Vue3.0 全面探索 - 基于 Composition Api 快速构建实战项目
Quick Start
本项目综合运用了 Vue3.0 的新特性,适合新手学习😁
- 基于
Composition API即Function-based API进行改造,配合Vue Cli,优先体验Vue3特性 - 使用单例对象模式进行组件通信
- 使用
axios库进行网络请求,weui库实现 UI 界面
# 安装依赖
npm install
# 在浏览器打开localhost:8080查看页面,并实时热更新
npm run serve
# 发布项目
npm run build
建议配合 Visual Studio Code 和 Vue 3 Snippets 代码插件食用Ψ( ̄∀ ̄)Ψ。
Dependencies
以下是项目运用到的依赖,@vue/composition-api 配合 vue 模块让我们 Vue2.0 版本可以抢先体验 Vue3.0 的新特性,axios 是辅助我们发送网络请求得到数据的工具库,weui是一套与微信原生视觉一致的基础样式库,方便我们快速搭建项目页面。
"@vue/composition-api": "^0.3.4",
"axios": "^0.19.0",
"core-js": "^3.4.3",
"vue": "^2.6.10",
"weui": "^2.1.3"
Directory Structure
├── src
│ ├── App.vue # 组件入口
│ ├── assets # 资源目录
│ ├── stores/index.js # 状态管理
│ ├── components # 组件目录
│ │ ├── Header.vue # 头部组件
│ │ ├── Search.vue # 搜索框组件
│ │ ├── Panel.vue # 列表组件
│ ├── main.js # 项目入口
├── public # 模板文件
├── vue.config.js # 脚手架配置文件
├── screenshot # 程序截图
Composition API
npm install @vue/composition-api --save
使用 npm 命令下载了 @vue/composition-api 插件以后,引入该模块后,需要显式调用 Vue.use(VueCompositionApi) ,按照文档在 main.js 引用便开启了 Composition API 的能力。
// main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1.引入Composition API模块
import VueCompositionApi from '@vue/composition-api'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 2.不要漏了显式调用 VueCompositionApi
Vue.use(VueCompositionApi)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
npm install weui --save
我们同样使用 npm 安装 weui 模块,然后在 main.js 中引入 weui的基础样式库,方便我们可以在全局使用微信基础样式构建项目页面。
// main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 全局引入 `weui` 的基础样式库
import 'weui'
import VueCompositionApi from '@vue/composition-api'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(VueCompositionApi)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
回到 App.vue,保留 components 属性值清空 <template> 模板的内容,删除 <style> 模板,等待重新引入新的组件。
<template>
<div id="app">
Hello World
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "app",
components: {}
};
</script>
在 src/components 目录下新建第一个组件,取名为 Header.vue 写入以下代码,点击查看源代码:
<template>
<header :style="{
backgroundColor: color?color:defaultColor
}">{{title}}</header>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive } from "@vue/composition-api";
export default {
// 父组件传递进来更改该头部组件的属性值
props: {
// 标题
title: String,
// 颜色
color: String
},
setup() {
const state = reactive({
defaultColor: "red"
});
return {
...state
};
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
header {
height: 50px;
width: 100%;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
}
</style>
setup
这里运用了一个全新的属性 setup ,这是一个组件的入口,让我们可以运用 Vue3.0 暴露的新接口,它运行在组件被实例化时候,props 属性被定义之后,实际上等价于 Vue2.0 版本的 beforeCreate 和 Created 这两个生命周期,setup 返回的是一个对象,里面的所有被返回的属性值,都会被合并到 Vue2.0 的 render 渲染函数里面,在单文件组件中,它将配合 <template> 模板的内容,完成 Model 到 View 之间的绑定,在未来版本中应该还会支持返回 JSX 代码片段。
<template>
<!-- View -->
<div>{{name}}</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive } from '@vue/composition-api'
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({ name: 'Eno Yao' });
// return 暴露到 template 中
return {
// Model
...state
}
}
}
</script>
reactive
在 setup 函数里面, 我们适应了 Vue3.0 的第一个新接口 reactive 它主要是处理你的对象让它经过 Proxy 的加工变为一个响应式的对象,类似于 Vue2.0 版本的 data 属性,需要注意的是加工后的对象跟原对象是不相等的,并且加工后的对象属于深度克隆的对象。
const state = reactive({ name: 'Eno Yao' })
props
在 Vue2.0 中我们可以使用 props 属性值完成父子通信,在这里我们需要定义 props 属性去定义接受值的类型,然后我们可以利用 setup 的第一个参数获取 props 使用。
export default {
props: {
// 标题
title: String,
// 颜色
color: String
},
setup(props) {
// 这里可以使用父组件传过来的 props 属性值
}
};
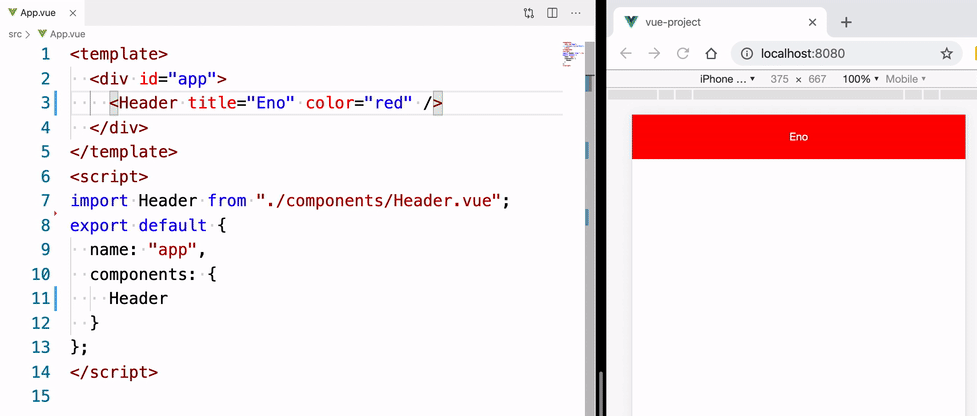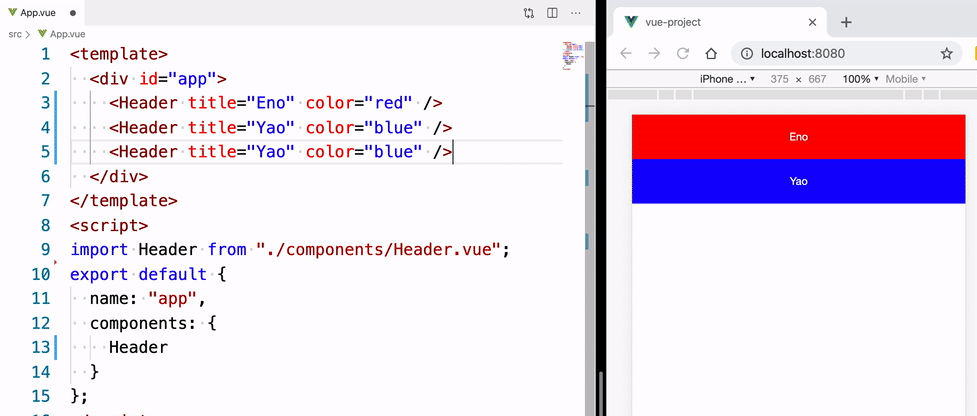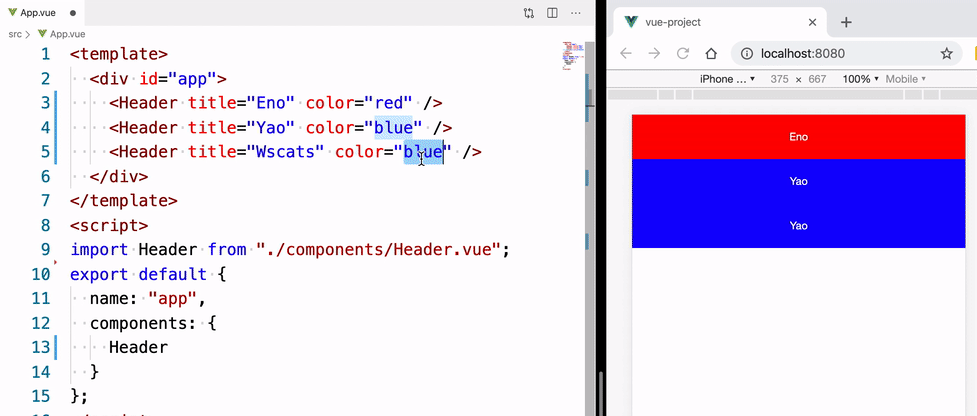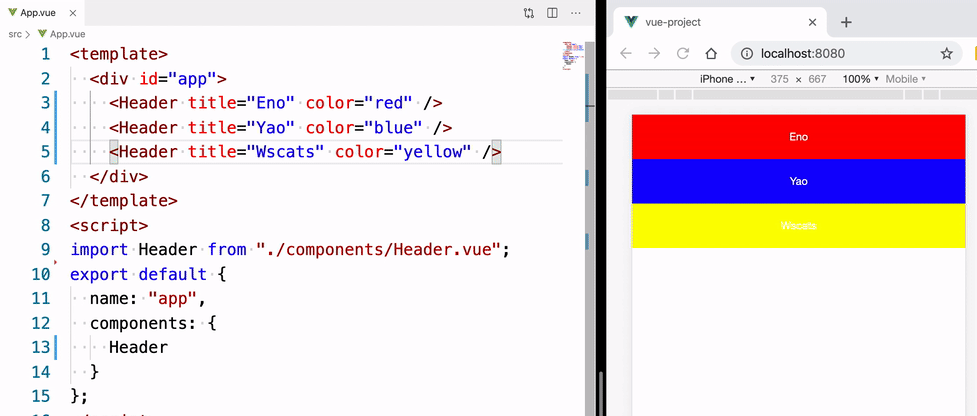
我们在 App.vue 里面就可以使用该头部组件,有了上面的 props 我们可以根据传进来的值,让这个头部组件呈现不同的状态。
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 复用组件,并传入 props 值,让组件呈现对应的状态 -->
<Header title="Eno" color="red" />
<Header title="Yao" color="blue" />
<Header title="Wscats" color="yellow" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Header from "./components/Header.vue";
export default {
name: "app",
components: {
Header,
}
};
</script>
context
setup 函数的第二个参数是一个上下文对象,这个上下文对象中包含了一些有用的属性,这些属性在 Vue2.0 中需要通过 this 才能访问到,在 vue3.0 中,访问他们变成以下形式:
setup(props, ctx) {
console.log(ctx) // 在 setup() 函数中无法访问到 this
console.log(this) // undefined
}
具体能访问到以下有用的属性:
- root
- parent
- refs
- attrs
- listeners
- isServer
- ssrContext
- emit
完成上面的 Header.vue 我们就编写 Search.vue 搜索框组件,继续再 src/components 文件夹下面新建 Search.vue 文件,点击查看源代码。
<template>
<div :class="['weui-search-bar', {'weui-search-bar_focusing' : isFocus}]" id="searchBar">
<form class="weui-search-bar__form">
<div class="weui-search-bar__box">
<i class="weui-icon-search"></i>
<input
v-model="searchValue"
ref="inputElement"
type="search"
class="weui-search-bar__input"
id="searchInput"
placeholder="搜索"
required
/>
<a href="javascript:" class="weui-icon-clear" id="searchClear"></a>
</div>
<label @click="toggle" class="weui-search-bar__label" id="searchText">
<i class="weui-icon-search"></i>
<span>搜索</span>
</label>
</form>
<a @click="toggle" href="javascript:" class="weui-search-bar__cancel-btn" id="searchCancel">取消</a>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRefs, watch } from "@vue/composition-api";
import store from "../stores";
export default {
// setup相当于2.x版本的beforeCreate生命周期
setup() {
// reactive() 函数接收一个普通对象,返回一个响应式的数据对象
const state = reactive({
searchValue: "",
// 搜索框两个状态,聚焦和非聚焦
isFocus: false,
inputElement: null
});
// 切换搜索框状态的方法
const toggle = () => {
// 让点击搜索后出现的输入框自动聚焦
state.inputElement.focus();
state.isFocus = !state.isFocus;
};
// 监听搜索框的值
watch(
() => {
return state.searchValue;
},
() => {
// 存储输入框到状态 store 中心,用于组件通信
store.setSearchValue(state.searchValue);
// window.console.log(state.searchValue);
}
);
return {
// 将 state 上的每个属性,都转化为 ref 形式的响应式数据
...toRefs(state),
toggle
};
}
};
</script>
toRefs
可以看到我们上面用了很多的新属性,我们先介绍 toRefs ,函数可以将 reactive() 创建出来的响应式对象,转换为普通的对象,只不过,这个对象上的每个属性节点,都是 ref() 类型的响应式数据,配合 v-model 指令能完成数据的双向绑定,在开发中非常高效。
import { reactive, toRefs } from "@vue/composition-api";
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({ name: 'Eno Yao' })
}
return {
// 直接返回 state 那么数据会是非响应式的, MV 单向绑定
// ...state,
// toRefs 包装后返回 state 那么数据会是响应式的, MVVM 双向绑定
...toRefs(state),
};
}
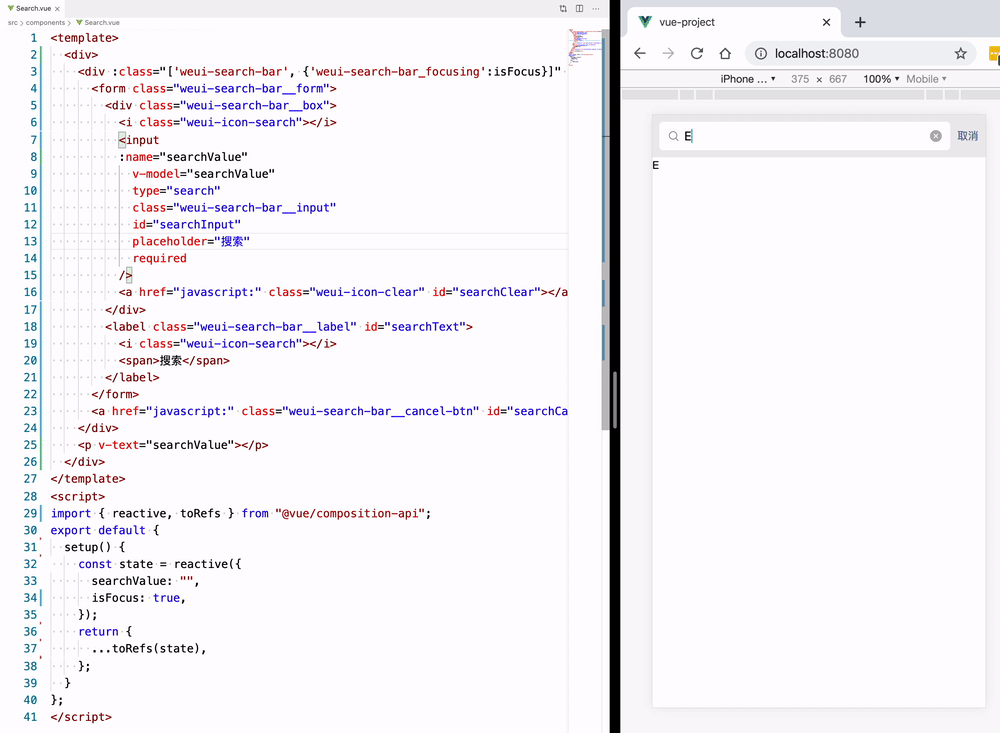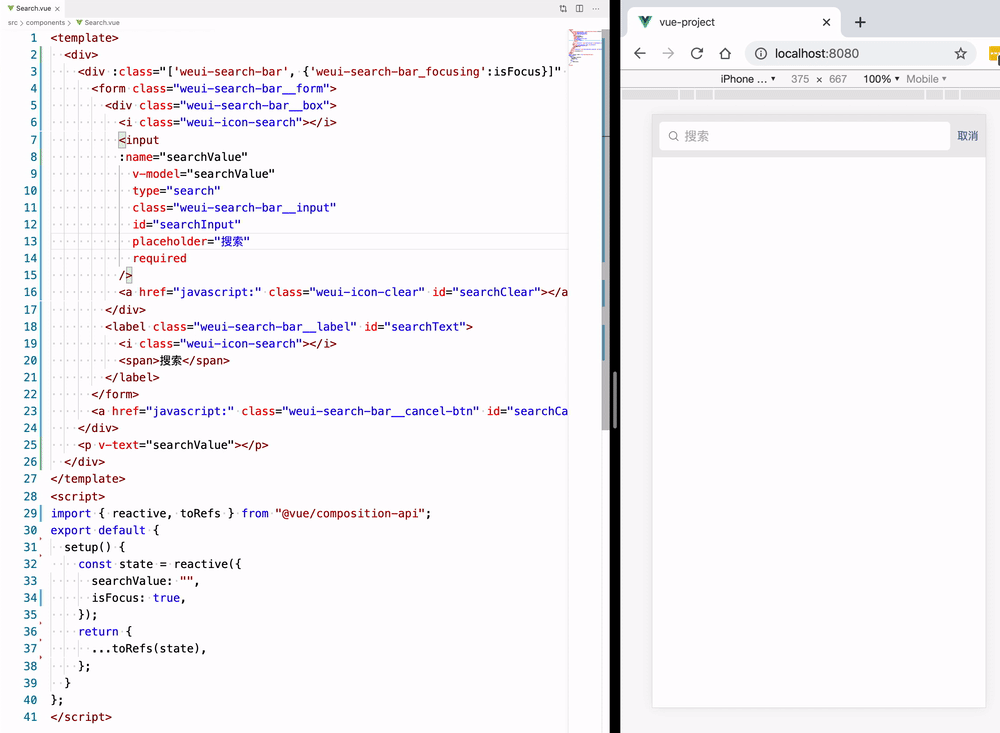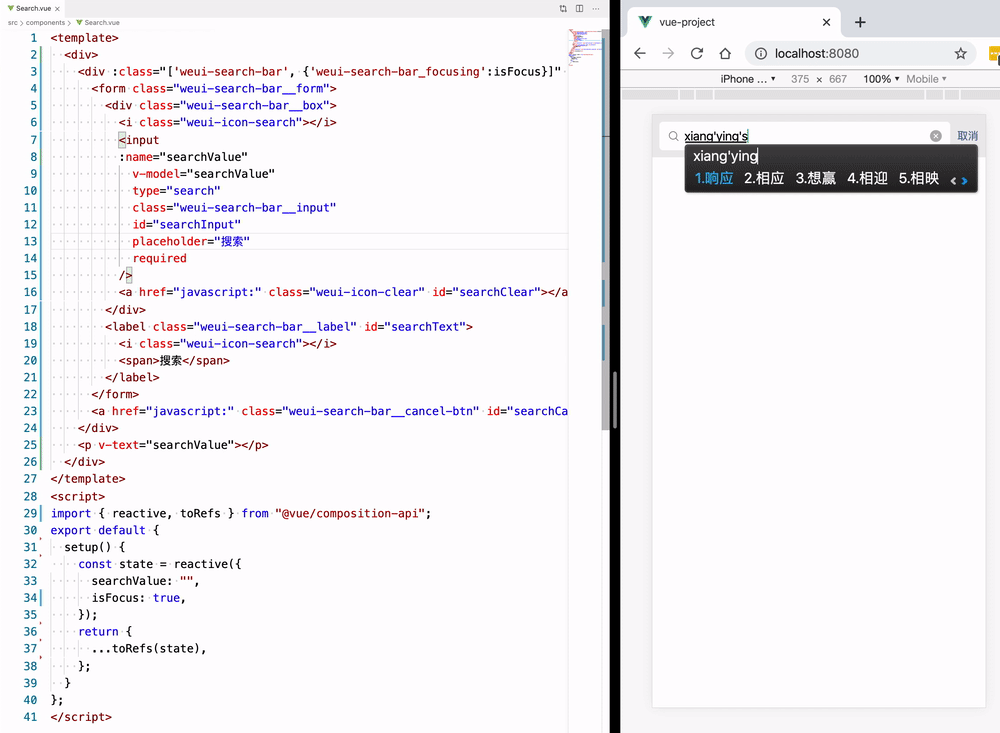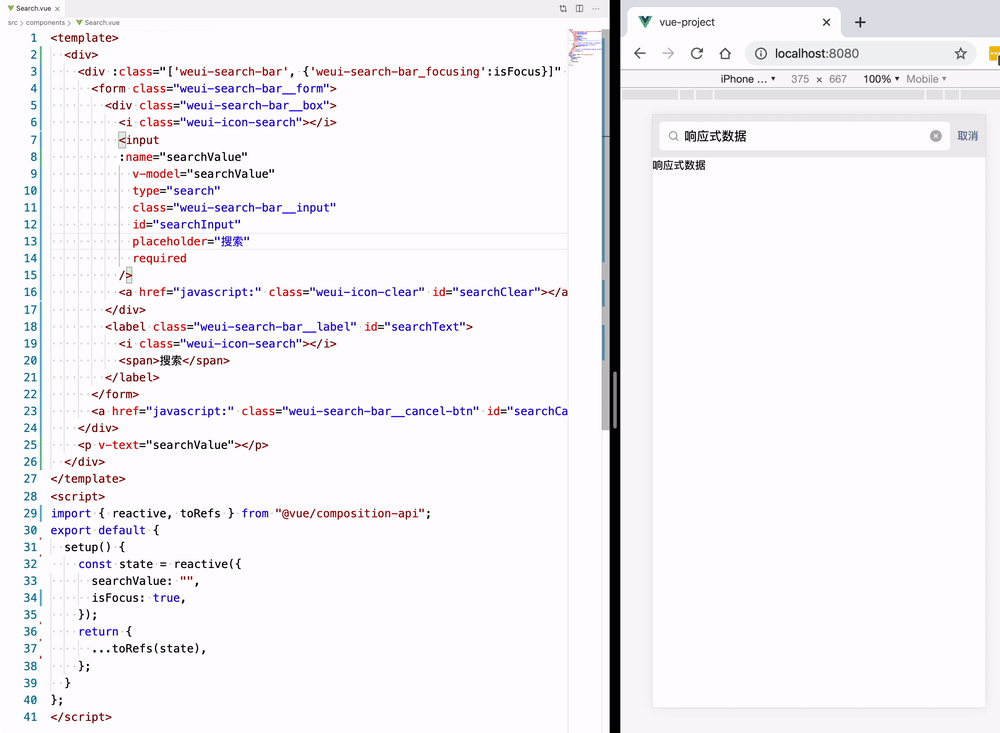
template refs
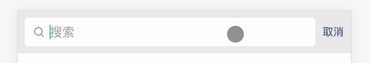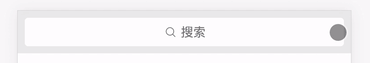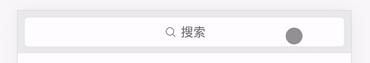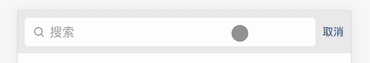
这里的输入框拥有两个状态,一个是有输入框的状态和无输入框的状态,所以我们需要一个布尔值 isFocus 来控制状态,封装了一个 toggle 方法,让 isFocus 值切换真和假两个状态。
const toggle = () => {
// isFocus 值取反
state.isFocus = !state.isFocus;
};
然后配合 v-bind:class 指令,让 weui-search-bar_focusing 类名根据 isFocus 值决定是否出现,从而更改搜索框的状态。
<div :class="['weui-search-bar', {'weui-search-bar_focusing' : isFocus}]" id="searchBar">
这里的搜索输入框放入了 v-model 指令,用于接收用户的输入信息,方便后面配合列表组件执行检索逻辑,还放入了 ref 属性,用于获取该 <input/> 标签的元素节点,配合state.inputElement.focus() 原生方法,在切换搜索框状态的时候光标自动聚焦到输入框,增强用户体验。
<input
v-model="searchValue"
ref="inputElement"
/>
watch
watch() 函数用来监视某些数据项的变化,从而触发某些特定的操作,使用之前还是需要按需导入,监听 searchValue 的变化,然后触发回调函数里面的逻辑,也就是监听用户输入的检索值,然后触发回调函数的逻辑把 searchValue 值存进我们创建 store 对象里面,方面后面和 Panel.vue 列表组件进行数据通信:
import { reactive, watch } from "@vue/composition-api";
import store from "../stores";
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
searchValue: "",
});
// 监听搜索框的值
watch(
() => {
return state.searchValue;
},
() => {
// 存储输入框到状态 store 中心,用于组件通信
store.setSearchValue(state.searchValue);
}
);
return {
...toRefs(state)
};
}
};
state management
在这里我们维护一份数据来实现共享状态管理,也就是说我们新建一个 store.js 暴露出一个 store 对象共享 Panel 和 Search 组件的 searchValue 值,当 Search.vue 组件从输入框接受到 searchValue 检索值,就放到 store.js 的 store 对象中,然后把该对象注入到 Search 组件中,那么两个组件都可以共享 store 对象中的值,为了方便调试我们还分别封装了 setSearchValue 和 getSearchValue 来去操作该 store 对象,这样我们就可以跟踪状态的改变。
// store.js
export default {
state: {
searchValue: ""
},
// 设置搜索框的值
setSearchValue(value) {
this.state.searchValue = value
},
// 获取搜索框的值
getSearchValue() {
return this.state.searchValue
}
}
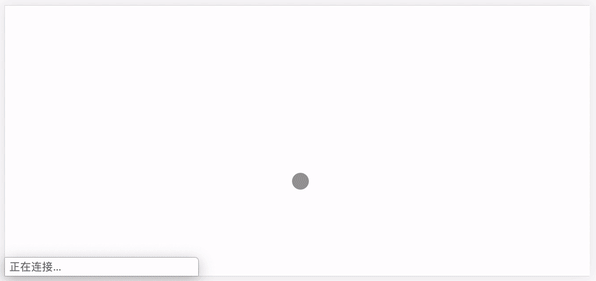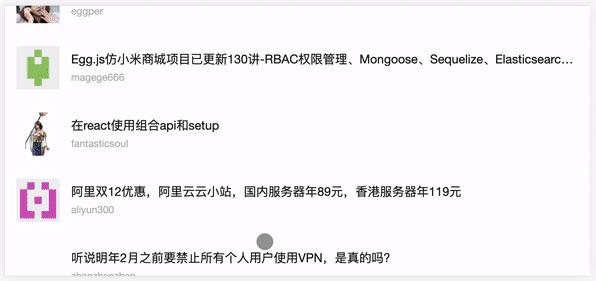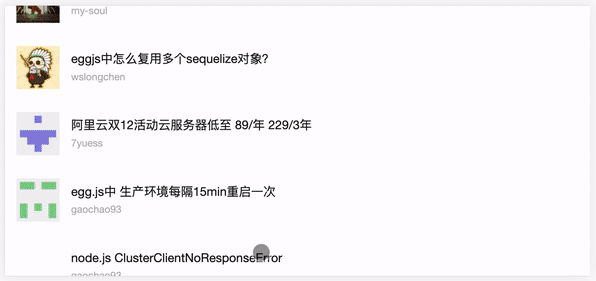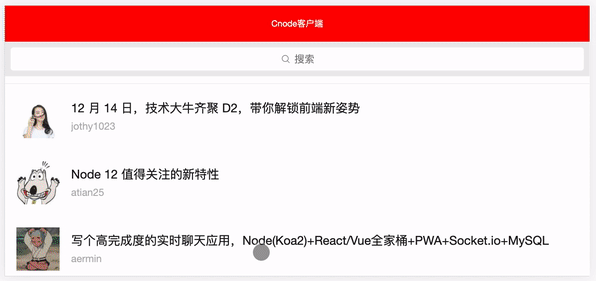
完成上面的 Search.vue 我们紧接着编写 Panel.vue 搜索框组件,继续再 src/components 文件夹下面新建 Panel.vue 文件,点击查看源代码。
<template>
<div class="weui-panel weui-panel_access">
<div v-for="(n,index) in newComputed" :key="index" class="weui-panel__bd">
<a href="javascript:void(0);" class="weui-media-box weui-media-box_appmsg">
<div class="weui-media-box__hd">
<img class="weui-media-box__thumb" :src="n.author.avatar_url" alt />
</div>
<div class="weui-media-box__bd">
<h4 class="weui-media-box__title" v-text="n.title"></h4>
<p class="weui-media-box__desc" v-text="n.author.loginname"></p>
</div>
</a>
</div>
<div @click="loadMore" class="weui-panel__ft">
<a href="javascript:void(0);" class="weui-cell weui-cell_access weui-cell_link">
<div class="weui-cell__bd">查看更多</div>
<span class="weui-cell__ft"></span>
</a>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { reactive, toRefs, onMounted, computed } from "@vue/composition-api";
import axios from "axios";
import store from "../stores";
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
// 页数
page: 1,
// 列表数据
news: [],
// 通过搜索框的值去筛选劣列表数据
newComputed: computed(() => {
// 判断是否输入框是否输入了筛选条件,如果没有返回原始的 news 数组
if (store.state.searchValue) {
return state.news.filter(item => {
if (item.title.indexOf(store.state.searchValue) >= 0) {
return item;
}
});
} else {
return state.news;
}
}),
searchValue: store.state
});
// 发送 ajax 请求获取列表数据
const loadMore = async () => {
// 获取列表数据
let data = await axios.get("https://cnodejs.org/api/v1/topics", {
params: {
// 每一页的主题数量
limit: 10,
// 页数
page: state.page
}
});
// 叠加页数
state.page += 1;
state.news = [...state.news, ...data.data.data];
};
onMounted(() => {
// 首屏加载的时候触发请求
loadMore();
});
return {
// 让数据保持响应式
...toRefs(state),
// 查看更多事件
loadMore
};
}
};
</script>
lifecycle hooks
Vue3.0 的生命周期钩子和之前不一样,新版本都是以 onXxx() 函数注册使用,同样需要局部引入生命周期的对应模块:
import { onMounted, onUpdated, onUnmounted } from "@vue/composition-api";
export default {
setup() {
const loadMore = () => {};
onMounted(() => {
loadMore();
});
onUpdated(() => {
console.log('updated!')
})
onUnmounted(() => {
console.log('unmounted!')
})
return {
loadMore
};
}
};
以下是新旧版本生命周期的对比:
beforeCreatesetup()createdsetup()beforeMount->onBeforeMountmounted->onMountedbeforeUpdate->onBeforeUpdateupdated->onUpdatedbeforeDestroy->onBeforeUnmountdestroyed->onUnmountederrorCaptured->onErrorCaptured
同时新版本还提供了两个全新的生命周期帮助我们去调试代码:
- onRenderTracked
- onRenderTriggered
在 Panel 列表组件中,我们注册 onMounted 生命周期,并在里面触发请求方法 loadMore 以便从后端获取数据到数据层,这里我们使用的是 axios 网络请求库,所以我们需要安装该模块:
npm install axios --save
封装了一个请求列表数据方法,接口指向的是 Cnode 官网提供的 API ,由于 axios 返回的是 Promise ,所以配合 async 和 await 可以完美的编写异步逻辑,然后结合onMounted 生命周期触发,并将方法绑定到视图层的查看更多按钮上,就可以完成列表首次的加载和点击查看更多的懒加载功能。
// 发送 ajax 请求获取列表数据
const loadMore = async () => {
// 获取列表数据
let data = await axios.get("https://cnodejs.org/api/v1/topics", {
params: {
// 每一页的主题数量
limit: 10,
// 页数
page: state.page
}
});
// 叠加页数
state.page += 1;
// 合并列表数据
state.news = [...state.news, ...data.data.data];
};
onMounted(() => {
// 首屏加载的时候触发请求
loadMore();
});
computed
接下来我们就使用另外一个属性 computed 计算属性,跟 Vue2.0 的使用方式很相近,同样需要按需导入该模块:
import { computed } from '@vue/composition-api';
计算属性分两种,只读计算属性和可读可写计算属性:
// 只读计算属性
let newsComputed = computed(() => news.value + 1)
// 可读可写
let newsComputed = computed({
// 取值函数
get: () => news.value + 2,
// 赋值函数
set: val => {
news.value = news.value - 3
}
})
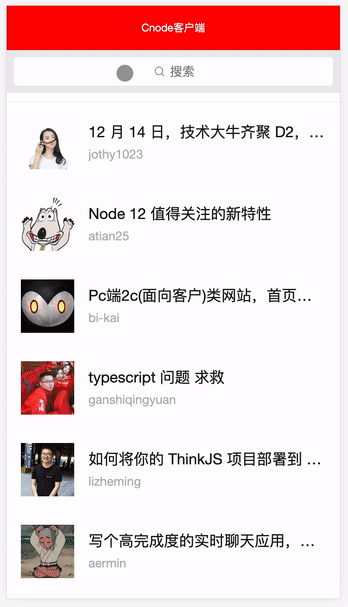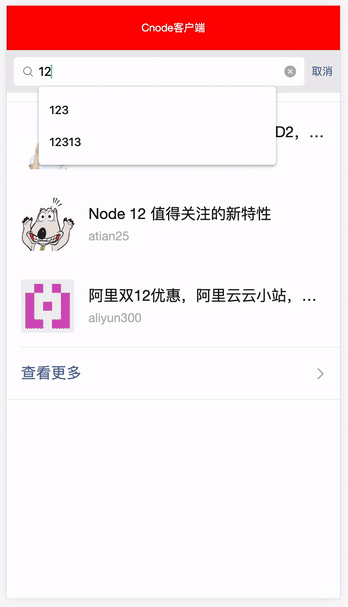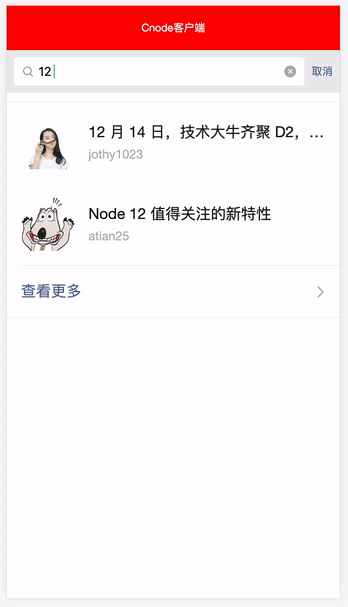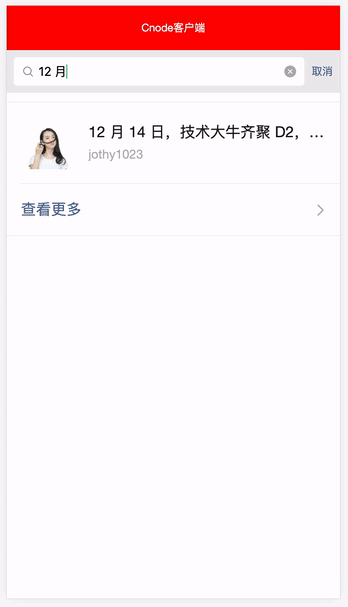
这里我们使用可读可写计算属性去处理列表数据,还记得我们上一个组件 Search.vue 吗,我们可以结合用户在搜索框输入的检索值,配合 computed 计算属性来筛选对我们用户有用列表数据,所以我们首先从 store 的共享实例里面拿到 Search.vue 搜索框共享的 searchValue ,然后利用原生字符串方法 indexOf 和 数组方法 filter 来过滤列表的数据,然后重新返回新的列表数据 newsComputed,并在视图层上配合 v-for 指令去渲染新的列表数据,这样做既可以在没搜索框检索值的时候返回原列表数据 news ,而在有搜索框检索值的时候返回新列表数据 newsComputed。
import store from "../stores";
export default {
setup() {
const state = reactive({
// 原列表数据
news: [],
// 通过搜索框的值去筛选后的新列表数据
newsComputed: computed(() => {
// 判断是否输入框是否输入了筛选条件,如果没有返回原始的 news 数组
if (store.state.searchValue) {
return state.news.filter(item => {
if (item.title.indexOf(store.state.searchValue) >= 0) {
return item;
}
});
} else {
return state.news;
}
}),
searchValue: store.state
});
}
}
项目源码
如果文章和笔记能带您一丝帮助或者启发,请不要吝啬你的赞和 Star,你的肯定是我前进的最大动力😁

 本项目综合运用了 Vue3.0 的新特性,适合新手学习😁
基于 Composition API 即 Function-based AP I进行改造,配合 Vue Cli,优先体验 Vue3 特性
使用单例对象模式进行组件通信
使用 axios 库进行网络请求,weui 库实现 UI 界面
本项目综合运用了 Vue3.0 的新特性,适合新手学习😁
基于 Composition API 即 Function-based AP I进行改造,配合 Vue Cli,优先体验 Vue3 特性
使用单例对象模式进行组件通信
使用 axios 库进行网络请求,weui 库实现 UI 界面

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号