ES6 一
为什么要学习
ES5语言的先天性不足。比如变量提升、内置对象的方法不灵活、模块化实现不完善等等
为了后面vue、尤其react框架做好了准备
目前大部分公司的项目都在使用ES6
ECMAScript6.0 是JavaScript语言的下一代标准 他的目标是使得JS语言可以用来编写复杂的大型应用程序 成为u企业界开发语言
新特性:
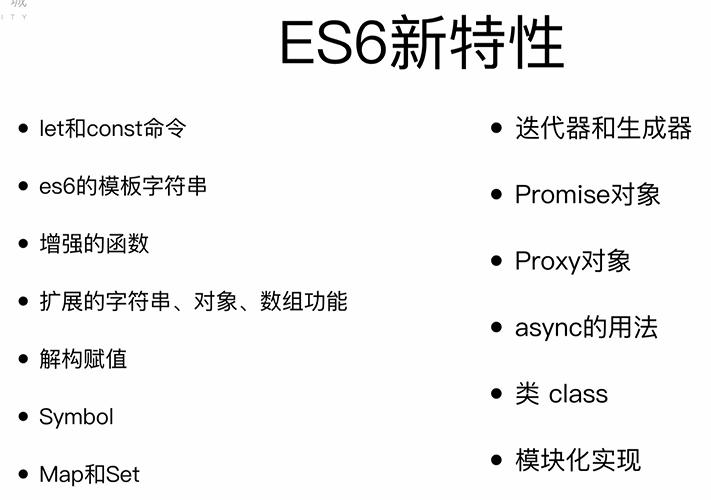


1、let和const
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>let和const</title> </head> <body> <script> // var a; // // var // console.log(a); // a = 2; // 1.let声明变量,没有变量提升(使用var声明一个变量的时候,该变量会被提升到作用域的顶端) // console.log(a); // let a = 10; // console.log(b); // 2.是一个块作用域(超出if作用域就会报错) // if(1===1){ // let b = 10; // } // console.log(b); // var a = 2; // var a = 4; // 3.不能重复声明 // let a = 1; // let a = 3; // console.log(a);
// const 声明常量 一旦被声明 无法修改 // console.log(max); // if(1===1){ // const max = 30; // } // const max = 30; // const max = 40; // max = 40; // console.log(max); /* const person = { name:'小马哥' } // person.name = 'alex'; person = { age:20 } console.log(person); */ //作用1: for循环是个经典例子 /* const arr = []; for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) { arr[i] = function() { return i; } } console.log(arr[5]()); */ // 作用2:不会污染全局变量 let RegExp = 10; console.log(RegExp); console.log(window.RegExp); // 建议:在默认情况下用const,而只有在你知道变量值需要被修改的情况使用let </script> </body> </html>
2、模板字符串
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>模板字符串</title> </head> <body> <div class="box"> </div> <script> // 模板字符串:使用tab键上面的反引号``,插入变量时使用${变量名} const oBox = document.querySelector('.box'); let id = 1, name = '小马哥'; let htmlStr = `<ul> <li> <p id=${id}>${name}</p> </li> </ul>`; // oBox.innerHTML = "<ul><li><p id=" + id + ">" + name + "</p></li></ul>"; oBox.innerHTML = htmlStr; </script> </body> </html>
3、强大的函数
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> // 1.带参数默认值的函数 // es5的写法(不传值) /* function add(a, b) { a = a || 10; // a 传值就用a 不传值就用默认值10 b = b || 20; return a + b; } console.log(add()); */ // function add(a, b = 20) { // return a + b; // } // console.log(add(30)); //这个30是传给a的 ,b用默认值20 // 2.默认的表达式也可以是一个函数 // function add(a, b = getVal(5)) { // return a + b; // } // function getVal(val) { // return val + 5; // } // console.log(add(10)); // 10传给a ,b用默认函数 // 3.剩余参数 // es5写法 // pick函数 /* function pick(obj) { let result = Object.create(null); for(let i = 1;i < arguments.length;i++){ // for循环这块有点麻烦 可以用es6的...keys指定 result[arguments[i]] = obj[arguments[i]] } return result; } let book = { title:'es6的教程', author:'小马哥', year:2019 } let bookData = pick(book,'title','year','author'); //通过pick方法选择书对象 当前标题奶奶分作者是谁 保存到一个对象中 console.log(bookData); */ // 剩余参数:由三个点...和一个紧跟着的具名参数指定 ...keys // function pick(obj, ...keys) { // obj 指的对象 book 剩余参数'year', 'author' 用 ...keys // // ...keys 解决了arguments 的问题 keys = { 'year', 'author'} // let result = Object.create(null); // for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) { // result[keys[i]] = obj[keys[i]]; // } // return result; // } // let book = { // title: 'es6的教程', // author: '小马哥', // year: 2019 // } // let bookData = pick(book, 'year', 'author'); // console.log(bookData); // 剩余参数...args // function checkArgs(...args) { // console.log(args); // console.log(arguments); // } // checkArgs('a', 'b', 'c'); // 4.扩展运算符 三个点 ... // 剩余运算符:把多个独立的合并到一个数组中 (合并) // 扩展运算符:将一个数组分割,并将各个项作为分离的参数传给函数 (分割) // const maxNum = Math.max(20,30); // 处理最大值 // console.log(maxNum); // es5 处理数组中的最大值,使用apply // const arr = [10, 20, 50, 30, 90, 100, 40]; // console.log(Math.max.apply(null,arr)); // es6 扩展运算法更方便(将一个数组分割,并将各个项作为分离的参数传给函数 arr = [10, 20, 50, 30, 90, 100, 40]) // console.log(Math.max(...arr)); //******** es6的箭头函数 ******** // 使用=>来定义 function(){}等于与 ()=>{} /* let add = function (a, b) { return a + b; } */ // 箭头函数来定义 // let add = (a, b) => { // return a + b; // } // 简便写法 两个参数 // let add = (val1, val2) => val1 + val2; // console.log(add(10, 20)); // 一个参数 // let add = val1 => val1 ; // console.log(add(10)); // 没有参数 // let fn = ()=> 'hello world' + 123; // console.log(fn()); /* let getObj = id => { return { id: id, name:'小马哥' } } */ // 上述简便写法 需要小括号返回对象 // let getObj = id => ({id:id,name:"小马哥"}); // let obj = getObj(1); // console.log(obj); // 闭包函数 /* let fn = (function() { return function() { console.log('hello es6'); } })(); */ // 简便写法 /* let fn = (() => { return () => { console.log('hello es6 2'); } })(); fn(); */ // 没有this绑定 // es5中this指向:取决于调用该函数的上下文对象 /* let PageHandle = { id: 123, init: function () { document.addEventListener('click',function(event) { // this.doSomeThings is not a function // console.log(this); // 这个this指向 document this.doSomeThings(event.type); // 报错 this.doSomeThings is not a function }) }, doSomeThings:function(type){ console.log(`事件类型:${type},当前id:${this.id}`); } } PageHandle.init(); */ let PageHandle = { id: 123, init: function () { // 箭头函数没有this指向,箭头函数内部this值只能通过查找作用域链来确定,一旦使用箭头函数,当前就不存在作用域链 查找上一层作用域链init: function () document.addEventListener('click', (event) => { // this.doSomeThings is not a function console.log(this); this.doSomeThings(event.type); }, false) }, doSomeThings: function (type) { console.log(`事件类型:${type},当前id:${this.id}`); } } PageHandle.init(); // 1.使用箭头函数的注意事项1:使用箭头函数 函数内部没有arguments // let getVal = (a, b) => { // console.log(arguments); // return a + b; // } // console.log(getVal(1, 3)); // 2.箭头函数不能使用new关键字来实例化对象 let Person = ()=>{ }; // function函数 也是一个对象,但是箭头函数不是一个对象,它其实就是一个语法糖 // console.log(Person); let p = new Person(); // 报错 </script> </body> </html>
4、解构赋值
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>解构赋值</title> </head> <body> <script> // 解构赋值是对赋值运算符的一种扩展 // 它针对数组和对象来进行操作 // 优点:代码书写上简洁易读 let node = { type:'iden', name:'foo' } // let type = node.type; // let name = node.name; // 完全解构 let {type,name} = node; console.log(type,name); let obj = { a:{ name:"张三" }, b:[], c:'hello,world' } // 不完全解构 可以忽略的一些属性 忽略b和c 取a // let {a} = obj; // console.log(a); // 剩余运算符解构 把b和c解构出来 // let {a,...res} = obj; // console.log(res); // 默认值解构 a的值是20 b取默认值30 // let {a,b = 30} = {a:20}; // 对数组解构 let arr = [1,2,3]; let [a,b] = arr; // 不完全解构 console.log(a,b); // 可嵌套 解构 let [a,[b],c] = [1,[2],3]; </script> </body> </html>
5、扩展的对象功能
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>扩展的对象的功能</title> </head> <body> <script> // 1、es6直接写入变量和函数,作为对象的属性和方法 // const name = '小马哥', // age = 20; // const person = { // name,//等价于name:name(原来的写法) // age, // sayName(){ // console.log(this.name); // } // } // person.sayName(); // 用法 // function fn(x,y) { // return {x,y}; // } // console.log(fn(10,20)); // let cart = { // wheel:4, // set(newVal){ // if(newVal < this.wheel){ // throw new Error('轮子数太少了') // } // this.wheel = newVal; // }, // get(){ // return this.wheel; // } // } // // console.log(cart.get()); // cart.set(6); // console.log(cart.get()) //例1 /* const obj = {}; obj.isShow = true; const name = 'a'; obj[name+'bc'] = 123; // abc :123 // console.log(obj); obj['f'+'bc'] = function () { console.log(this); // this的作用域在function中 箭头函数是没有this指向的 } console.log(obj); */ // fbc : f // 例2 /* const name = 'a'; const obj = { isShow:true, [name+'bc']:123, ['f'+name](){ console.log(this); } } console.log(obj); */ {isShow:true , abc:123 , fa:f} // 对象的方法 is() === assign() // is() === // 比较两个值是否严格相等 // console.log(NaN === NaN); //小缺陷 flase console.log(Object.is(NaN,NaN)); // true // ***** assign() *** // 对象的合并 target 目标对象 // Object.assign(target,obj1,obj2....) // 返回合并之后的新对象 let newObj = Object.assign({},{a:1},{b:2}); console.log(newObj); // {a:1,b:2} </script> </body> </html>
6、Symbol类型
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Symbol</title> </head> <body> <script> // es6提供了原始数据类型Symbol ,它表示是独一无二的值 // 最大的用途:用来定义对象的私有变量 const name = Symbol('name'); const name2 = Symbol('name'); console.log(name === name2);// name和name2是独一无二的 内存地址是不同的 let s1 = Symbol('s1'); console.log(s1); // Symbol('s1') let obj = { [s1]:'小马哥' }; // obj[s1] = '小马哥'; // 如果用Symbol定义的对象中的变量,取值时一定要用中括号 [变量名] console.log(obj[s1]); // Symbol('s1'):'小马哥' // console.log(obj.s1); // 不支持遍历 /* for(let key in obj){ console.log(key); // 没有输出的 } */ // console.log(Object.keys(obj)); // 获取Symbol声明的属性名(作为对象的key) // 1、通过getOwnPropertySymbols方法来返回值 // let s = Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(obj); // console.log(s[0]); // 2、通过反射Reflect来得到对应的值 let m = Reflect.ownKeys(obj); console.log(m); </script> </body> </html>
7、Set集合和Map数据类型
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> // 集合:表示无重复值的有序列表 let set = new Set(); console.log(set); // 添加元素 set.add(2); set.add('4'); set.add('4'); // set.add(['hello','world',3]); // 删除元素 set.delete(2); // 校验某个值是否在set中 console.log(set.has('4')); console.log(set.size); // 无意义 把前的键作为值当前的值作为键 key和val都一样 /* set.forEach((val,key)=>{ console.log(val); console.log(key); }) */ // 将set转换成数组(就可以添加一些重复元素了) let set2 = new Set([1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4]); console.log(set2) // 结果会去重 {1, 2, 3, 4} // 通过扩展运算符转换成数组了 let arr = [...set2] // 转换成数组了 console.log(arr);//[1,2,3,4] // 了解 // 1.set中对象的引用无法被释放 // let set3 = new Set(),obj = {}; //建空集合 空对象 // set3.add(obj); // // 释放当前的资源 不想用了 // obj = null; //释放当前对象 // console.log(set3); // 但是集合中还保留着该对象obj // 解决方法 let set4 = new WeakSet(), obj = {}; set4.add(obj); // 释放当前的资源 obj = null; console.log(set4); // WeakSet // 1.不能传入非对象类型的参数 // 2.不可迭代 // 3.没有forEach() // 4.没有size属性 // Map类型是键值对的有序列表,键和值是任意类型 /* let map = new Map(); map.set('name','张三'); map.set('age',20); console.log(map.get('name')); console.log(map); map.has('name');//true map.delete('name'); map.clear(); console.log(map); map.set(['a',[1,2,3]],'hello'); console.log(map); */ let m = new Map([ ['a', 1], ['c', 2] ]); console.log(m); </script> </body> </html>
8、数组的扩展功能
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <ul> <li>1</li> <li>2</li> <li>3</li> <li>4</li> </ul> <script> // 数组的方法 from() of() // 1.from() 将伪数组转换成真正的数组 function add() { // console.log(arguments); // es5转换 // let arr = [].slice.call(arguments); // console.log(arr); // es6写法 let arr = Array.from(arguments); console.log(arr); } add(1, 2, 3);// [1,2,3] let lis = document.querySelectorAll('li') // console.log(Array.from(lis)); // [li,li,li,li] // 也可以用扩展运算符 将伪数组转换成真正的数组 // console.log([...lis]); // from() 还可以接收第二个参数,第二个参数用来对每个元素进行处理 let liContents = Array.from(lis, ele => ele.textContent); //ele => ele.textContent将每个标签的文本返回 // console.log(liContents);// [1234] // 2.of() 将任意的数据类型,转换成数组 console.log(Array.of(3, 11, 20, [1, 2, 3], { id: 1 }));//[3, 11, 20, [1, 2, 3], {id: 1})] // 3.copywithin() 数组内部将制定位置的元素复制到其它的位置,返回当前数组 // 从3位置往后的所有数值,替换从0位置往后的三个数值 console.log([1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10].copyWithin(0, 3)); //[8,9,10,8,9,10] // 4.find()查元素 findIndex()查索引 // find()找出数组第一个符合条件的数组成员 let num = [1, 2, -10, -20, 9, 2].find(n => n < 0) // console.log(num); // -10 // findIndex()找出第一个符合条件的数组成员的索引 let numIndex = [1, 2, -10, -20, 9, 2].findIndex(n => n < 0) // console.log(numIndex); // 5.entries() keys() values() 返回一个遍历器 可以使用for...of循环进行遍历 // keys() 对键名遍历 // values() 对值遍历 // entries() 对键值对遍历 // console.log(['a','b'].keys()); // 返回一个遍历器['a','b'].keys() for (let index of ['a', 'b'].keys()) { console.log(index); // 0 ,1 } for (let ele of ['a', 'b'].values()) { console.log(ele); // 'a', 'b' } for(let [index,ele] of ['a','b'].entries()){ console.log(index,ele); } let letter = ['a','b','c']; // 数组 let it = letter.entries(); // 返回一个遍历器 // console.log(it.next().value); // 遍历器里有个方法next() [0:a] // console.log(it.next().value);// [1:b] // console.log(it.next().value); // [2:c] // console.log(it.next().value); // undefind // 6.includes() 返回一个布尔值,表示某个数组是否包含给定的值 console.log([1,2,3].includes(2)); console.log([1,2,3].includes('4')); // 之前 indexof() console.log([1,2,3].indexOf('2')); </script> </body> </html>





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)