java—TestNG单元测试框架
//依赖坐标 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.testng/testng --> <dependency> <groupId>org.testng</groupId> <artifactId>testng</artifactId> <version>6.14.3</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency>
TestNG的常用注解
1、@Test
标记为测试方法

2、 @BeforeMethod/@AfterMethod
在某个测试方法(method)执行之前/结束之后
3、@BeforeClass/@AfterClass
在某个测试类(class)所有开始之前/结束之后
4、@BeforeTest/@AfterTest
在某个测试(test)所有测试方法执行开始之前/结束之后
5、@BeforeSuite/@AfterSuite
在某个测试套件(suite)所有测试方法执行开始之前/结束之后
package com.learn.testing; import org.testng.annotations.*; public class TestingTest { @BeforeMethod public void setUpMethod(){ System.out.println("测试方法之前"); } @AfterMethod public void tearDownMethod(){ System.out.println("测试方法之后"); } @BeforeClass public void setUpClass(){ System.out.println("测试类之前"); } @AfterClass public void tearDownClass(){ System.out.println("测试类之后"); } @Test public void printA(){ System.out.println("A"); } @Test public void printB(){ System.out.println("B"); } } 结果: 测试类之前 测试方法之前 A 测试方法之后 测试方法之前 B 测试方法之后 测试类之后
Test注解常用属性
1、忽略测试:
当我们在测试的过程中,因为某些方面的原因,比如测试方法没有写完,或者有问题,我们暂时希望它不得到执行,我们就可以添加忽略标签来跳过此方法的运行。
@Test(enabled = false)
2、超时测试:
“超时”表示如果自动化测试花费的时间超过指定的毫秒数,那么TestNG将会中止它并将其标记为失败。这样在某些业务场景下,我们认为一个请求时间过长我们就可以直接宣判他因为超时而失败。
@Test(timeout=1000)
timeout属性的单位为毫秒。
@Test(timeOut=1000) public void printA() throws InterruptedException { Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("A"); }
3、依赖测试:
测试方法依赖于某些方法
示例:
@Test(dependsOnMethods={"test2"})
方法执行顺序
step1:先执行被依赖的方法
step2:再依次执行没配置依赖的方法
step3:最后执行需要依赖的测试方法
(本来的执行顺序是按照字母先后执行的)
public class TestingTest02 { @Test(dependsOnMethods = {"printC", "printB"}) public void printA() { System.out.println("A"); } @Test public void printB() { System.out.println("B"); } @Test public void printC() { System.out.println("C"); } } 结果: B C A //A依赖于BC,所以先执行BC
4、测试方法优先级:
@Test(priority = 1)
数字越小,优先级越高
注:如果在一个测试类里面设置了优先级,那么其他的测试类都要设置优先级,不然执行TestNG.xml文件的时候可能会有问题
TestNG常用断言
1、Assert.assertTrue();
判断是否为True
2、Assert.assertFalse();
判断是否为false
3、Assert.assertEquals()
判断是否相等
String expectedValue ="lemon";
int statusCode=200;
Assert.assertEquals("lemo",expectedValue);
Assert.assertEquals(404,statusCode);
Assert.assertTrue(statusCode==404);
Assert.assertTrue(statusCode==200);
//web自动化一般根据什么来去做断言:
//1、URL地址 2、title 3、页面提示信息 4、元素属性
TestNG.xml配置文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="TestSuite">
<test name="testngLearn">
<classes>
<class name="com.learn.testing.TestingTest"></class>
<class name="com.learn.testing.TestingTest02"></class>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>



调用Maven命令执行测试用例
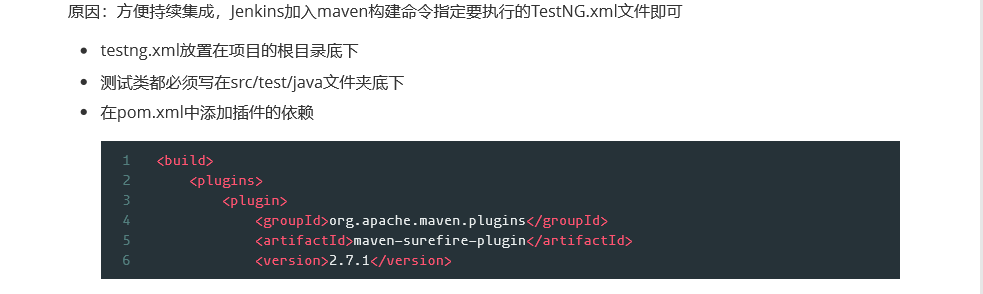
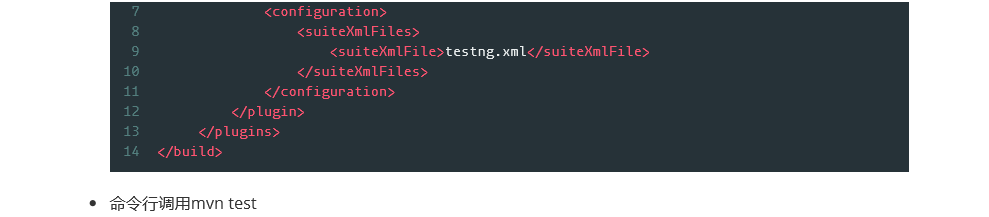
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.7.1</version>
<configuration>
<suiteXmlFiles>
<suiteXmlFile>TestNG.xml</suiteXmlFile> ----注意这里的TestNG.xml与项目根目录下的TestNG.xml同名
</suiteXmlFiles>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
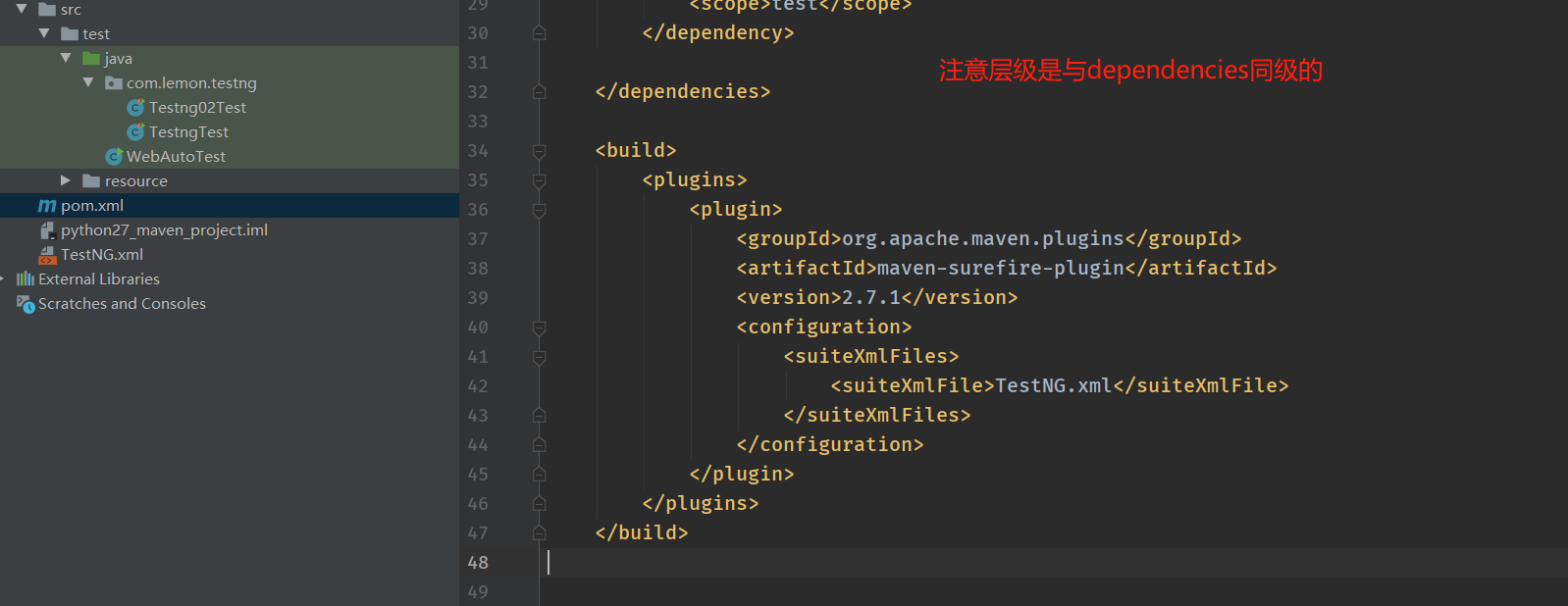
删除通过构建产生的target文件夹方法:
1、手动删除
2、在命令行通过mvn clean删除

maven构建后结果乱码问题解决:
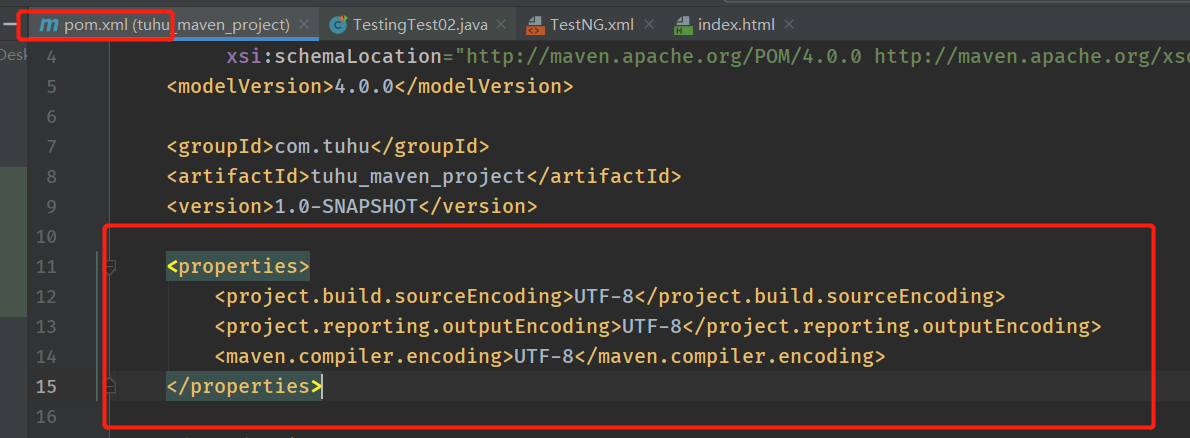
在pom.xml中加入如下配置指定编码UTF-8
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<maven.compiler.encoding>UTF-8</maven.compiler.encoding>
</properties>
TestNG参数化
(参数化后不能直接运行测试方法,不然读不到testng.xml里面的参数,要去运行testng.xml文件)






