海豚调度Dolphinscheduler源码分析(三)
今天继续分析海豚调度的源码
上回分析的是dolphinscheduler-service模块zookeeper相关的代码
这回分析是dolphinscheduler-server模块zookeeper相关的代码
ZkMasterClient master服务zk客户端类
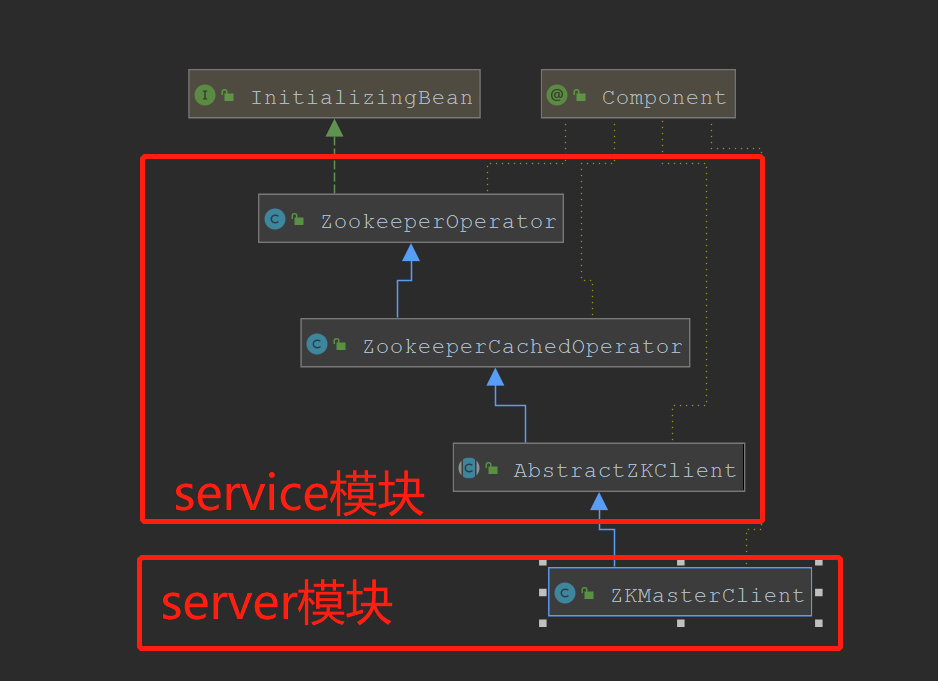
类继承的关系如下:
这个类的方法如下:
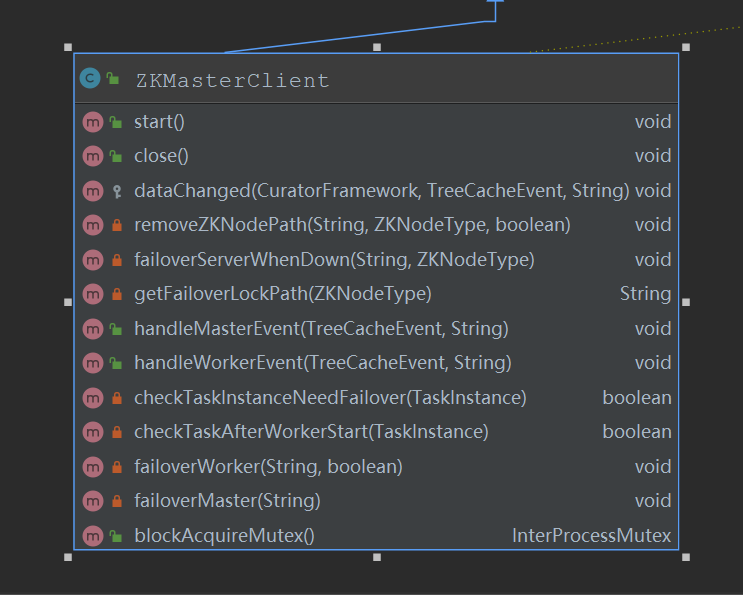
方法介绍:
- start() 根据路径dolphinscheduler/lock/failover/master 创建一个分布式锁,并进行初始化,检查是否有master节点竞争锁,确保只有一个主master,如果只有一个master节点,那么无法进行master服务的故障转移
- dataChange() 变更zk节点
- removeZKNodePath(String path, ZKNodeType zkNodeType, boolean failover) 移除zookeeper 节点,并在/dead路径添加节点,并会判断是否需要容错
- handleDeadServer() 父类方法,就是处理宕机服务的zookeeper路径,将获取节点删除,添加/dead路径数据
- failoverServerWhenDown() 当服务宕机后,转移服务,分为master服务和server服务
- checkTaskInstanceNeedFailover()
- failoverWorker() 将worker上的task任务进行故障转移
- 如果是yarn任务,干掉yarn任务
- 将任务状态变更为需要故障转移
- 当工作节点全部为null时,将所有任务进行故障转移
zk分布式锁获取代码如下:
public void start() {
//Curator是zk的一个客户端框架,其中分装了分布式公平可重入互斥锁,最为常见是InterProcessMutex
InterProcessMutex mutex = null;
try {
// create distributed lock with the root node path of the lock space as /dolphinscheduler/lock/failover/master
///根据这个路径dolphinscheduler/lock/failover/master 创建一个分布式锁
String znodeLock = getMasterStartUpLockPath();
//InterProcessMutex的构造方法,需要一个客户端和路径
mutex = new InterProcessMutex(getZkClient(), znodeLock);
//获取锁,锁的获取,最后必须释放
mutex.acquire();
// init system znode
this.initSystemZNode();
//检查是否有master节点
while (!checkZKNodeExists(NetUtils.getHost(), ZKNodeType.MASTER)){
ThreadUtils.sleep(SLEEP_TIME_MILLIS);
}
// self tolerant
//如果活动的master节点只有1个,无法进行master服务的容错,故failoverMaster(null)
if (getActiveMasterNum() == 1) {
failoverWorker(null, true);
failoverMaster(null);
}
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("master start up exception",e);
}finally {
//释放锁,这个方法是父类AbstractZKClient的,在finally中释放,保证锁最后能够释放
releaseMutex(mutex);
}
}
对于InterProcessMutex,Curator是ZooKeeper的一个客户端框架,其中封装了分布式互斥锁的实现,最为常用的是InterProcessMutex
InterProcessMutex基于Zookeeper实现了分布式的公平可重入互斥锁,类似于单个JVM进程内的ReentrantLock(fair=true)
全局同步的可重入分布式锁,任何时刻不会有两个客户端同时持有该锁。Reentrant和JDK的ReentrantLock类似, 意味着同一个客户端在拥有锁的同时,可以多次获取,不会被阻塞
相关链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hosaos/article/details/89521537
相关链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/a-du/p/9876314.html
相关链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34021712/article/details/82878396
主要方法:
//获取锁,若失败则阻塞等待直到成功,支持重入 public void acquire() throws Exception //超时获取锁,超时失败 public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception //释放锁,一般在finally中释放 public void release() throws Exception
注意点,调用acquire()方法后需相应调用release()来释放锁
private void removeZKNodePath(String path, ZKNodeType zkNodeType, boolean failover) 移除zk节点
/**
* remove zookeeper node path
* * @param path zookeeper node path * @param zkNodeType zookeeper node type * @param failover is failover */ private void removeZKNodePath(String path, ZKNodeType zkNodeType, boolean failover) { logger.info("{} node deleted : {}", zkNodeType.toString(), path); InterProcessMutex mutex = null; try { String failoverPath = getFailoverLockPath(zkNodeType); // create a distributed lock mutex = new InterProcessMutex(getZkClient(), failoverPath); mutex.acquire(); String serverHost = getHostByEventDataPath(path); // handle dead server
//处理 宕机服务,删除原来节点,在dead路径增加节点,
handleDeadServer(path, zkNodeType, Constants.ADD_ZK_OP); //failover server
//是否故障转移服务
if(failover){ failoverServerWhenDown(serverHost, zkNodeType); } }catch (Exception e){ logger.error("{} server failover failed.", zkNodeType.toString()); logger.error("failover exception ",e); } finally { releaseMutex(mutex); } }
zookeeper分布式锁详解
在分布式环境中 ,为了保证数据的一致性,经常在程序的某个运行点(例如,减库存操作或者流水号生成等)需要进行同步控制。以一个"流水号生成"的场景为例,普通的后台应用通常都是使用时间戳来生成流水号,但是在用户访问量很大的情况下,可能会出现并发问题。下面通过示例程序就演示一个典型的并发问题:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { CountDownLatch down = new CountDownLatch(1); for (int i=0;i<10;i++){ new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { down.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss|SSS"); String orderNo = sdf.format(new Date()); System.out.println("生成的订单号是:"+orderNo); } }).start(); } down.countDown(); }
输出结果如下:
Thread[Thread-8,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|098 Thread[Thread-4,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|107 Thread[Thread-9,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108 Thread[Thread-3,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108 Thread[Thread-0,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108 Thread[Thread-6,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108 Thread[Thread-7,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108 Thread[Thread-2,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108 Thread[Thread-5,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108 Thread[Thread-1,5,main]生成的订单号是:14:41:26|108
不难发现,生成的10个订单不少都是重复的,如果是实际的生产环境中,这显然没有满足我们的也无需求。究其原因,就是因为在没有进行同步的情况下,出现了并发问题。下面我们来看看如何使用Curator实现分布式锁功能。
Shared Reentrant Lock(分布式可重入锁)
全局同步的可重入分布式锁,任何时刻不会有两个客户端同时持有该锁。Reentrant和JDK的ReentrantLock类似, 意味着同一个客户端在拥有锁的同时,可以多次获取,不会被阻塞。
相关的类
InterProcessMutex
使用
创建InterProcessMutex实例
InterProcessMutex提供了两个构造方法,传入一个CuratorFramework实例和一个要使用的节点路径,InterProcessMutex还允许传入一个自定义的驱动类,默认是使用StandardLockInternalsDriver。
public InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path); public InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, LockInternalsDriver driver);
获取锁
使用acquire方法获取锁,acquire方法有两种:
public void acquire() throws Exception;
获取锁,一直阻塞到获取到锁为止。获取锁的线程在获取锁后仍然可以调用acquire() 获取锁(可重入)。 锁获取使用完后,调用了几次acquire(),就得调用几次release()释放。
public boolean acquire(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception;
与acquire()类似,等待time * unit时间获取锁,如果仍然没有获取锁,则直接返回false。
释放锁
使用release()方法释放锁
线程通过acquire()获取锁时,可通过release()进行释放,如果该线程多次调用 了acquire()获取锁,则如果只调用 一次release()该锁仍然会被该线程持有。
注意:同一个线程中InterProcessMutex实例是可重用的,也就是不需要在每次获取锁的时候都new一个InterProcessMutex实例,用同一个实例就好。
锁撤销
InterProcessMutex 支持锁撤销机制,可通过调用makeRevocable()将锁设为可撤销的,当另一线程希望你释放该锁时,实例里的listener会被调用。 撤销机制是协作的。
示例代码(官网)
共享资源
public class FakeLimitedResource { //总共250张火车票 private Integer ticket = 250; public void use() throws InterruptedException { try { System.out.println("火车票还剩"+(--ticket)+"张!"); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
使用锁操作资源
public class ExampleClientThatLocks { /** 锁 */ private final InterProcessMutex lock; /** 共享资源 */ private final FakeLimitedResource resource; /** 客户端名称 */ private final String clientName; public ExampleClientThatLocks(CuratorFramework client, String lockPath, FakeLimitedResource resource, String clientName) { this.resource = resource; this.clientName = clientName; lock = new InterProcessMutex(client, lockPath); } public void doWork(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception { if ( !lock.acquire(time, unit) ) { throw new IllegalStateException(clientName + " could not acquire the lock"); } try { System.out.println(clientName + " has the lock"); //操作资源 resource.use(); } finally { System.out.println(clientName + " releasing the lock"); lock.release(); //总是在Final块中释放锁。 } } }
客户端
public class LockingExample { private static final int QTY = 5; private static final int REPETITIONS = QTY * 10; private static final String CONNECTION_STRING = "172.20.10.9:2181"; private static final String PATH = "/examples/locks"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //FakeLimitedResource模拟某些外部资源,这些外部资源一次只能由一个进程访问 final FakeLimitedResource resource = new FakeLimitedResource(); ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(QTY); try { for ( int i = 0; i < QTY; ++i ){ final int index = i; Callable<Void> task = new Callable<Void>() { @Override public Void call() throws Exception { CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.newClient(CONNECTION_STRING, new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3,Integer.MAX_VALUE)); try { client.start(); ExampleClientThatLocks example = new ExampleClientThatLocks(client, PATH, resource, "Client " + index); for ( int j = 0; j < REPETITIONS; ++j ) { example.doWork(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } }catch ( InterruptedException e ){ Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); }catch ( Exception e ){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ CloseableUtils.closeQuietly(client); } return null; } }; service.submit(task); } service.shutdown(); service.awaitTermination(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
起五个线程,即五个窗口卖票,五个客户端分别有50张票可以卖,先是尝试获取锁,操作资源后,释放锁。
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34021712/article/details/82878396


