Dubbo的源码解析
Dubbo源码的关键类:
DubboInvoker
NioEventLoop
NettyClientHandler
IdleStateHandler
HeaderExchangeClient
io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel
一、SPI机制:
1、首先创建ExtensionLoader
2、然会根据ExtensionLoader获取和搜索类的实例
(1)类上有@Adaptive注解的,直接创建该类的实例
(2)方法上有@Adaptive注解的,直接创建该类的代理类,有相应的代理模板
根据代理类的实现获取真正的实现类
ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Container.class)
1、ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ExtensionFactory.class).getAdaptiveExtension()获取适应能强的实力(两种方式)
2、ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getExtension(name)获取指定的实例
3、@SPI获取默认的实例
AdaptiveExtensionFactory【SpiExtensionFactory,SpringExtensionFactory】依据容器进行依赖注入
Wrapper的dubbo的AOP机制
IOC+AOP+DI
单例模式、工程模式、动态代理模式、装饰器模式
dubbo的动态生成代码机制
ServiceBean发布服务接口的类(读取注册中心的信息)
1、暴露本地服务
ProxyFactory getInvoker(把实现类放入对象包装成有个Invoker的对象)
getProxy(针对客户端)
2、暴露远程服务
injvm和registry
InjvmProtocol
RegistryProtocol
DubboProtocol
---------------
①把接口实现类转换成Invoker
②把Invoker转换成exporter(经过protocol)
InjvmProtocol对应的是InjvmExporter
DubboProtocol对应的是dubboExporter
1、暴露本地服务
2、暴露远程服务
3、启动netty
4、连接zookeeper
5、创建节点,注册服务
6、客户端订阅服务
exporterMap
客户端:接口-->Invoker-->客户端动态代理对象
服务端:实现类-->Invoker-->exporter
provider的流程:serviceBean-->实现类-->Invoker-->protocol-->exporter-->netty-->zookeeper
consumer的流程:referenceBean-->zookeeper-->加入集群路由-->返回动态代理对象InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker)
服务端节点:创建:providers,订阅:configurations
客户端节点:创建:consumers,订阅:providers,routers,configurations
javassit动态代理
集群容错:
1、RegistryDirectory(Invoker的map是来源于注册中心,并且实现了listener)(刷新缓冲中的Invoker列表)
2、router规则(从Directory里面帅选Invoker的子集)(应用隔离,读写分离,灰度发布)默认轮询方式toMethodInvokers
加路由规则就刷新Invoker的map列表
ConditionRouter(后台管理系统路由配置)
MockInvokersSelector
3、Cluster将多个Invoker伪装成一个Invoker(FailoverCluster失败转移默认重试3次)【失败以后会充实其他的服务器】
FailFastCluster快速失败
4、LoadBanlance负载均衡(RandomLoadBanlance(默认)权重设置随机概率,RoundRobinLoadbanlance(权重),LeastActiveLoadBanlance最少活跃度,Hash一致性算法)
5、SOA服务降级【服务器压力大时,为了保证核心业务正常使用,从而对辅助业务进行降级】
mock机制:容器、屏蔽MockClusterInvoker
屏蔽压根就不请求
屏蔽和容错
服务器调用超时设置优先级:消费者优先,生产者继后
MockClusterInvoker-->FailOverClusterInvoker-->(loadBalance)-->dubboInvoker
stub本地存根
Mockb本地伪装
两个都配置的话,以Mock为准
dubbo的怎么利用netty接收响应的:
这个原理就是在传输消息的过程中协议里要维护一个id,这样子才能找到发起请求的一方的future
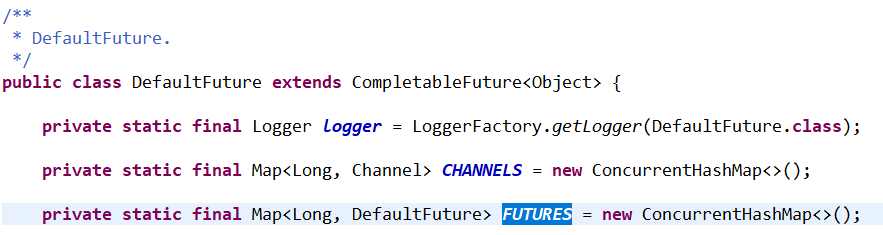
具体的方法:
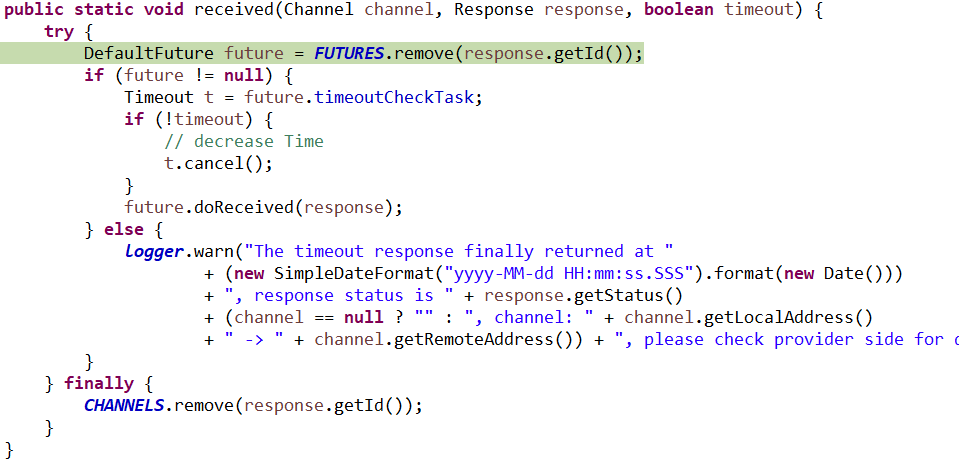
接着就是:
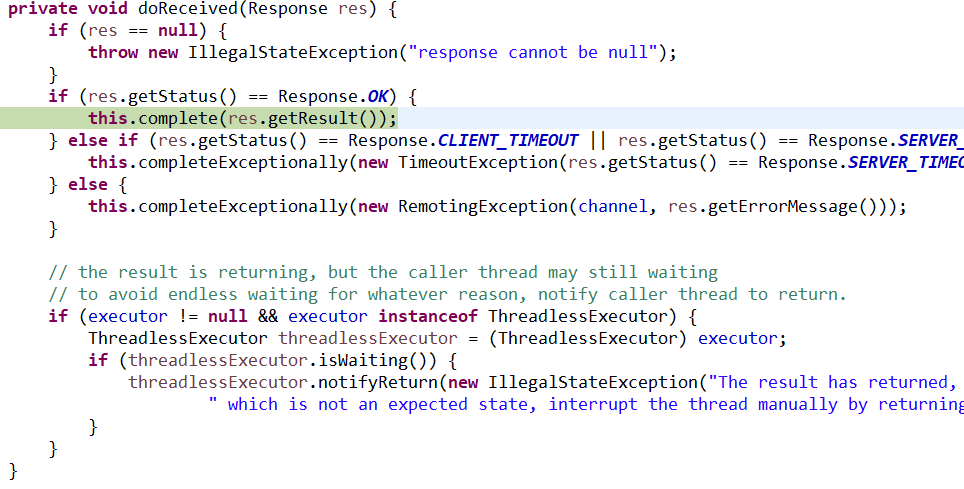
dubbo的router是如何起作用的:

这个类下的这个方法:
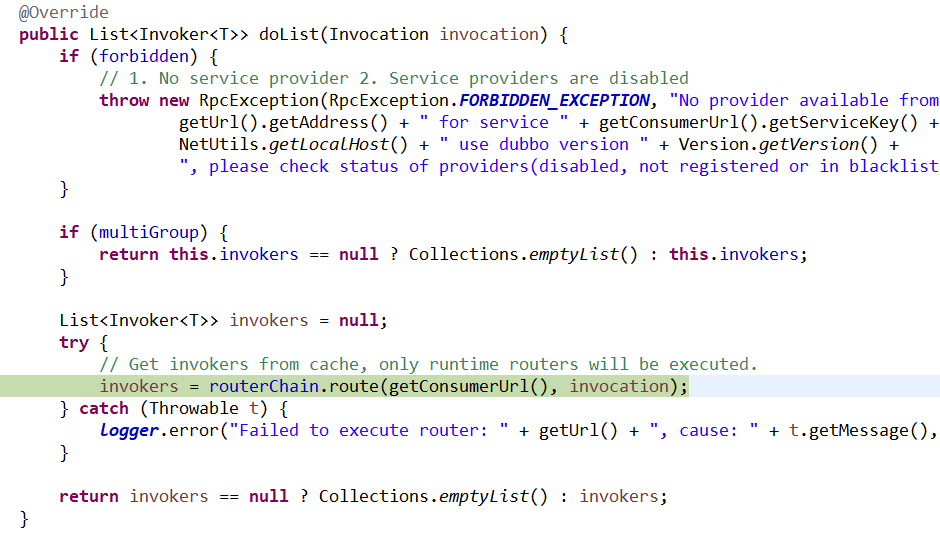
dubbo服务端(provider)是如何接收请求的:
1、这个是个服务端的handler

具体的方法对于熟悉netty的来说就已经很熟悉了:
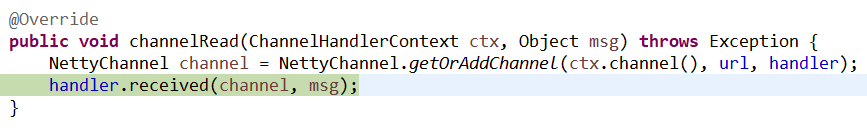
2、NettyServer类
具体的方法如下:

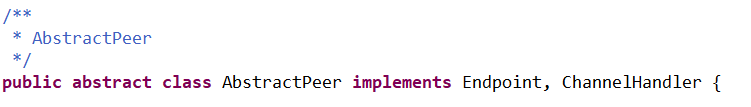
3、批量消息处理器

具体的处理方法:
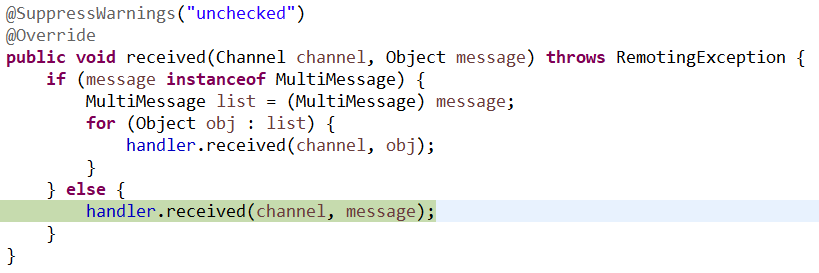
4、心跳处理器:

具体的处理方法:
5、多线程处理器(默认200个线程)

具体表的方法如下:
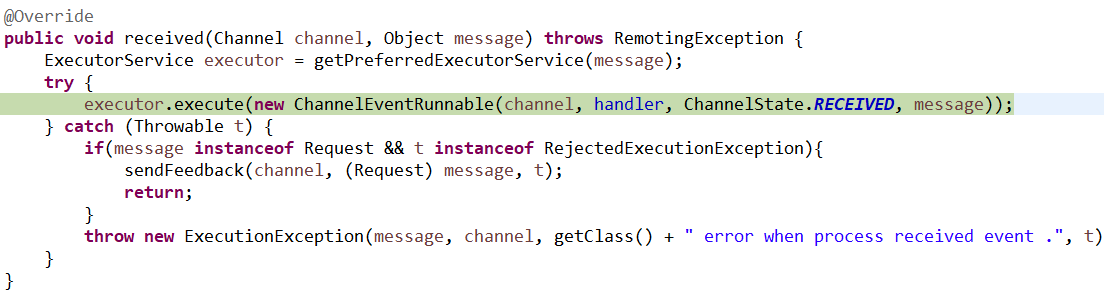
6、执行具体的线程的类:

具体的方法如下:
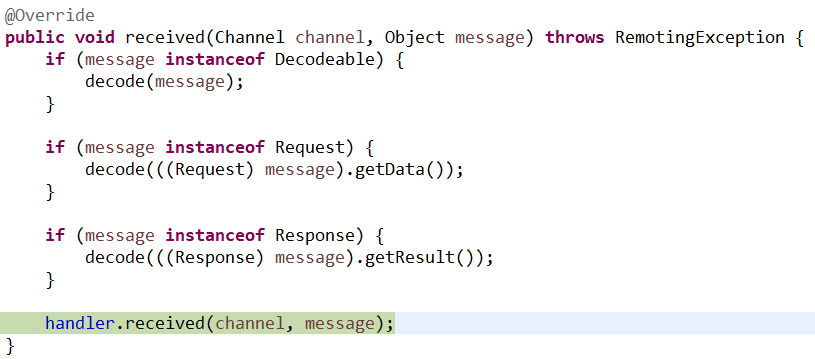
7、解码处理器。反序列化处理器

具体的方法:
8、具体的请求头处理器:

具体的处理方法为:
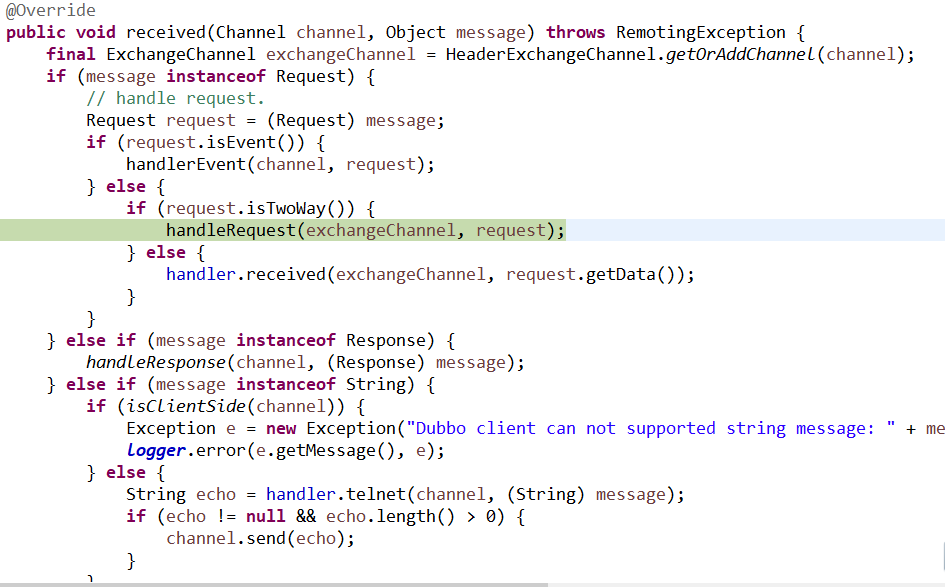
具体的处理流程如下:
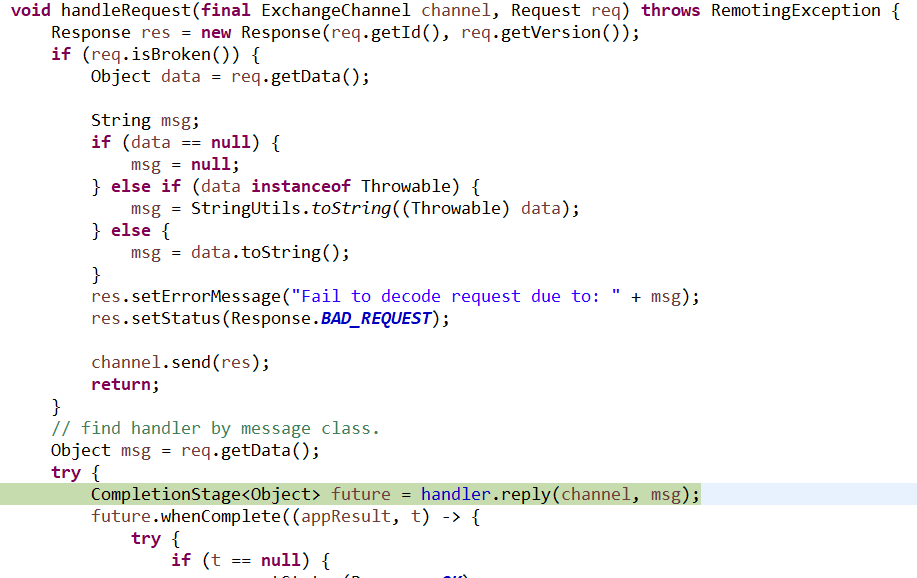
9、dubbo协议类

具体的代码为:
@Override public CompletableFuture<Object> reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { if (!(message instanceof Invocation)) { throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: " + (message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message)) + ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress()); } Invocation inv = (Invocation) message; Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv); // need to consider backward-compatibility if it's a callback if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getObjectAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))) { String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods"); boolean hasMethod = false; if (methodsStr == null || !methodsStr.contains(",")) { hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr); } else { String[] methods = methodsStr.split(","); for (String method : methods) { if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)) { hasMethod = true; break; } } } if (!hasMethod) { logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName " + inv.getMethodName() + " not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored." + " please update the api interface. url is:" + invoker.getUrl()) + " ,invocation is :" + inv); return null; } } RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress()); Result result = invoker.invoke(inv);//具体调用代码的地方 return result.thenApply(Function.identity()); }
10、filter包装类:

具体的方法为:
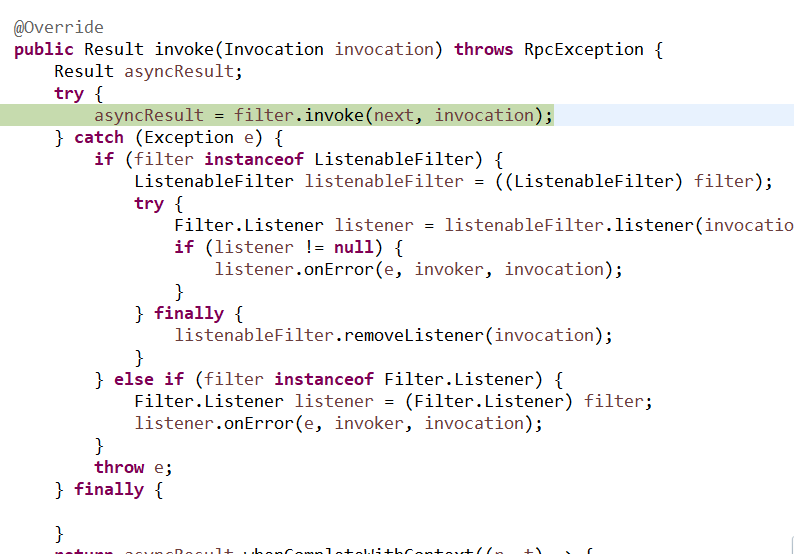
这里会执行一系列的filter方法和invoker方法
11、代理工厂类
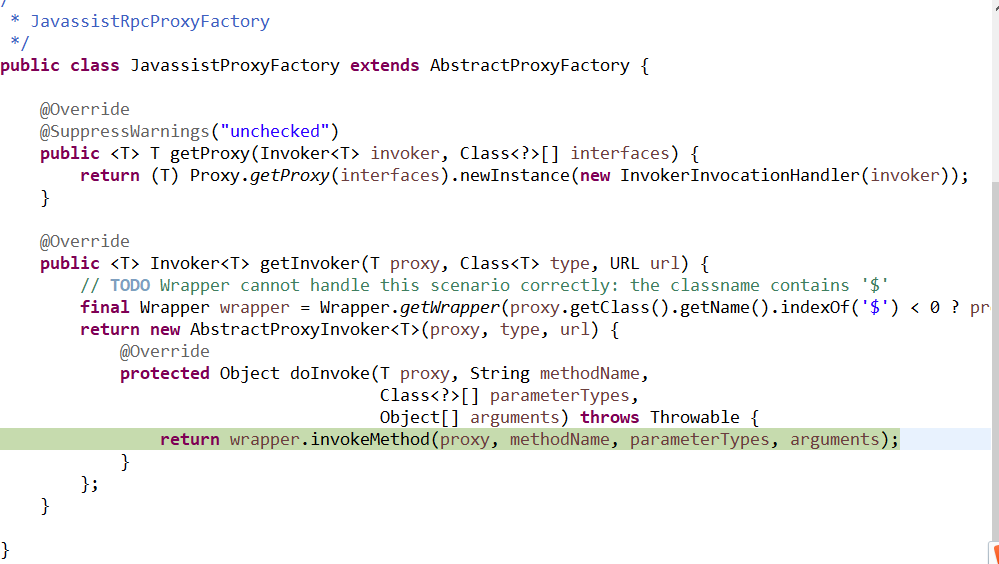
这个类之后就会调用到我们写的具体的实现类了。
netty的时间轮定时器是干什么的?(hashedwheeltimer)
1、redis的分布式锁需要不同的刷新过期时间来延长时间,需要用什么定时器
2、dubbo是怎么使用时间轮定时器的
Dubbo客户端是如何拿到结果的,以及它的线程模型是什么样子的
1、AsyncToSyncInvoker(这里面的第61行就是取结果的)

2、AsyncRpcResult

3、ThreadlessExecutor
public void waitAndDrain() throws InterruptedException { /** * Usually, {@link #waitAndDrain()} will only get called once. It blocks for the response for the first time, * once the response (the task) reached and being executed waitAndDrain will return, the whole request process * then finishes. Subsequent calls on {@link #waitAndDrain()} (if there're any) should return immediately. * * There's no need to worry that {@link #finished} is not thread-safe. Checking and updating of * 'finished' only appear in waitAndDrain, since waitAndDrain is binding to one RPC call (one thread), the call * of it is totally sequential. */ if (finished) { return; } Runnable runnable = queue.take(); synchronized (lock) { waiting = false; runnable.run(); } runnable = queue.poll(); while (runnable != null) { try { runnable.run(); } catch (Throwable t) { logger.info(t); } runnable = queue.poll(); } // mark the status of ThreadlessExecutor as finished. finished = true; }
这里面的queue是阻塞队列,在这里等着结果,这个结果会有两种情况,一个是会由NettyClientWorker线程(ChannelEventRunnable)即响应线程把结果放进去,或者由超时线程HashedWheelTimer(TimeoutCheckTask)把超时结果放进去。下面就详细讲一下这两个线程。
(4~15是接收正常数据的处理流程)
(16~19是超时的数据处理流程)
4、NettyClientHandler

5、AbstractPeer

6、MultiMessageHandler
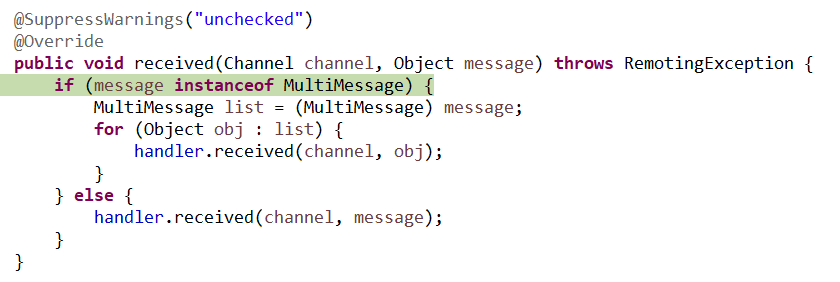
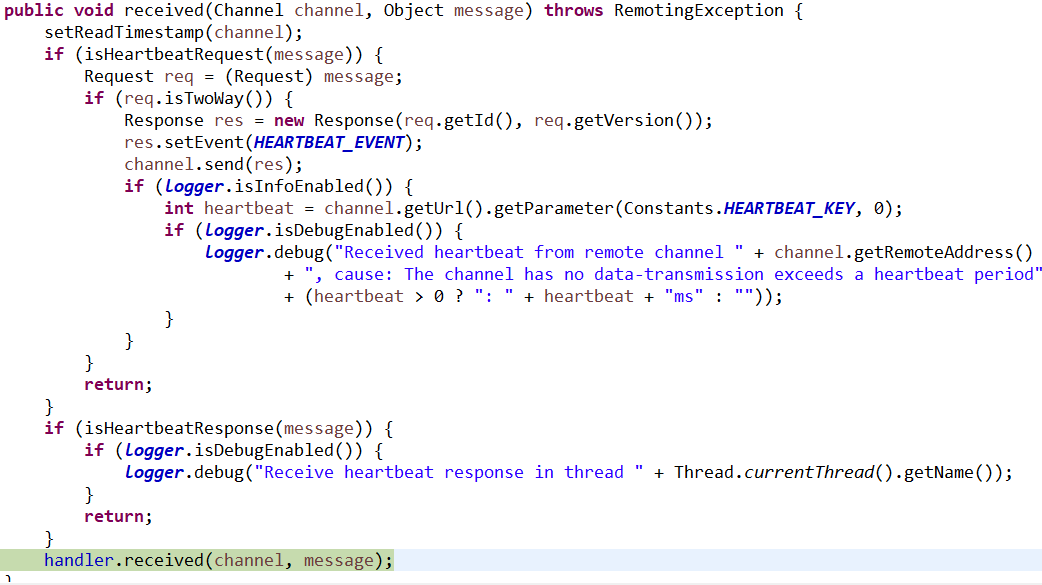
7、HeartbeatHandler
@Override public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { setReadTimestamp(channel); if (isHeartbeatRequest(message)) { Request req = (Request) message; if (req.isTwoWay()) { Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion()); res.setEvent(HEARTBEAT_EVENT); channel.send(res); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { int heartbeat = channel.getUrl().getParameter(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, 0); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Received heartbeat from remote channel " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + ", cause: The channel has no data-transmission exceeds a heartbeat period" + (heartbeat > 0 ? ": " + heartbeat + "ms" : "")); } } } return; } if (isHeartbeatResponse(message)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Receive heartbeat response in thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } return; } handler.received(channel, message); }
8、AllChannelHandler
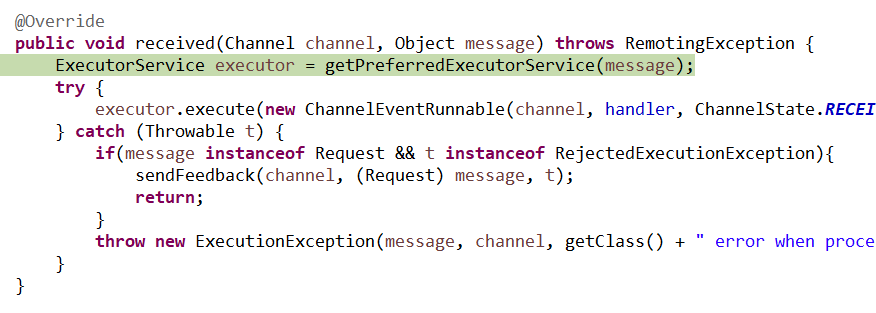
9、ThreadlessExecutor
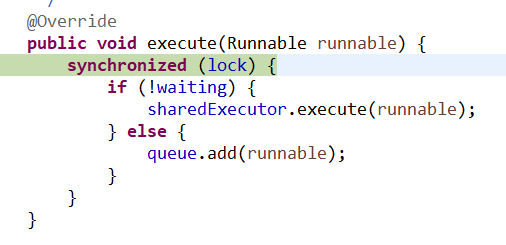
这里的lock和waiting都要注意,这里的lock是防止对结果进行重复处理也就是说结果只能处理一次。这里的waiting的意思是是指结果已经被处理过不需要再次加入队列当中所以直接执行就可以了,但是这里的直接执行也没有多大意义了,因为最终在FUTURES容器里得到的futrue=null。
sharedExecutor的线程指的是DubboClientHandler相关的线程。
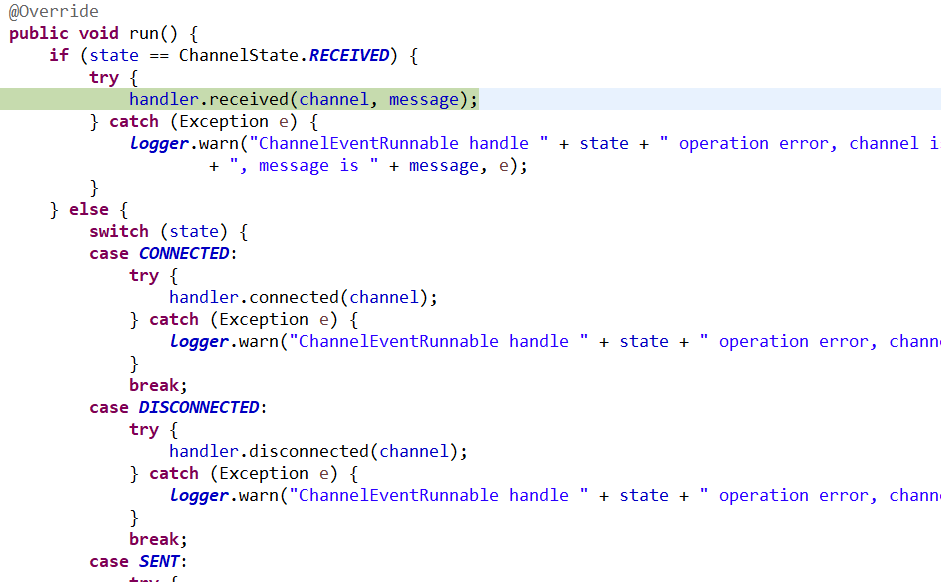
10、ChannelEventRunnable
@Override public void run() { if (state == ChannelState.RECEIVED) { try { handler.received(channel, message); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel + ", message is " + message, e); } } else { switch (state) { case CONNECTED: try { handler.connected(channel); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel, e); } break; case DISCONNECTED: try { handler.disconnected(channel); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel, e); } break; case SENT: try { handler.sent(channel, message); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel + ", message is " + message, e); } break; case CAUGHT: try { handler.caught(channel, exception); } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("ChannelEventRunnable handle " + state + " operation error, channel is " + channel + ", message is: " + message + ", exception is " + exception, e); } break; default: logger.warn("unknown state: " + state + ", message is " + message); } } }
11、DecodeHandler
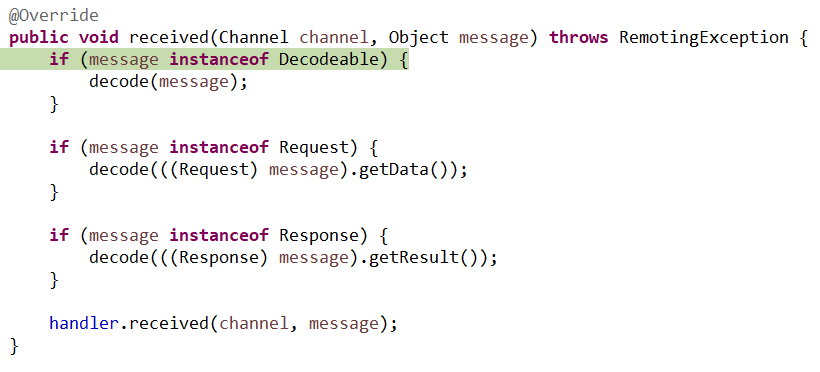
12、HeaderExchangeHandler(handleResponse(channel, (Response) message);)
@Override public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { final ExchangeChannel exchangeChannel = HeaderExchangeChannel.getOrAddChannel(channel); if (message instanceof Request) { // handle request. Request request = (Request) message; if (request.isEvent()) { handlerEvent(channel, request); } else { if (request.isTwoWay()) { handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request); } else { handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData()); } } } else if (message instanceof Response) { handleResponse(channel, (Response) message); } else if (message instanceof String) { if (isClientSide(channel)) { Exception e = new Exception("Dubbo client can not supported string message: " + message + " in channel: " + channel + ", url: " + channel.getUrl()); logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } else { String echo = handler.telnet(channel, (String) message); if (echo != null && echo.length() > 0) { channel.send(echo); } } } else { handler.received(exchangeChannel, message); } }
13、HeaderExchangeHandler

14、DefaultFuture
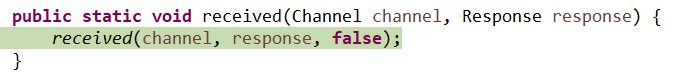
15、DefaultFuture
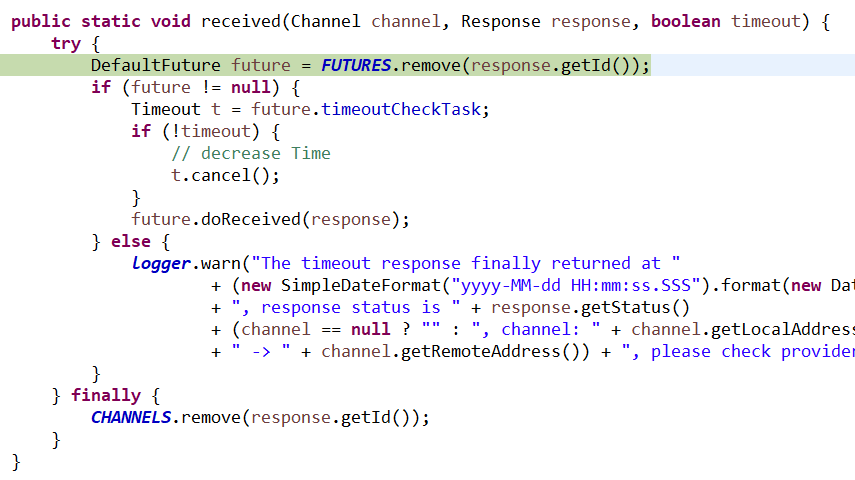
16、DefaultFuture.TimeoutCheckTask

17、ThreadlessExecutor

18、ThreadlessExecutor

19、DefaultFuture
参考文献:
Dubbo协议:http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/blog/dubbo-protocol.html




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 解答了困扰我五年的技术问题
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf
· Java 中堆内存和栈内存上的数据分布和特点
· 开发中对象命名的一点思考
· DeepSeek 解答了困扰我五年的技术问题。时代确实变了!
· PPT革命!DeepSeek+Kimi=N小时工作5分钟完成?
· What?废柴, 还在本地部署DeepSeek吗?Are you kidding?
· DeepSeek企业级部署实战指南:从服务器选型到Dify私有化落地
· 程序员转型AI:行业分析