unittest框架
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/11494077.html unittest单元测试框架,它还能应用于web测试中。
unittest框架:
-
丰富断言类型
-
做数据驱动测试
-
自动化测试
-
测试报告
unittest框架的下载
在python3中,unittest框架是python的内置模块,无需下载
runTest
用例:

import unittest from case_set import CaseSet class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def runTest(self): if CaseSet().get_status_code() == 200: print('断言成功') else: print('断言失败') def aaa(self): if CaseSet().get_status_code() == 200: print('断言成功') else: print('断言失败') if __name__ == '__main__': case = MyCase(methodName='aaa') case.run()
在命令框用python Mycase.py 命令 来执行用例文件
Case_set.py:

import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup class CaseSet(object): def get_status_code(self, url=None): """ 用于返回 状态码 """ return requests.get(url="https://www.baidu.com").status_code def get_json_data(self, url="http://www.neeo.cc:6001/get?k1=v1"): """ 返回json数据 """ return requests.get(url).json() def get_text_data(self, url=None): """ 返回页面的title """ response = requests.get(url="https://www.baidu.com") response.encoding = 'UTF-8' soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser') # print(response.encoding) return soup.find(name="title").text if __name__ == '__main__': url = "https://www.baidu.com" case = CaseSet() print(case.get_status_code()) print(case.get_text_data()) print(case.get_json_data())
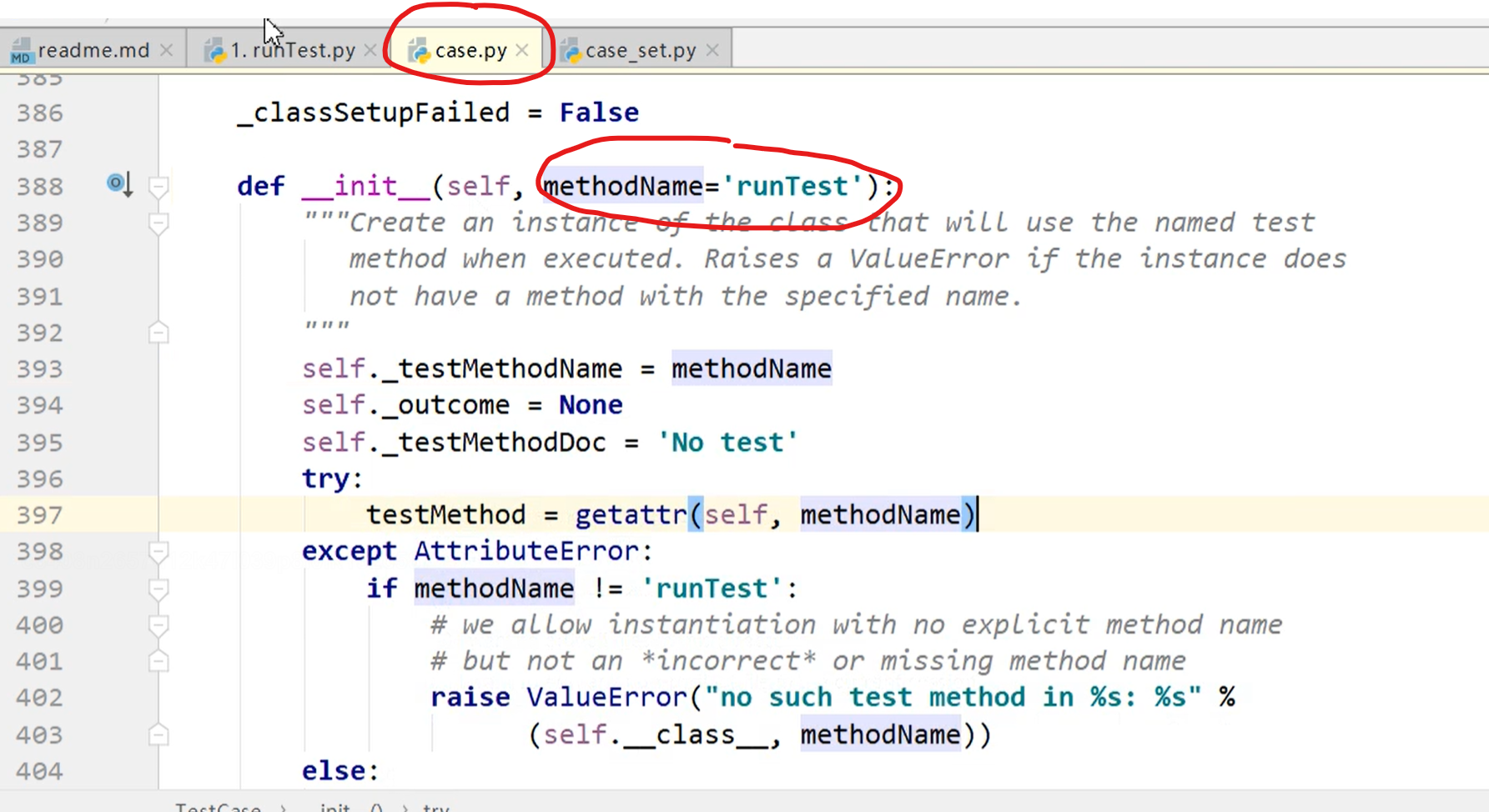
注意:
-
类名可以自定义,但是必须继承unittest.TestCase
-
当run的时候,会自动的找以methodName指定的方法名默认是runTest(),也可以自定义传参case = MyCase(methodName='aaa')然后执行它aaa
setUp/tearDown
用例三剑客:用例执行前setUp 用例执行后tearDown

import unittest import requests class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self): print("用例执行前 先获取状态码") self.code = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com").status_code # def tearDown(self): print("用例执行之后") def runTest(self): if self.code == 200: print('断言成功') else: print('断言失败') if __name__ == '__main__': MyCase().run()
在用例执行执之前做的操作,写在setUp中;必须叫setUp, 做初始化的配置 在用例执行之后,要做的操作,在tearDown中实现,必须叫tearDown,用于收尾工作
unittest断言和unittest.main

import unittest import requests class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def setUp(self): self.code = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com").status_code print("用力执行之前 200", self.code) def tearDown(self): print("用例执行之后") def test_case(self): # 断言assertEqual 判断第一个参数和第二个参数是否相等 self.assertEqual(self.code, 201, msg="实际值:{} 预期值 {}".format(self.code, 201)) # 实际值,预期值,错误描述 def test_case_02(self): """ 第二个测试用例 """ print(self._testMethodDoc, self._testMethodName) self.assertTrue(1) if __name__ == '__main__': unittest.main()
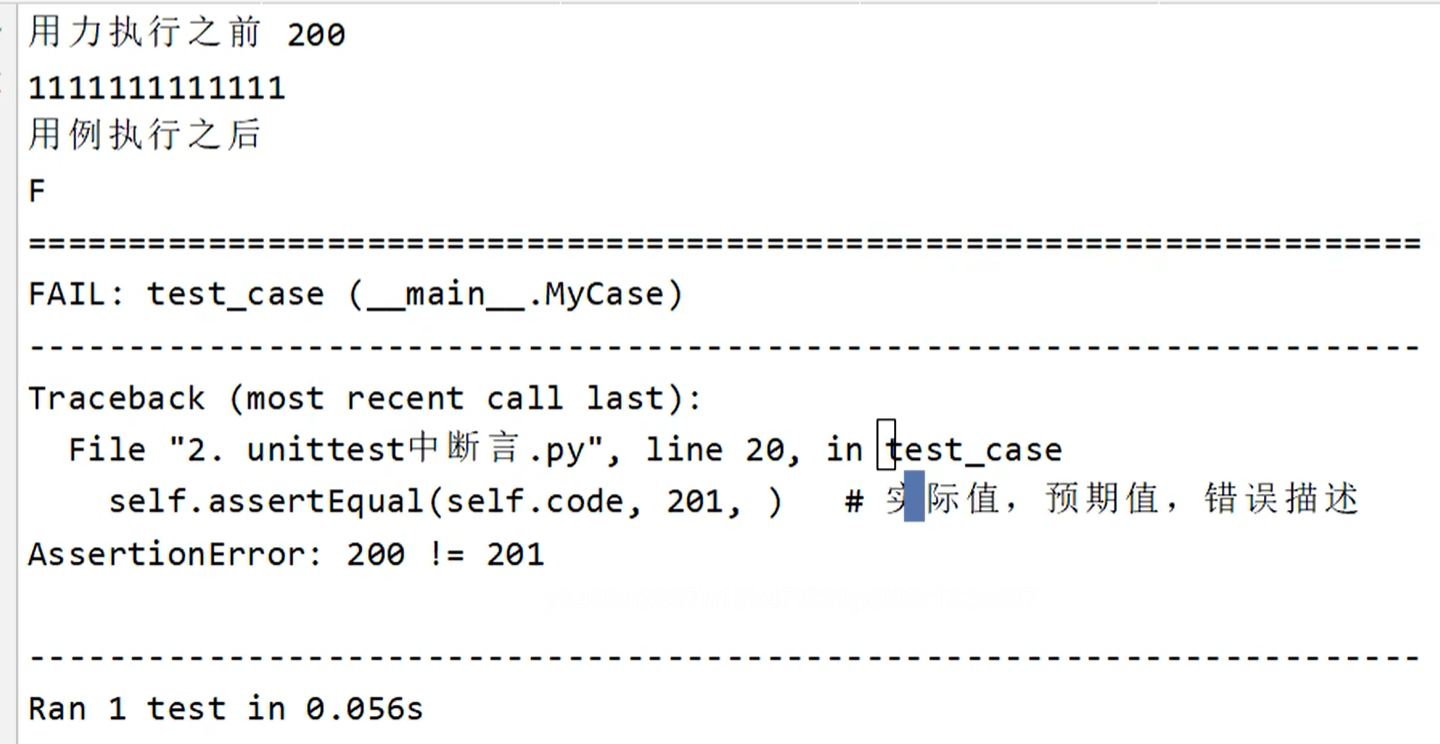
编写用例用test开头,用unittest.main()执行用例,断言再main()里用
用例执行成功用.表示,执行失败是F表示。 unittest.main()会自动的找到当前模块的unittest.TestCase的子类,然后找该子类内部以test开头的用例名,完事去一一的执行它们。
常用的断言:
-
assertEqual(a, b, msg), a == b ,否则断言失败
-
assertNotEqual(a, b, msg), a != b, 否则断言失败
-
assertTrue(x, msg), 判断bool(x) == True, 否则断言失败
-
assertFalse(x, msg), 判断bool(x) == False, 否则断言失败
如何输出用例名和用例描述信息(在用例中输出):
-
self._testMethodDoc,用例描述信息,即方法的注释内容
-
self._testMethodName, 返回用例名
unittest.TestSuite
TestSuite是测试套件,简单理解为承载多个用例的集合,或者把它想象成一个盒子,该盒子有多个用例。 当所有用例都添加到了盒子中,然后找一个执行器,去执行盒子中的测试用例。
我们要做的是:
-
实例化所有的用例
-
创建一个盒子
-
将用例添加到盒子中
-
当所有用例都收集到盒子中后,使用执行器执行盒子中的测试用例

import unittest class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_is_upper(self): # 断言 self.assertTrue('Foo'.isupper()) def test_is_lower(self): # 断言 self.assertTrue('foo'.islower()) if __name__ == '__main__': # 实例化用例 # case_01 = MyCase(methodName='test_is_upper') # case_02 = MyCase(methodName='test_is_lower') # 优化用map case_obj = map(MyCase, ['test_is_upper', 'test_is_lower']) # print(case_obj, list(case_obj)) # 创建盒子suite suite = unittest.TestSuite() # 将用例添加到盒子中 suite.addTests(case_obj) # 返suite中测试用例的个数 # print(11111111, suite.countTestCases()) # 使用执行器TextTestRunner()执行suite中的测试用例 runner = unittest.TextTestRunner() runner.run(suite)
在unittest.TestSuite中的方法:
-
addTest,一个一个添加
-
addTests,批量添加
-
suite.countTestCases(),返回suite中用例个数
unittest.makeSuite
unittest.makeSuite在实例化suite的时候,就同时做了收集用例的操作,直接返回一个收集用例完毕的suite;之后交给执行器去执行就行了。

import unittest class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_is_upper(self): self.assertTrue('Foo'.isupper()) def test_is_lower(self): self.assertTrue('foo'.islower()) def foo_is_instance(self): self.assertIsInstance([1, 2], list) if __name__ == '__main__': # prefix="test"收集用例以test开头的 suite = unittest.makeSuite(testCaseClass=MyCase, prefix="test") # 将foo_is_instance用例也加入到suite中 suite.addTest(MyCase("foo_is_instance")) # 执行器执行 unittest.TextTestRunner().run(suite)
unittest.TestLoader()
pycharm中导包只会识别包(包含init文件的)不识别普通文件
发现其他目录中的脚本用例:
-
unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromModule((ff_case)),找到指定模块(ff_case)下面的TestCase的子类,获取其中以test开头的用例。
-
unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromNames,获取指定模块中的,指定的用例

import unittest from scripts import ff_case class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_is_upper(self): self.assertTrue('Foo'.isupper()) def test_is_lower(self): self.assertTrue('foo'.islower()) def foo_is_instance(self): self.assertIsInstance([1, 2], list) if __name__ == '__main__': from scripts import ff_case # suite = unittest.makeSuite(MyCase) # 找到**指定模块**(ff_case)下面的TestCase的子类,获取其中以test开头的用例。 # suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromModule(ff_case) # 获取指定模块中的,指定的用例 (ff_case.TestCase) # suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromName( # name="MyTestCase.test_case_02", # 类.用例名称 # module=ff_case # 模块名 # ) # 获取指定模块中的,指定的用例 (ff_case.TestCase) 多个用例 suite = unittest.TestLoader().loadTestsFromNames( names=[ "MyTestCase.test_case_01", "MyTestCase.test_case_02", ], module=ff_case )
比较重要的一个:发现指定目录中的所有的合法的脚本中的合法的测试用例
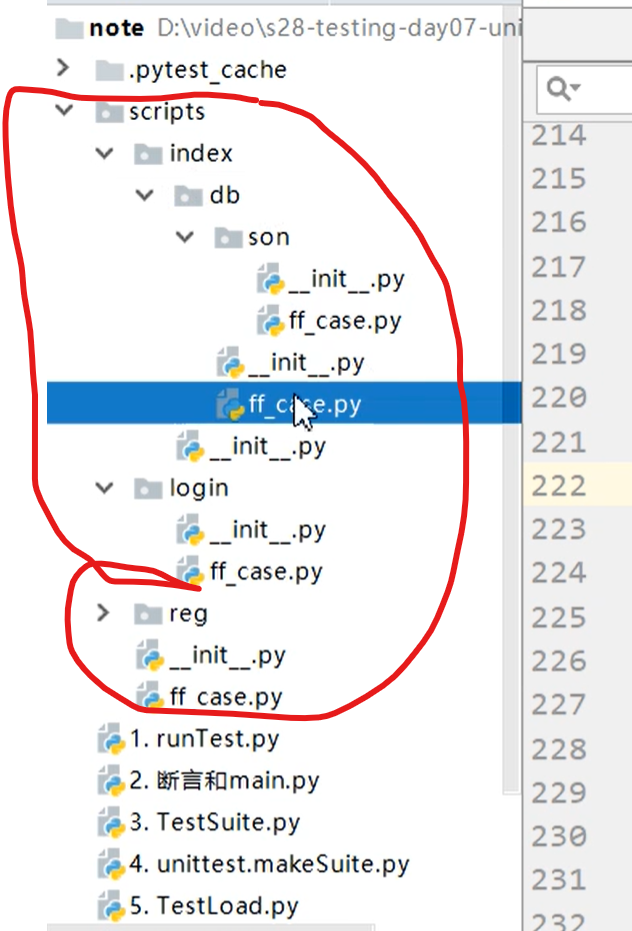

import unittest from scripts import ff_case class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_is_upper(self): self.assertTrue('Foo'.isupper()) def test_is_lower(self): self.assertTrue('foo'.islower()) def foo_is_instance(self): self.assertIsInstance([1, 2], list) if __name__ == '__main__': # 发现指定目录中的所有合法的脚本中的合法的测试用例 import os SCRIPTS_DIR = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), 'scripts') index_dir = os.path.join(SCRIPTS_DIR, 'index') suite = unittest.TestLoader().discover( top_level_dir=SCRIPTS_DIR, start_dir= index_dir, pattern='ff_*' ) unittest.TextTestRunner( verbosity=2 ).run(suite)
-
suite = unittest.TestLoader().discover( top_level_dir=SCRIPTS_DIR, # 顶级目录 start_dir=index_dir, # 开始收集用例的目录 pattern='ff_*' )
-
top_level_dir和start_dir的关系:
-
top_level_dir == start_dir,没问题
-
top_level_dir > start_dir, 没问题
-
top_level_dir < start_dir, 有问题
-
-
注意,discover只会收集Python的包(含init文件的文件夹)中以pattern开头'ff_*'的脚本,再找脚本中unittest.TestCase的子类中的以test开头的测试用例
-
verbosity

import unittest class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_is_upper(self): self.assertTrue('Foo'.isupper()) def test_is_lower(self): self.assertTrue('foo'.islower()) def foo_is_instance(self): self.assertIsInstance([1, 2], list) if __name__ == '__main__': unittest.main(verbosity=2)
verbosity用来控制用例输出结果的详细程度。
-
verbosity=0, 精简模式。只输出执行错误的记录。
-
verbosity=1, 默认模式,输出用例执行结果
-
verbosity=2, 详细模式输出,用例来自于哪个模块下的哪个类中的哪个用例和它的执行结果。
setupClass/tearDownClass

import unittest class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): @classmethod def setUpClass(cls): print('所有用例执行之前') @classmethod def tearDownClass(cls): print('所有用例执行之后') def setUp(self): print('{}执行之前'.format(self._testMethodName)) def tearDown(self): print('{}执行之后'.format(self._testMethodName)) def test_is_upper(self): self.assertTrue('FOO'.isupper()) def test_is_lower(self): self.assertTrue('foo'.islower()) if __name__ == '__main__': unittest.main(verbosity=2)
在用例前/后执行的:
-
setup/teardown
在所有的用例执行前/后执行的:
-
setUpClass/tearDownClass
跳过用例
有的情况下不需要某个用例执行,就用到了unittest.skip来完成:
无条件跳过:
-
unittest.skip(reason),跳过用例的描述
有条件跳过:
-
unittest.skipif(condition, reason) # 跳过的条件(条件为真跳过),跳过的原因

import unittest class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_case_01(self): self.assertTrue(1) @unittest.skip(reason='无条件跳过') def test_case_02(self): self.assertTrue("") @unittest.skipIf(condition=3 < 2, reason='有条件跳过') def test_case_03(self): self.assertTrue(0) if __name__ == '__main__': unittest.main(verbosity=2)
在输出的窗口中,跳过的用例用s表示;断言成功.表示;断言失败F表示。
将结果输出到文件

import unittest class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_case_01(self): self.assertTrue(1) # @unittest.skip(reason='无条件跳过') def test_case_02(self): self.assertTrue("") # @unittest.skipIf(condition=3 < 2, reason='有条件跳过') def test_case_03(self): self.assertTrue(0) if __name__ == '__main__': suite = unittest.makeSuite(testCaseClass=MyCase, prefix='test') print(suite) # stream=f 屏幕流到文件流 f = open('a.txt', 'w') unittest.TextTestRunner(stream=f).run(suite)
主要使用stream参数,给个文件句柄即可。
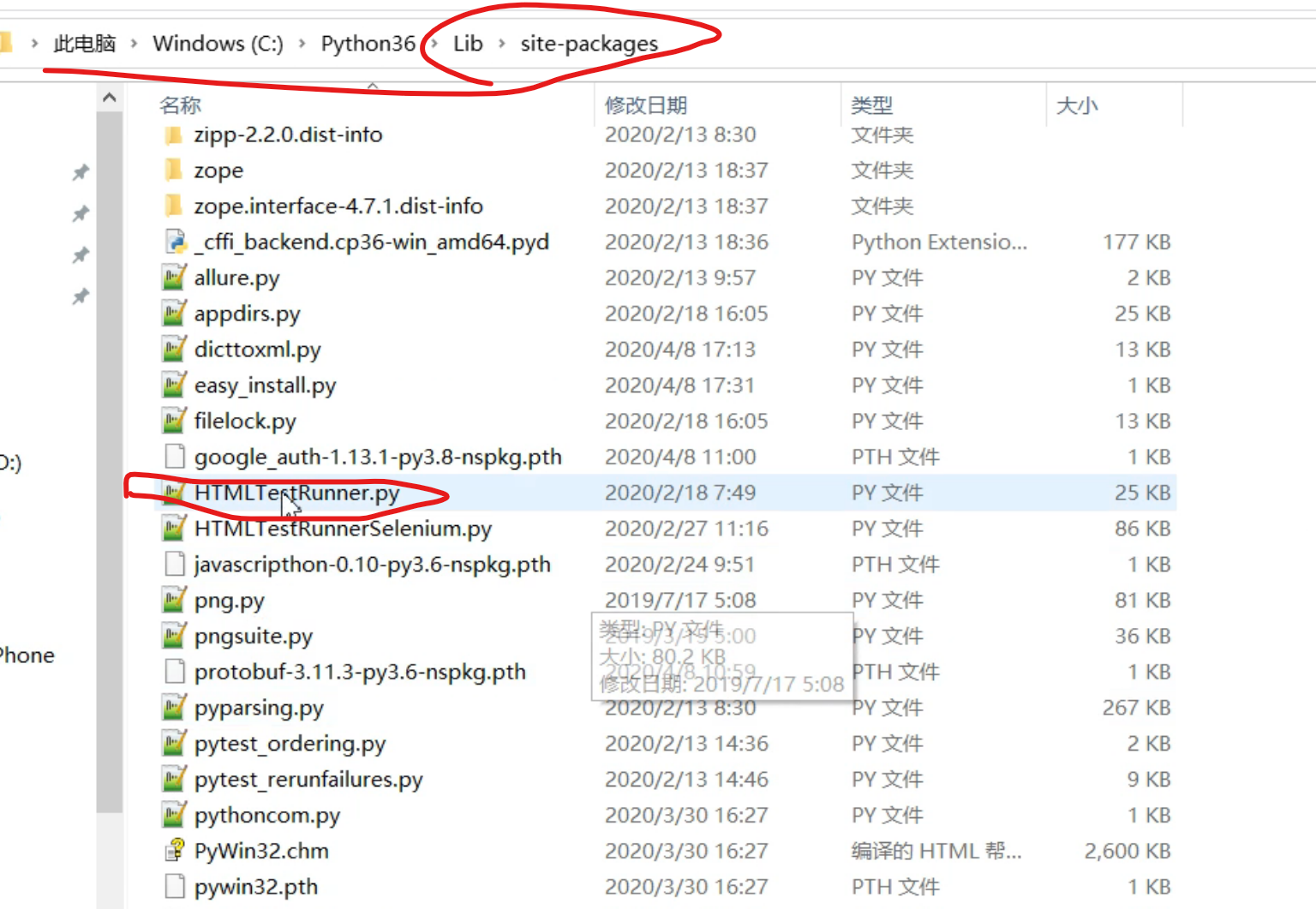
unittest生成测试报告
unittest搭配HTMLTestRunner模块来完成生成测试报告的操作。 unittest还可以跟BSTestRunner来生成测试报告。 HTMLTestRunner下载 该模块暂时没有在官网维护。只能私人搜索。 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/7942613.html 将HTMLTestRunner.py/BSTestRunner.py放到python的第三方包中,lib/site-packages/
HTMLTestRunner.py:(适用于python3)

# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ A TestRunner for use with the Python unit testing framework. It generates a HTML report to show the result at a glance. The simplest way to use this is to invoke its main method. E.g. import unittest import HTMLTestRunner ... define your tests ... if __name__ == '__main__': HTMLTestRunner.main() For more customization options, instantiates a HTMLTestRunner object. HTMLTestRunner is a counterpart to unittest's TextTestRunner. E.g. # output to a file fp = file('my_report.html', 'wb') runner = HTMLTestRunner.HTMLTestRunner( stream=fp, title='My unit test', description='This demonstrates the report output by HTMLTestRunner.' ) # Use an external stylesheet. # See the Template_mixin class for more customizable options runner.STYLESHEET_TMPL = '<link rel="stylesheet" href="my_stylesheet.css" type="text/css">' # run the test runner.run(my_test_suite) ------------------------------------------------------------------------ Copyright (c) 2004-2007, Wai Yip Tung All rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * Neither the name Wai Yip Tung nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission. THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. """ # URL: http://tungwaiyip.info/software/HTMLTestRunner.html __author__ = "Wai Yip Tung" __version__ = "0.9.1" """ Change History Version 0.9.1 * 用Echarts添加执行情况统计图 (灰蓝) Version 0.9.0 * 改成Python 3.x (灰蓝) Version 0.8.3 * 使用 Bootstrap稍加美化 (灰蓝) * 改为中文 (灰蓝) Version 0.8.2 * Show output inline instead of popup window (Viorel Lupu). Version in 0.8.1 * Validated XHTML (Wolfgang Borgert). * Added description of test classes and test cases. Version in 0.8.0 * Define Template_mixin class for customization. * Workaround a IE 6 bug that it does not treat <script> block as CDATA. Version in 0.7.1 * Back port to Python 2.3 (Frank Horowitz). * Fix missing scroll bars in detail log (Podi). """ # TODO: color stderr # TODO: simplify javascript using ,ore than 1 class in the class attribute? import datetime import sys import io import time import unittest from xml.sax import saxutils # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ # The redirectors below are used to capture output during testing. Output # sent to sys.stdout and sys.stderr are automatically captured. However # in some cases sys.stdout is already cached before HTMLTestRunner is # invoked (e.g. calling logging.basicConfig). In order to capture those # output, use the redirectors for the cached stream. # # e.g. # >>> logging.basicConfig(stream=HTMLTestRunner.stdout_redirector) # >>> class OutputRedirector(object): """ Wrapper to redirect stdout or stderr """ def __init__(self, fp): self.fp = fp def write(self, s): self.fp.write(s) def writelines(self, lines): self.fp.writelines(lines) def flush(self): self.fp.flush() stdout_redirector = OutputRedirector(sys.stdout) stderr_redirector = OutputRedirector(sys.stderr) # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # Template class Template_mixin(object): """ Define a HTML template for report customerization and generation. Overall structure of an HTML report HTML +------------------------+ |<html> | | <head> | | | | STYLESHEET | | +----------------+ | | | | | | +----------------+ | | | | </head> | | | | <body> | | | | HEADING | | +----------------+ | | | | | | +----------------+ | | | | REPORT | | +----------------+ | | | | | | +----------------+ | | | | ENDING | | +----------------+ | | | | | | +----------------+ | | | | </body> | |</html> | +------------------------+ """ STATUS = { 0: u'通过', 1: u'失败', 2: u'错误', } DEFAULT_TITLE = 'Unit Test Report' DEFAULT_DESCRIPTION = '' # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ # HTML Template HTML_TMPL = r"""<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <title>%(title)s</title> <meta name="generator" content="%(generator)s"/> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/> <link href="http://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.0/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet"> <script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/echarts/3.8.5/echarts.common.min.js"></script> <!-- <script type="text/javascript" src="js/echarts.common.min.js"></script> --> %(stylesheet)s </head> <body> <script language="javascript" type="text/javascript"><!-- output_list = Array(); /* level - 0:Summary; 1:Failed; 2:All */ function showCase(level) { trs = document.getElementsByTagName("tr"); for (var i = 0; i < trs.length; i++) { tr = trs[i]; id = tr.id; if (id.substr(0,2) == 'ft') { if (level < 1) { tr.className = 'hiddenRow'; } else { tr.className = ''; } } if (id.substr(0,2) == 'pt') { if (level > 1) { tr.className = ''; } else { tr.className = 'hiddenRow'; } } } } function showClassDetail(cid, count) { var id_list = Array(count); var toHide = 1; for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) { tid0 = 't' + cid.substr(1) + '.' + (i+1); tid = 'f' + tid0; tr = document.getElementById(tid); if (!tr) { tid = 'p' + tid0; tr = document.getElementById(tid); } id_list[i] = tid; if (tr.className) { toHide = 0; } } for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) { tid = id_list[i]; if (toHide) { document.getElementById('div_'+tid).style.display = 'none' document.getElementById(tid).className = 'hiddenRow'; } else { document.getElementById(tid).className = ''; } } } function showTestDetail(div_id){ var details_div = document.getElementById(div_id) var displayState = details_div.style.display // alert(displayState) if (displayState != 'block' ) { displayState = 'block' details_div.style.display = 'block' } else { details_div.style.display = 'none' } } function html_escape(s) { s = s.replace(/&/g,'&'); s = s.replace(/</g,'<'); s = s.replace(/>/g,'>'); return s; } /* obsoleted by detail in <div> function showOutput(id, name) { var w = window.open("", //url name, "resizable,scrollbars,status,width=800,height=450"); d = w.document; d.write("<pre>"); d.write(html_escape(output_list[id])); d.write("\n"); d.write("<a href='javascript:window.close()'>close</a>\n"); d.write("</pre>\n"); d.close(); } */ --></script> <div id="div_base"> %(heading)s %(report)s %(ending)s %(chart_script)s </div> </body> </html> """ # variables: (title, generator, stylesheet, heading, report, ending, chart_script) ECHARTS_SCRIPT = """ <script type="text/javascript"> // 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例 var myChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('chart')); // 指定图表的配置项和数据 var option = { title : { text: '测试执行情况', x:'center' }, tooltip : { trigger: 'item', formatter: "{a} <br/>{b} : {c} ({d}%%)" }, color: ['#95b75d', 'grey', '#b64645'], legend: { orient: 'vertical', left: 'left', data: ['通过','失败','错误'] }, series : [ { name: '测试执行情况', type: 'pie', radius : '60%%', center: ['50%%', '60%%'], data:[ {value:%(Pass)s, name:'通过'}, {value:%(fail)s, name:'失败'}, {value:%(error)s, name:'错误'} ], itemStyle: { emphasis: { shadowBlur: 10, shadowOffsetX: 0, shadowColor: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)' } } } ] }; // 使用刚指定的配置项和数据显示图表。 myChart.setOption(option); </script> """ # variables: (Pass, fail, error) # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Stylesheet # # alternatively use a <link> for external style sheet, e.g. # <link rel="stylesheet" href="$url" type="text/css"> STYLESHEET_TMPL = """ <style type="text/css" media="screen"> body { font-family: Microsoft YaHei,Consolas,arial,sans-serif; font-size: 80%; } table { font-size: 100%; } pre { white-space: pre-wrap;word-wrap: break-word; } /* -- heading ---------------------------------------------------------------------- */ h1 { font-size: 16pt; color: gray; } .heading { margin-top: 0ex; margin-bottom: 1ex; } .heading .attribute { margin-top: 1ex; margin-bottom: 0; } .heading .description { margin-top: 2ex; margin-bottom: 3ex; } /* -- css div popup ------------------------------------------------------------------------ */ a.popup_link { } a.popup_link:hover { color: red; } .popup_window { display: none; position: relative; left: 0px; top: 0px; /*border: solid #627173 1px; */ padding: 10px; /*background-color: #E6E6D6; */ font-family: "Lucida Console", "Courier New", Courier, monospace; text-align: left; font-size: 8pt; /* width: 500px;*/ } } /* -- report ------------------------------------------------------------------------ */ #show_detail_line { margin-top: 3ex; margin-bottom: 1ex; } #result_table { width: 99%; } #header_row { font-weight: bold; color: #303641; background-color: #ebebeb; } #total_row { font-weight: bold; } .passClass { background-color: #bdedbc; } .failClass { background-color: #ffefa4; } .errorClass { background-color: #ffc9c9; } .passCase { color: #6c6; } .failCase { color: #FF6600; font-weight: bold; } .errorCase { color: #c00; font-weight: bold; } .hiddenRow { display: none; } .testcase { margin-left: 2em; } /* -- ending ---------------------------------------------------------------------- */ #ending { } #div_base { position:absolute; top:0%; left:5%; right:5%; width: auto; height: auto; margin: -15px 0 0 0; } </style> """ # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Heading # HEADING_TMPL = """ <div class='page-header'> <h1>%(title)s</h1> %(parameters)s </div> <div style="float: left;width:50%%;"><p class='description'>%(description)s</p></div> <div id="chart" style="width:50%%;height:400px;float:left;"></div> """ # variables: (title, parameters, description) HEADING_ATTRIBUTE_TMPL = """<p class='attribute'><strong>%(name)s:</strong> %(value)s</p> """ # variables: (name, value) # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Report # REPORT_TMPL = u""" <div class="btn-group btn-group-sm"> <button class="btn btn-default" onclick='javascript:showCase(0)'>总计</button> <button class="btn btn-default" onclick='javascript:showCase(1)'>失败</button> <button class="btn btn-default" onclick='javascript:showCase(2)'>全部</button> </div> <p></p> <table id='result_table' class="table table-bordered"> <colgroup> <col align='left' /> <col align='right' /> <col align='right' /> <col align='right' /> <col align='right' /> <col align='right' /> </colgroup> <tr id='header_row'> <td>测试套件/测试用例</td> <td>总数</td> <td>通过</td> <td>失败</td> <td>错误</td> <td>查看</td> </tr> %(test_list)s <tr id='total_row'> <td>总计</td> <td>%(count)s</td> <td>%(Pass)s</td> <td>%(fail)s</td> <td>%(error)s</td> <td> </td> </tr> </table> """ # variables: (test_list, count, Pass, fail, error) REPORT_CLASS_TMPL = u""" <tr class='%(style)s'> <td>%(desc)s</td> <td>%(count)s</td> <td>%(Pass)s</td> <td>%(fail)s</td> <td>%(error)s</td> <td><a href="javascript:showClassDetail('%(cid)s',%(count)s)">详情</a></td> </tr> """ # variables: (style, desc, count, Pass, fail, error, cid) REPORT_TEST_WITH_OUTPUT_TMPL = r""" <tr id='%(tid)s' class='%(Class)s'> <td class='%(style)s'><div class='testcase'>%(desc)s</div></td> <td colspan='5' align='center'> <!--css div popup start--> <a class="popup_link" onfocus='this.blur();' href="javascript:showTestDetail('div_%(tid)s')" > %(status)s</a> <div id='div_%(tid)s' class="popup_window"> <pre>%(script)s</pre> </div> <!--css div popup end--> </td> </tr> """ # variables: (tid, Class, style, desc, status) REPORT_TEST_NO_OUTPUT_TMPL = r""" <tr id='%(tid)s' class='%(Class)s'> <td class='%(style)s'><div class='testcase'>%(desc)s</div></td> <td colspan='5' align='center'>%(status)s</td> </tr> """ # variables: (tid, Class, style, desc, status) REPORT_TEST_OUTPUT_TMPL = r"""%(id)s: %(output)s""" # variables: (id, output) # ------------------------------------------------------------------------ # ENDING # ENDING_TMPL = """<div id='ending'> </div>""" # -------------------- The end of the Template class ------------------- TestResult = unittest.TestResult class _TestResult(TestResult): # note: _TestResult is a pure representation of results. # It lacks the output and reporting ability compares to unittest._TextTestResult. def __init__(self, verbosity=1): TestResult.__init__(self) self.stdout0 = None self.stderr0 = None self.success_count = 0 self.failure_count = 0 self.error_count = 0 self.verbosity = verbosity # result is a list of result in 4 tuple # ( # result code (0: success; 1: fail; 2: error), # TestCase object, # Test output (byte string), # stack trace, # ) self.result = [] self.subtestlist = [] def startTest(self, test): TestResult.startTest(self, test) # just one buffer for both stdout and stderr self.outputBuffer = io.StringIO() stdout_redirector.fp = self.outputBuffer stderr_redirector.fp = self.outputBuffer self.stdout0 = sys.stdout self.stderr0 = sys.stderr sys.stdout = stdout_redirector sys.stderr = stderr_redirector def complete_output(self): """ Disconnect output redirection and return buffer. Safe to call multiple times. """ if self.stdout0: sys.stdout = self.stdout0 sys.stderr = self.stderr0 self.stdout0 = None self.stderr0 = None return self.outputBuffer.getvalue() def stopTest(self, test): # Usually one of addSuccess, addError or addFailure would have been called. # But there are some path in unittest that would bypass this. # We must disconnect stdout in stopTest(), which is guaranteed to be called. self.complete_output() def addSuccess(self, test): if test not in self.subtestlist: self.success_count += 1 TestResult.addSuccess(self, test) output = self.complete_output() self.result.append((0, test, output, '')) if self.verbosity > 1: sys.stderr.write('ok ') sys.stderr.write(str(test)) sys.stderr.write('\n') else: sys.stderr.write('.') def addError(self, test, err): self.error_count += 1 TestResult.addError(self, test, err) _, _exc_str = self.errors[-1] output = self.complete_output() self.result.append((2, test, output, _exc_str)) if self.verbosity > 1: sys.stderr.write('E ') sys.stderr.write(str(test)) sys.stderr.write('\n') else: sys.stderr.write('E') def addFailure(self, test, err): self.failure_count += 1 TestResult.addFailure(self, test, err) _, _exc_str = self.failures[-1] output = self.complete_output() self.result.append((1, test, output, _exc_str)) if self.verbosity > 1: sys.stderr.write('F ') sys.stderr.write(str(test)) sys.stderr.write('\n') else: sys.stderr.write('F') def addSubTest(self, test, subtest, err): if err is not None: if getattr(self, 'failfast', False): self.stop() if issubclass(err[0], test.failureException): self.failure_count += 1 errors = self.failures errors.append((subtest, self._exc_info_to_string(err, subtest))) output = self.complete_output() self.result.append((1, test, output + '\nSubTestCase Failed:\n' + str(subtest), self._exc_info_to_string(err, subtest))) if self.verbosity > 1: sys.stderr.write('F ') sys.stderr.write(str(subtest)) sys.stderr.write('\n') else: sys.stderr.write('F') else: self.error_count += 1 errors = self.errors errors.append((subtest, self._exc_info_to_string(err, subtest))) output = self.complete_output() self.result.append( (2, test, output + '\nSubTestCase Error:\n' + str(subtest), self._exc_info_to_string(err, subtest))) if self.verbosity > 1: sys.stderr.write('E ') sys.stderr.write(str(subtest)) sys.stderr.write('\n') else: sys.stderr.write('E') self._mirrorOutput = True else: self.subtestlist.append(subtest) self.subtestlist.append(test) self.success_count += 1 output = self.complete_output() self.result.append((0, test, output + '\nSubTestCase Pass:\n' + str(subtest), '')) if self.verbosity > 1: sys.stderr.write('ok ') sys.stderr.write(str(subtest)) sys.stderr.write('\n') else: sys.stderr.write('.') class HTMLTestRunner(Template_mixin): def __init__(self, stream=sys.stdout, verbosity=1, title=None, description=None): self.stream = stream self.verbosity = verbosity if title is None: self.title = self.DEFAULT_TITLE else: self.title = title if description is None: self.description = self.DEFAULT_DESCRIPTION else: self.description = description self.startTime = datetime.datetime.now() def run(self, test): "Run the given test case or test suite." result = _TestResult(self.verbosity) test(result) self.stopTime = datetime.datetime.now() self.generateReport(test, result) print('\nTime Elapsed: %s' % (self.stopTime - self.startTime), file=sys.stderr) return result def sortResult(self, result_list): # unittest does not seems to run in any particular order. # Here at least we want to group them together by class. rmap = {} classes = [] for n, t, o, e in result_list: cls = t.__class__ if cls not in rmap: rmap[cls] = [] classes.append(cls) rmap[cls].append((n, t, o, e)) r = [(cls, rmap[cls]) for cls in classes] return r def getReportAttributes(self, result): """ Return report attributes as a list of (name, value). Override this to add custom attributes. """ startTime = str(self.startTime)[:19] duration = str(self.stopTime - self.startTime) status = [] if result.success_count: status.append(u'通过 %s' % result.success_count) if result.failure_count: status.append(u'失败 %s' % result.failure_count) if result.error_count: status.append(u'错误 %s' % result.error_count) if status: status = ' '.join(status) else: status = 'none' return [ (u'开始时间', startTime), (u'运行时长', duration), (u'状态', status), ] def generateReport(self, test, result): report_attrs = self.getReportAttributes(result) generator = 'HTMLTestRunner %s' % __version__ stylesheet = self._generate_stylesheet() heading = self._generate_heading(report_attrs) report = self._generate_report(result) ending = self._generate_ending() chart = self._generate_chart(result) output = self.HTML_TMPL % dict( title=saxutils.escape(self.title), generator=generator, stylesheet=stylesheet, heading=heading, report=report, ending=ending, chart_script=chart ) self.stream.write(output.encode('utf8')) def _generate_stylesheet(self): return self.STYLESHEET_TMPL def _generate_heading(self, report_attrs): a_lines = [] for name, value in report_attrs: line = self.HEADING_ATTRIBUTE_TMPL % dict( name=saxutils.escape(name), value=saxutils.escape(value), ) a_lines.append(line) heading = self.HEADING_TMPL % dict( title=saxutils.escape(self.title), parameters=''.join(a_lines), description=saxutils.escape(self.description), ) return heading def _generate_report(self, result): rows = [] sortedResult = self.sortResult(result.result) for cid, (cls, cls_results) in enumerate(sortedResult): # subtotal for a class np = nf = ne = 0 for n, t, o, e in cls_results: if n == 0: np += 1 elif n == 1: nf += 1 else: ne += 1 # format class description if cls.__module__ == "__main__": name = cls.__name__ else: name = "%s.%s" % (cls.__module__, cls.__name__) doc = cls.__doc__ and cls.__doc__.split("\n")[0] or "" desc = doc and '%s: %s' % (name, doc) or name row = self.REPORT_CLASS_TMPL % dict( style=ne > 0 and 'errorClass' or nf > 0 and 'failClass' or 'passClass', desc=desc, count=np + nf + ne, Pass=np, fail=nf, error=ne, cid='c%s' % (cid + 1), ) rows.append(row) for tid, (n, t, o, e) in enumerate(cls_results): self._generate_report_test(rows, cid, tid, n, t, o, e) report = self.REPORT_TMPL % dict( test_list=''.join(rows), count=str(result.success_count + result.failure_count + result.error_count), Pass=str(result.success_count), fail=str(result.failure_count), error=str(result.error_count), ) return report def _generate_chart(self, result): chart = self.ECHARTS_SCRIPT % dict( Pass=str(result.success_count), fail=str(result.failure_count), error=str(result.error_count), ) return chart def _generate_report_test(self, rows, cid, tid, n, t, o, e): # e.g. 'pt1.1', 'ft1.1', etc has_output = bool(o or e) tid = (n == 0 and 'p' or 'f') + 't%s.%s' % (cid + 1, tid + 1) name = t.id().split('.')[-1] doc = t.shortDescription() or "" desc = doc and ('%s: %s' % (name, doc)) or name tmpl = has_output and self.REPORT_TEST_WITH_OUTPUT_TMPL or self.REPORT_TEST_NO_OUTPUT_TMPL script = self.REPORT_TEST_OUTPUT_TMPL % dict( id=tid, output=saxutils.escape(o + e), ) row = tmpl % dict( tid=tid, Class=(n == 0 and 'hiddenRow' or 'none'), style=(n == 2 and 'errorCase' or (n == 1 and 'failCase' or 'none')), desc=desc, script=script, status=self.STATUS[n], ) rows.append(row) if not has_output: return def _generate_ending(self): return self.ENDING_TMPL ############################################################################## # Facilities for running tests from the command line ############################################################################## # Note: Reuse unittest.TestProgram to launch test. In the future we may # build our own launcher to support more specific command line # parameters like test title, CSS, etc. class TestProgram(unittest.TestProgram): """ A variation of the unittest.TestProgram. Please refer to the base class for command line parameters. """ def runTests(self): # Pick HTMLTestRunner as the default test runner. # base class's testRunner parameter is not useful because it means # we have to instantiate HTMLTestRunner before we know self.verbosity. if self.testRunner is None: self.testRunner = HTMLTestRunner(verbosity=self.verbosity) unittest.TestProgram.runTests(self) main = TestProgram ############################################################################## # Executing this module from the command line ############################################################################## if __name__ == "__main__": main(module=None)

import unittest from HTMLTestRunner import HTMLTestRunner class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_case_01(self): self.assertTrue(1) def test_case_02(self): self.assertTrue("") def test_case_03(self): self.assertTrue(0) if __name__ == '__main__': suite = unittest.makeSuite(testCaseClass=MyCase) # print(suite) f = open('./result.html', 'wb') # 新的执行器 HTMLTestRunner( stream=f, title='s28第一个unittest测试用例', description="s28的测试报告", verbosity=2 ).run(suite) # BSTestRunner( # stream=f, # title='s28第一个unittest测试用例', # description="s28的测试报告", # verbosity=2 # # ).run(suite)
发送邮件
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/11478853.html 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/articles/11199127.html#%E9%80%9A%E8%BF%87smtp%E5%8F%91%E9%82%AE%E4%BB%B6
-
去QQ邮箱配置SMTP服务器和获取授权码
-
编写测试用例
-
生成测试报告
-
使用第三方邮件服务发送测试报告

import unittest import smtplib from email.mime.text import MIMEText from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart from email.header import Header from HTMLTestRunner import HTMLTestRunner class MyCase(unittest.TestCase): def test_case_01(self): self.assertTrue(1) def test_case_02(self): self.assertTrue("") def test_case_03(self): self.assertTrue(0) def get_result(): suite = unittest.makeSuite(testCaseClass=MyCase, prefix="test") file_path = './result.html' f = open(file_path, 'wb') HTMLTestRunner( stream=f, title="发邮件", description="将测试报告发邮件", verbosity=2 ).run(suite) f.close() f1 = open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') return f1.read() def send_mail(): # 第三方 SMTP 服务 mail_host = "smtp.qq.com" # 设置服务器 # 勿动 mail_user = "1206180814@qq.com" # 用户名 mail_pass = "hrcjrrkrdzdabaej" # 口令 # 设置收件人和发件人 sender = '1206180814@qq.com' receivers = ['1206180814@qq.com', 'tingyuweilou@163.com'] # 接收邮件,可设置为你的QQ邮箱或者其他邮箱 # 创建一个带附件的实例对象 message = MIMEMultipart() # 邮件主题、收件人、发件人 subject = '请查阅--s28的第一个测试报告' # 邮件主题 message['Subject'] = Header(subject, 'utf-8') message['From'] = Header("{}".format(sender), 'utf-8') # 发件人 message['To'] = Header("{}".format(';'.join(receivers)), 'utf-8') # 收件人 # 邮件正文内容 send_content = 'hi man,你收到附件了吗?' content_obj = MIMEText(send_content, 'plain', 'utf-8') # 第一个参数为邮件内容 message.attach(content_obj) # 构造附件 att = MIMEText(_text=send_content, _subtype='base64', _charset='utf-8') att["Content-Type"] = 'application/octet-stream' file_name = 'result.html' att["Content-Disposition"] = 'attachment; filename="{}"'.format(file_name) # # filename 为邮件附件中显示什么名字 message.attach(att) try: smtp_obj = smtplib.SMTP() smtp_obj.connect(mail_host, 25) # 25 为 SMTP 端口号 smtp_obj.login(mail_user, mail_pass) smtp_obj.sendmail(sender, receivers, message.as_string()) smtp_obj.quit() print("邮件发送成功") except smtplib.SMTPException: print("Error: 无法发送邮件") if __name__ == '__main__': send_mail() # get_result()




