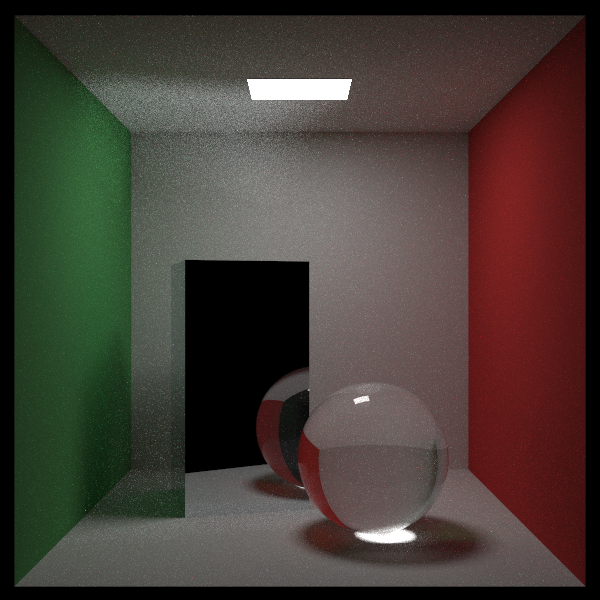
本文来自博客园,作者:ETHERovo,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/etherovo/p/17355882.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具