ThreadLocal详解
一、简介
ThreadLocal 是JDK提供的一个操作线程本地变量的工具,填充的数据隶属于当前操作线程栈,变量数据相对于其他线程是不可见的,起到数据隔离的作用,规避线程安全问题。
一个简单的代码示例如下:
public class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
Thread.currentThread().setName("main-test");
threadLocal.set("123");
System.out.println("one:" + threadLocal.get());
}
}
二、原理
1、结构
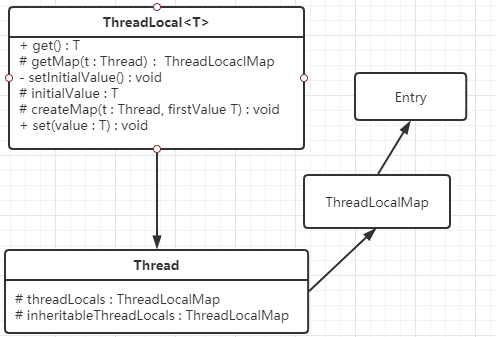
Thread 中定义两个类型均为 ThreadLocalMap 的变量 threadLocals(独占) 和 inherittableThreadLocals(可共享),主要用于存储线程本地变量。ThreadLocalMap 是 ThreadLocal 的静态内部类,类似于Map的 KV 存储结构。ThreadLocal 可以理解为操作线程本地变量的工具,通过 set 方法将 value 添加到 threadLocals 中去,通过 get 方法可以去获取当前线程变量中的 threadLocals 值。如果需要移除值,则调用 remove 方法。
2、源码
2.1、set
public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前线程对象 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //获取当前线程的threadLocals if (map != null) map.set(this, value); //如果 threadLocals 非空,添加 threadLocals 值,key为当前 ThreadLocal实例对象,value为传入的待设值 else createMap(t, value); //如果 threadLocals 为空, 则进行创建初始化操作 }
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; } void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) { t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue); //创建初始化,key为当前 ThreadLocal 实例对象 }
2.2、get
public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前线程对象 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //获取threadLocals if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); // threadLocals非空,以当前 ThreadLocal的实例对象为key在查找map中 if (e != null) { //有值获取返回 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } return setInitialValue(); //没有获取到值,则进行初始化操作 } private T setInitialValue() { T value = initialValue(); //初始 value Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //当前操作线程 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //获取threadLocals if (map != null) map.set(this, value); //不为null,直接设值 else createMap(t, value); //为null,创建初始化 return value; //返回初始化创建的 value,即为null } protected T initialValue() { return null; }
2.3、remove
public void remove() { ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); //根据当前线程对象,获取 threadLocals if (m != null) m.remove(this); //不为空,以当前 ThreadLocal 实例对象为 key 去删除 threadLocals 中相应的值 }
2.4、ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
static class ThreadLocalMap { static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> { /** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */ Object value; Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) { super(k); value = v; } } }
(1)ThreadLocalMap 类似于Map的 KV存储,只有基本的数组结构,并没有链表或者红黑树去解决hash冲突问题,发生冲突的时候,如果同一个 ThreadLocal,则进行覆盖作业。如果不同的话,则顺次的往后查找可存储的空间。

(2)key设计为弱引用结构,在 ThreadLocal 没有外部强引用的时候,只要发生GC回收,则会被资源回收掉,避免一定的内存泄漏。Java的对象引用可查看 https://www.cnblogs.com/eric-fang/p/10310399.html
3、问题
ThreadLocal 在保存的时候将自己当做 key 存在 ThreadLocalMap 中,并被设计成WeakReference弱引用,当 ThreadLocal 没有外部的强引用的时候,会被GC资源回收,这时候创建线程依旧存活运行的话,Entry 中 value就一直不可回收,产生内存泄漏问题。比如在使用线程池的时候,因为线程的回收再利用,之前设置的 value 就可能一直得不到释放回收,一直占据内存资源。
下面上实验对象:
(1)断点
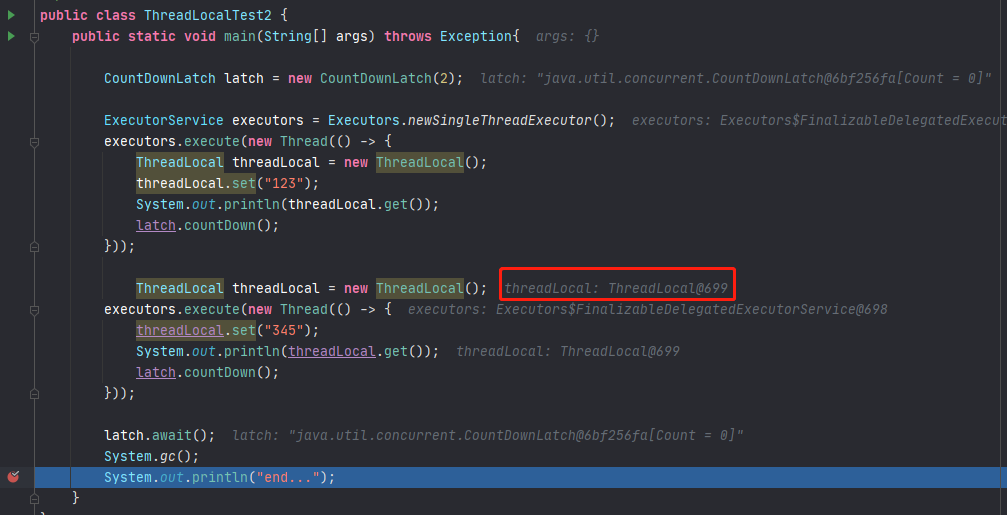
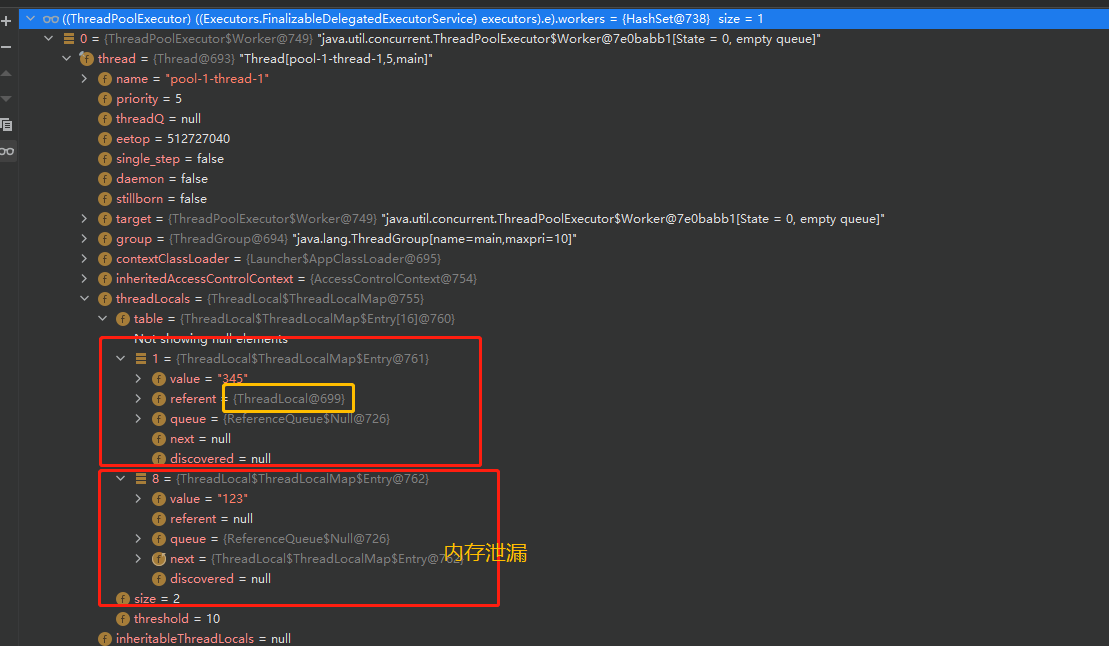
(2) 解决
线程使用完毕,清理 threadLocals,调用ThreadLocal.remove()
4、共享 inheritTableThreadLocals
上面说明的是线程独占的threadLocals,使用看起来简单明了。JDK也提供了父子线程共享的 inheritTableThreadLocals,用于在线程间共享资源。
4.1、示例
public class ThreadLocalTest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread.currentThread().setName("main-test"); ThreadLocal threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal(); threadLocal.set("123"); new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(threadLocal.get()); }).start(); } }
4.2、原理
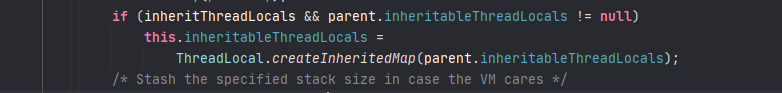
截取 Thread 初始化最关键部分的代码,通过new Thread(Runnable target) 创建对象的时候,init 最终会执行到上图中的代码中位置,标志位 inheritThreadLocals 为 true,parent 为父线程,当父线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量非空的时候,将父线程的 inheritableThreadLocals 塞给当前线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量,完成线程间的数据传递。
5、应用
5.1、RequestContextHolder
public abstract class RequestContextHolder { private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder = new NamedThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request attributes"); private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder = new NamedInheritableThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request context"); public static void setRequestAttributes(RequestAttributes attributes, boolean inheritable) { if (attributes == null) { resetRequestAttributes(); } else { if (inheritable) { inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.set(attributes); requestAttributesHolder.remove(); } else { requestAttributesHolder.set(attributes); inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.remove(); } } } public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() { RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get(); if (attributes == null) { attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get(); } return attributes; } }
Spring 的 RequestContextHolder 类中,使用到 ThreadLocal 保证 request 中的 value 的数据线程安全。
5.2、DateTimeContextHolder
5.3、TransactionSynchronizationManager 事务管理
6、一道面试题结束
package com.cfang.threadlocal; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; /** * @author cfang 2020/9/16 17:52 * @description */ public class ThreadLocalTest5 { private static ThreadLocal<Long> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal(); public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1); new Thread(() -> { set(); System.out.println(get()); latch.countDown(); }).start(); latch.await(); System.out.println(get()); } public static void set() { threadLocal.set(1L); } public static long get() { return threadLocal.get(); } }
输出结果为:

为什么不是 1 null 呢? 注意看 ThreadLocal 泛型为封装类 Long,get()方法返回基本数据类型 long,触发自动拆箱 null.longValue(),完美的空指针异常了。




