<二>函数调用过程中对象优化
代码1
using namespace std;
class TestV2 {
public:
TestV2(int a = 10) : ma(a)
{
cout << "TestV2(int) " << ma <<" 对象地址="<<this << endl;
}
~TestV2()
{
cout << "~TestV2()" << ma <<"析构对象地址="<<this<<endl;
}
TestV2(const TestV2 & t) :ma(t.ma)
{
cout << "TestV2(const Test & t),拷贝构造地址 原对象地址"<<&t <<"目标对象地址="<<this << endl;
}
TestV2 & operator =(const TestV2 & t)
{
if (this == &t) { return *this; }
ma = t.ma;
cout << "operator=源对象地址="<< &t<< "目标对象地址=" <<this << endl;
return *this;
}
int getData()
{
return ma;
}
private: int ma;
};
TestV2 getObject(TestV2 tep)
{
int data = tep.getData();
TestV2 temp(data + 100);
return temp;
}
int main()
{
TestV2 t1(20);
TestV2 t2=getObject(t1);
cout << "t2对象地址= "<< &t2 << endl; //对象2的地址带入getObject()函数,TestV2 temp(data + 100) 直接在t3上构建对象
system("pause");
return 0;
}
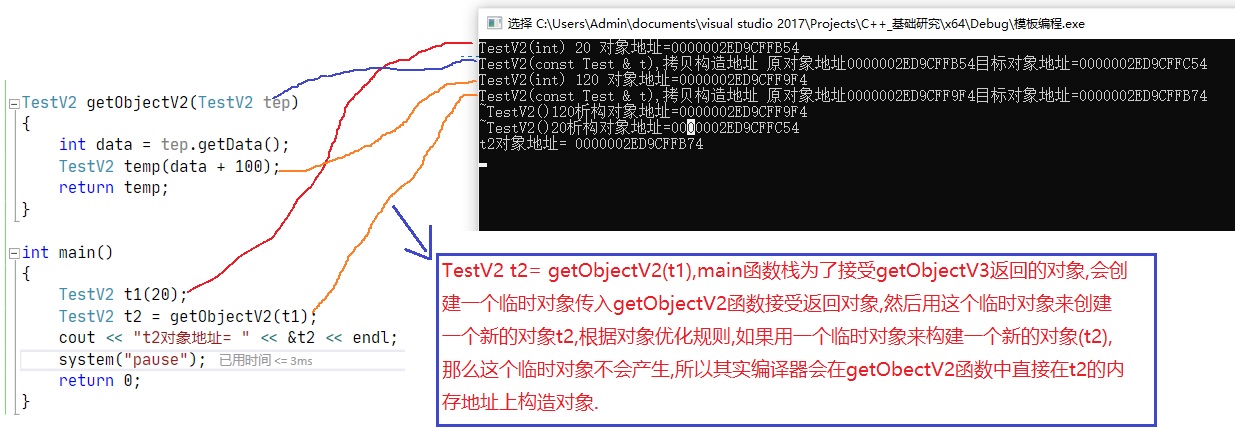
// 针对上面优化
//1:函数参数传递过程汇总,对象优先按引用传递,不要按值传递(可以解决 形参的拷贝构造,和形参的析构)
//2:
TestV2 getObject(TestV2 &tep)
{
int data = tep.getData();
TestV2 temp(data + 100);
return temp;
}
改为
TestV2 getObject(TestV2 &tep)
{
return TestV2 temp(tep.getData()+ 100
);
//用一个临时对象拷贝构造一个新的对象的时候,这个临时对象会被编译器优化掉,不再产生
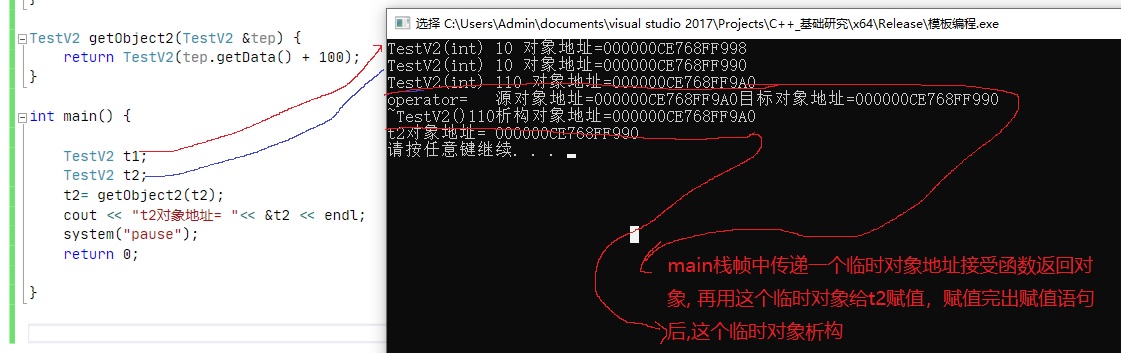
3:接受函数返回是对象的时候,优先用初始化的方式接受,不要用赋值的方式接受


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号