Java数据结构——红黑树
红黑树介绍
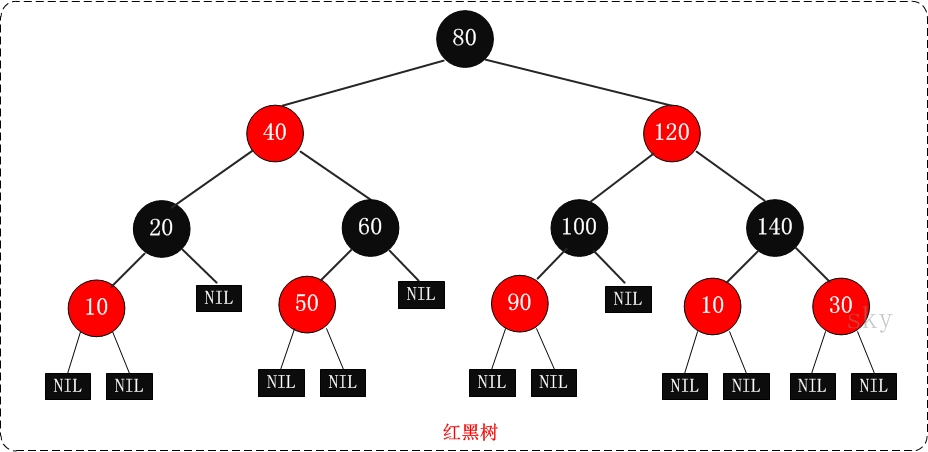
红黑树(Red-Black Tree),它一种特殊的二叉查找树。执行查找、插入、删除等操作的时间复杂度为O(logn)。
红黑树是特殊的二叉查找树,意味着它满足二叉查找树的特征:任意一个节点所包含的键值,大于等于左孩子的键值,小于等于右孩子的键值。
红黑树的每个节点上都有存储位表示节点的颜色,颜色是红(Red)或黑(Black)。
红黑树的特性:
- 每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色。
- 根节点是黑色。
- 每个叶子节点是黑色。 (注意:这里叶子节点,是指为空的叶子节点)
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
- 从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
关于红黑树,需要注意的是:
- 特性(3)中的叶子节点,是只为空(NIL或null)的节点。
- 特性(5),确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出俩倍。因而,红黑树是相对是接近平衡的二叉树。
- 红黑树是保持“黑平衡”的二叉树,严格意义上来说,它并不是真正的平衡二叉树,因为它可以不满足平衡的定义,即左右子树高度差不大于1,
- 红黑树的最大高度是2logn,它的复杂度是O(logn),与AVL树的复杂度一样。
红黑树的基本操作
红黑树的基本操作是添加、删除和旋转。在对红黑树进行添加或删除后,会用到旋转方法。因为添加或删除红黑树中的节点之后,红黑树会发生变化,可能不满足红黑树的5条性质,也就不再是一颗红黑树了。而通过旋转,可以使这颗树重新成为红黑树。简单点说,旋转的目的是让树保持红黑树的特性。
旋转包括两种:左旋 和 右旋。下面分别图解对红黑树的基本操作进行介绍。
左旋、右旋操作
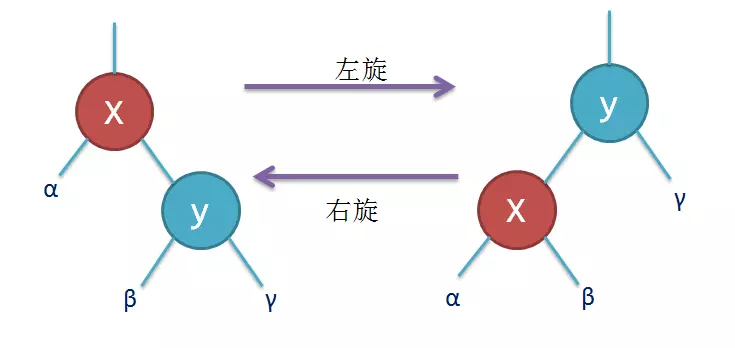
对x进行左旋,意味着"将x变成一个左节点"。
对y进行右旋,意味着"将y变成一个右节点"。

// 左旋转过程 // node x // / \ 左旋转 / \ // T1 x -----> node T3 // / \ / \ // T2 T3 T1 T2 private TreeNode leftRotate(TreeNode node) { TreeNode x = node.rightChild; // 左旋转 node.rightChild = x.leftChild; x.leftChild = node; x.color = node.color; node.color = RED; return x; } // 右旋转过程 // node x // / \ 右旋转 / \ // x T1 -----> y node // / \ / \ // y T2 T1 T2 private TreeNode rightRotate(TreeNode node) { TreeNode x = node.leftChild; // 右旋转 node.leftChild = x.rightChild; x.rightChild = node; x.color = node.color; node.color = RED; return x; }
颜色翻转操作
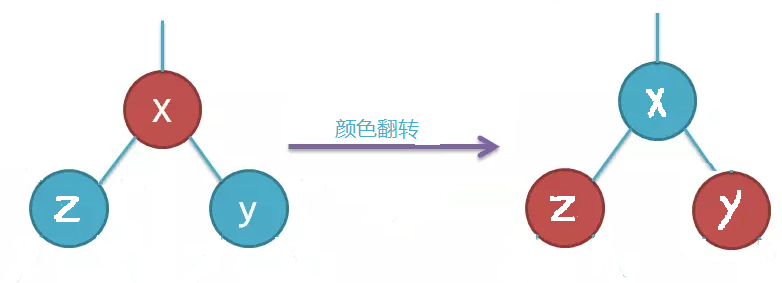

// 颜色翻转 private void flipColors(TreeNode node) { node.color = RED; node.leftChild.color = BLACK; node.rightChild.color = BLACK; }
添加操作
将一个节点插入到红黑树中的步骤:
- 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入。
- 将插入的节点着色为"红色"。
- 通过一系列的旋转或着色等操作,使之重新成为一颗红黑树。

// 向红黑树中添加节点 public void add(int data) { root = add(root, data); root.color = BLACK; } // 添加节点后返回红黑树的根节点 public TreeNode add(TreeNode node, int data) { if (node == null) { TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(data); return treeNode; } else { if (data < node.data) { node.leftChild = add(node.leftChild, data); } else if (data > node.data) { node.rightChild = add(node.rightChild, data); } else { node.data = data; } // node // \ // 红 if (isRED(node.rightChild) && !isRED(node.leftChild)) { node = leftRotate(node); } // node // / // 红 // / // 红 if (isRED(node.leftChild) && isRED(node.leftChild.leftChild)) { node = rightRotate(node); } // node // / \ // 红 红 if (isRED(node.leftChild) && isRED(node.rightChild)) { flipColors(node); } return node; } }
查找操作

// 查找节点 public TreeNode search(int data) { TreeNode current = root; while (current.data != data) { if (data < current.data) { current = current.leftChild; } else { current = current.rightChild; } if (current == null) { return null; } } return current; }
删除操作
将红黑树内的某一个节点删除的步骤
- 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点删除。
- 被删除节点没有儿子,即为叶节点。那么,直接将该节点删除就OK了。
- 被删除节点只有一个儿子。那么,直接删除该节点,并用该节点的唯一子节点顶替它的位置。
- 被删除节点有两个儿子。那么,先找出它的后继节点;然后把“它的后继节点的内容”复制给“该节点的内容”;之后,删除“它的后继节点”。在这里,后继节点相当于替身,在将后继节点的内容复制给"被删除节点"之后,再将后继节点删除。 在被删除节点有两个非空子节点的情况下,它的后继节点不可能是双子非空,意味着该节点的后继节点要么没有儿子,要么只有一个儿子。若没有儿子,则按情况①进行处理;若只有一个儿子,则按情况②进行处理。
- 通过"旋转和重新着色"等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。

/* * 删除结点(node),并返回被删除的结点 */ private void remove(TreeNode node) { TreeNode child, parent; boolean color; // 被删除节点的左右孩子都不为空时 if ( (node.leftChild!=null) && (node.rightChild!=null) ) { // 被删节点的后继节点取代"被删节点"的位置,然后再将被删节点去掉。 TreeNode replace = node; // 获取后继节点 replace = replace.rightChild; while (replace.leftChild != null) replace = replace.leftChild; // node不是根节点 if (parentOf(node)!=null) { if (parentOf(node).leftChild == node) parentOf(node).leftChild = replace; else parentOf(node).rightChild = replace; } else { // node是根节点,更新根节点。 this.root = replace; } // child是取代节点的右孩子,也是需要调整的节点。 // 取代节点肯定不存在左孩子,因为它是一个后继节点。 child = replace.rightChild; parent = parentOf(replace); // 保存取代节点的颜色 color = colorOf(replace); // 被删除节点是它的后继节点的父节点 if (parent == node) { parent = replace; } else { // child不为空 if (child!=null) setParent(child, parent); parent.leftChild = child; replace.rightChild = node.rightChild; setParent(node.rightChild, replace); } replace.parent = node.parent; replace.color = node.color; replace.leftChild = node.leftChild; node.leftChild.parent = replace; if (color == BLACK) removeFixUp(child, parent); node = null; return ; } if (node.leftChild !=null) { child = node.leftChild; } else { child = node.rightChild; } parent = node.parent; // 保存取代节点的颜色 color = node.color; if (child!=null) child.parent = parent; // node不是根节点 if (parent!=null) { if (parent.leftChild == node) parent.leftChild = child; else parent.rightChild = child; } else { this.root = child; } if (color == BLACK) removeFixUp(child, parent); node = null; } public void remove(int data) { TreeNode node; if ((node = search(data)) != null) remove(node); } /* * 红黑树删除修正函数 * 在从红黑树中删除插入节点之后(红黑树失去平衡),再调用该函数; * 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。 */ private void removeFixUp(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent) { TreeNode other; while ((node==null || isBlack(node)) && (node != this.root)) { if (parent.leftChild == node) { other = parent.rightChild; if (isRed(other)) { //x的兄弟是红色的 setBlack(other); setRed(parent); leftRotate(parent); other = parent.rightChild; } if ((other.leftChild==null || isBlack(other.leftChild)) && (other.rightChild==null || isBlack(other.rightChild))) { //x的兄弟是黑色,且兄弟的两个孩子也是黑色的 setRed(other); node = parent; parent = parentOf(node); } else { if (other.rightChild==null || isBlack(other.rightChild)) { //x的兄弟是黑色的,并且兄弟的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。 setBlack(other.leftChild); setRed(other); rightRotate(other); other = parent.rightChild; } //x的兄弟是黑色的;并且兄弟的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。 setColor(other, colorOf(parent)); setBlack(parent); setBlack(other.rightChild); leftRotate(parent); node = this.root; break; } } else { other = parent.leftChild; if (isRed(other)) { //x的兄弟是红色的 setBlack(other); setRed(parent); rightRotate(parent); other = parent.leftChild; } if ((other.leftChild==null || isBlack(other.leftChild)) && (other.rightChild==null || isBlack(other.rightChild))) { //x的兄弟是黑色,且兄弟的两个孩子也都是黑色的 setRed(other); node = parent; parent = parentOf(node); } else { if (other.leftChild==null || isBlack(other.leftChild)) { // x的兄弟是黑色的,并且兄弟的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。 setBlack(other.rightChild); setRed(other); leftRotate(other); other = parent.leftChild; } // x的兄弟是黑色的;并且兄弟的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。 setColor(other, colorOf(parent)); setBlack(parent); setBlack(other.leftChild); rightRotate(parent); node = this.root; break; } } } if (node!=null) setBlack(node); }
红黑树性能总结
1.对于完全随机的数据,普通的二叉搜索树效率较高,但极端下会退化成链表;
2.对于查询较多的情况,AVL树效率较高;
3.红黑树牺牲了平衡性,综合增删改查的所有操作,红黑树的统计性能较优。




