RocketMQ源码详解 | Producer篇 · 其一:Start,然后 Send 一条消息
概述
DefaultMQProducer producer = new DefaultMQProducer("please_rename_unique_group_name");
producer.start();
try {
/*
* Create a message instance, specifying topic, tag and message body.
*/
Message msg = new Message("TopicTest" /* Topic */,
"TagA" /* Tag */,
("Hello RocketMQ " + i).getBytes(RemotingHelper.DEFAULT_CHARSET) /* Message body */
);
/*
* Call send message to deliver message to one of brokers.
*/
SendResult sendResult = producer.send(msg);
System.out.printf("%s%n", sendResult);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*
* Shut down once the producer instance is not longer in use.
*/
producer.shutdown();
Start
DefaultMQProducer#start
首先进入 start 方法,可以看出主要的功能实现在于 defaultMQProducerImpl.start(),先忽略细枝末节,接着进去看看
public void start() throws MQClientException {
this.setProducerGroup(withNamespace(this.producerGroup));
this.defaultMQProducerImpl.start();
if (null != traceDispatcher) {
try {
traceDispatcher.start(this.getNamesrvAddr(), this.getAccessChannel());
} catch (MQClientException e) {
log.warn("trace dispatcher start failed ", e);
}
}
}
DefaultMQProducerImpl#start()
然后,我们可以看到会根据当前生产者的状态来进行不同的行为
记得在设计模式里,这叫做"状态模式"
具体的状态有:
- CREATE_JUST
- RUNNING
- START_FAILED
- SHUTDOWN_ALREADY
在进入 start 后状态会变成 START_FAILED ,完成后变成 RUNNING 状态
public void start() throws MQClientException {
this.start(true);
}
public void start(final boolean startFactory) throws MQClientException {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
// -- 跳过 --
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case RUNNING:
case START_FAILED:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
throw new MQClientException("The producer service state not OK, maybe started once, "
+ this.serviceState
+ FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.CLIENT_SERVICE_NOT_OK),
null);
default:
break;
}
}
进入 CREATE_JUST 后开始对元信息进行检查与注册
this.checkConfig();
// 如果自定义了生产者组,则修改PID
if (!this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup().equals(MixAll.CLIENT_INNER_PRODUCER_GROUP)) {
this.defaultMQProducer.changeInstanceNameToPID();
}
// 从MQ工厂获取实例
// MQ工厂保证ClientID唯一
this.mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getOrCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQProducer, rpcHook);
// 注册生产者组
boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerProducer(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(), this);
if (!registerOK) {
this.serviceState = ServiceState.CREATE_JUST;
throw new MQClientException("The producer group[" + this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup()
+ "] has been created before, specify another name please." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.GROUP_NAME_DUPLICATE_URL),
null);
}
this.topicPublishInfoTable.put(this.defaultMQProducer.getCreateTopicKey(), new TopicPublishInfo());
if (startFactory) {
mQClientFactory.start();
}
log.info("the producer [{}] start OK. sendMessageWithVIPChannel={}", this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup(),
this.defaultMQProducer.isSendMessageWithVIPChannel());
然后具体看 mQClientFactory.start() 方法
MQClientInstance#start
MQClientInstance 是由一个 JAVA 程序所共用的,其可以从 ClientId 的生成方法看出
public String buildMQClientId() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(this.getClientIP());
sb.append("@");
sb.append(this.getInstanceName());
if (!UtilAll.isBlank(this.unitName)) {
sb.append("@");
sb.append(this.unitName);
}
return sb.toString();
}
由以上代码可以得知,一台机器上的一个 JVM 进程只拥有一个实例,所以以下的初始化方法也是全局的
首先对当前对象加锁来避免多线程带来的问题,然后又进行了一次状态判断来保证状态正确。然后就启动了一堆服务。
synchronized (this) {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
// NameSrv 地址为空时,尝试通过设定的地址使用HTTP获取NameSrv地址
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
}
// 开启 Netty 的请求响应的 Channel
this.mQClientAPIImpl.start();
// 开启调度任务
this.startScheduledTask();
// 开启拉取服务
this.pullMessageService.start();
// 开启再均衡服务
this.rebalanceService.start();
// 开启push服务
this.defaultMQProducer.getDefaultMQProducerImpl().start(false);
log.info("the client factory [{}] start OK", this.clientId);
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case START_FAILED:
throw new MQClientException("The Factory object[" + this.getClientId() + "] has been created before, and failed.", null);
default:
break;
}
}
其中的 pullMessageService 和 rebalanceService 等服务都是继承于 ServiceThread 抽象类,这个类被用于在多线程的情况下保证服务启动的正确性。
public void start() {
log.info("Try to start service thread:{} started:{} lastThread:{}", getServiceName(), started.get(), thread);
// 只会被启动一次
if (!started.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return;
}
stopped = false;
// 启动子类的实现线程,从子类获取服务名
this.thread = new Thread(this, getServiceName());
this.thread.setDaemon(isDaemon);
this.thread.start();
}
其中 RebalanceService 和 PullMessageService 我们在其他章节再具体分析。
此外,其中的 startScheduledTask() 又开启了一些定时运行的任务
// 从远程服务器不断更新 NameServer 地址
if (null == this.clientConfig.getNamesrvAddr()) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.mQClientAPIImpl.fetchNameServerAddr();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask fetchNameServerAddr exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 10, 1000 * 60 * 2, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 定时从NameServer更新Topic的路由信息
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer exception", e);
}
}
}, 10, this.clientConfig.getPollNameServerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 定期清除离线的Broker地址,同时发送心跳
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.cleanOfflineBroker();
MQClientInstance.this.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask sendHeartbeatToAllBroker exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000, this.clientConfig.getHeartbeatBrokerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 持久化所有的拥有的消费者偏移量
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.persistAllConsumerOffset();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask persistAllConsumerOffset exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 10, this.clientConfig.getPersistConsumerOffsetInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 动态对所有消费者的线程池容量进行调整
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.adjustThreadPool();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask adjustThreadPool exception", e);
}
}
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
从这里可以看出,消费者不仅是在内存保存了偏移量,还会定期持久化以保证不丢失。
运行这些任务的,是一个 SingleThreadScheduledExecutor ,这是一个由一个线程去执行需要被定时执行的任务的线程池。
在完成以上任务后,回到我们的 DefaultMQProducerImpl.start() 方法看剩下的两段
// 为所有Broker发送心跳
this.mQClientFactory.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
// 开启所有的调度任务
this.startScheduledTask();
首先来看第一个方法
public void sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock() {
if (this.lockHeartbeat.tryLock()) {
try {
// 发送心跳,但第一次的时候是空的,所以不用考虑
this.sendHeartbeatToAllBroker();
// 上传过滤器Class,消费者相关
this.uploadFilterClassSource();
} catch (final Exception e) {
log.error("sendHeartbeatToAllBroker exception", e);
} finally {
this.lockHeartbeat.unlock();
}
} else {
log.warn("lock heartBeat, but failed. [{}]", this.clientId);
}
}
在发送心跳的时候,由于这时候还没有从 NameServer 获取 Broker 地址,所以不会发送,而上传过滤器 Class 我们留到消费者的章节再讲。
第二个方法比较简单,开启一个调度任务来处理所有的 Request 状态,对异步的请求根据状态处理回调函数。
private void startScheduledTask() {
// 原子增加生产者数量
if (RequestFutureTable.getProducerNum().incrementAndGet() == 1) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 处理异步回调请求,扫描所有Request状态
RequestFutureTable.scanExpiredRequest();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scan RequestFutureTable exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 3, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
需要注意的是,这个异步请求指的并不是在
send中的异步回调机制,而是在 rockmq-4.7.0 后加入的 Request-Reply 特性,用来支持 RPC 调用。实现的方法是:
- Producer 投递消息到 Broker,然后阻塞直到收到 返回结果
- Broker 收到后像正常消息一样 ack,Consumer 通过 pull\push 从 Broker 中获取
- Consumer 获取后进行处理,然后响应 返回结果
- Broker 收到 返回结果 后将其发回对应的 Producer
核心的方法与类有:
DefaultMQProducerImpl#request() RequestResponseFuture#waitResponseMessage()#putResponseMessage() MessageUtil#createReplyMessage() ReplyMessageProcessor#processReplyMessageRequest() ClientRemotingProcessor#receiveReplyMessage()
自此,Start 方法就完成了。
Start 总体流程
-
设置生产者组
-
检查当前状态,只允许为 CreateJust
-
从 MQClientManage 获取 MQClient 工厂
3.1 已经被创建则直接返回
-
注册生产者组
-
启动 MQClient 工厂
5.1 NameSrv 地址为空时,尝试通过设定的地址使用HTTP获取NameSrv地址
5.2 开启 Netty 的请求响应的 Channel
5.3 开启调度任务
5.3.1 从远程服务器不断更新 NameServer 地址
5.3.2 定时从NameServer更新Topic的路由信息
5.3.3 定期清除离线的Broker地址,同时发送心跳
5.3.4 持久化所有的拥有的消费者偏移量
5.3.5 动态对所有消费者的线程池容量进行调整
5.4 开启拉取服务
5.5 开启再均衡服务
5.6 开启push服务
-
启动 trace dispatcher 服务
Send
进入 send 后会进行完整检查,且默认工作模式为 Sync,send 的主要工作的方法如下
DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendDefaultImpl
这个方法很长,我们一段段来看
// 确保是 Start 状态
this.makeSureStateOK();
Validators.checkMessage(msg, this.defaultMQProducer);
final long invokeID = random.nextLong();
long beginTimestampFirst = System.currentTimeMillis();
long beginTimestampPrev = beginTimestampFirst;
long endTimestamp = beginTimestampFirst;
// 得到Topic信息
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic());
// 返回为Null的结果只有Topic不存在且自动创建Topic没有打开
if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) { /* pass */ }
// 检查下是不是NameSev地址填错了
validateNameServerSetting();
throw new MQClientException("No route info of this topic: " + msg.getTopic() + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.NO_TOPIC_ROUTE_INFO),
null).setResponseCode(ClientErrorCode.NOT_FOUND_TOPIC_EXCEPTION);
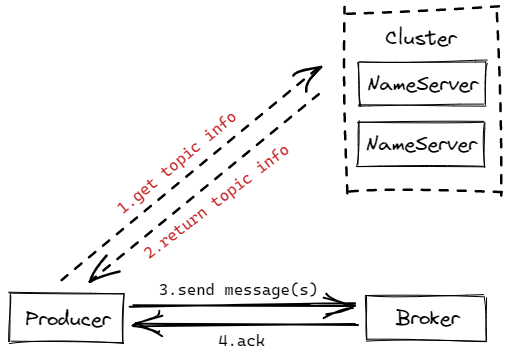
首先是确保状态正确,然后记录启动时间作为度量和超时检查,然后调用 tryToFindTopicPublishInfo 获得具体的 Topic 信息以发送消息,如果找不到则抛异常。
然后进入 tryToFindTopicPublishInfo 看看具体实现
// 寻找消息应该被发到哪
private TopicPublishInfo tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(final String topic) {
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
// 本地没有、或未就绪,从NameServ请求
if (null == topicPublishInfo || !topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
this.topicPublishInfoTable.putIfAbsent(topic, new TopicPublishInfo());
// 没有信息则从NameServ拉取
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic);
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
}
if (topicPublishInfo.isHaveTopicRouterInfo() || topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
return topicPublishInfo;
} else {
// 拉取不到?说明我们要发送的目标Topic不存在
// 那就打开isDefault开关,向默认Topic发送
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, true, this.defaultMQProducer);
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
return topicPublishInfo;
}
}
这个方法可以看到,在本地会有一个本地 Topic 表,没有会尝试去 NameServer 拉取。
而拉取分为两阶段,第一次拉取会去找对应的 Topic ,失败则第二次会去找 Default Topic。为什么会这样做呢?我们都知道自动创建 Topic 只会在 Broker 打开自动创建 Topic 的开关才有效,而具体的实现方法需要我们再往下看
MQClientInstance#updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer
又进入了 MQClientInstance ,我们刚刚已经了解到它会由 MQClientManager 创建一个全局的实例,而它内部有几个重要的 Map。
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* group */, MQProducerInner> producerTable;
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* group */, MQConsumerInner> consumerTable;
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* group */, MQAdminExtInner> adminExtTable;
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* Topic */, TopicRouteData> topicRouteTable;
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* Broker Name */, HashMap<Long/* brokerId */, String/* address */>> brokerAddrTable;
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* Broker Name */, HashMap<String/* address */, Integer>> brokerVersionTable;
从变量名和和注释我们不难理解它们是做什么的。我们可以发现, Client 的元信息是由所有的消费者和生产者共享。
回归正题,接着看更新路由信息的方法
TopicRouteData topicRouteData;
// 使用默认 Topic ,因为目标Topic不存在,所以需要新建
if (isDefault && defaultMQProducer != null) {
// 获取默认Topic路由信息
topicRouteData = this.mQClientAPIImpl.getDefaultTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(defaultMQProducer.getCreateTopicKey(),
1000 * 3);
// 获得了信息后,接下来都是新的Topic都是继承于默认Topic的信息
if (topicRouteData != null) {
// 修正读写Queue数量
for (QueueData data : topicRouteData.getQueueDatas()) {
int queueNums = Math.min(defaultMQProducer.getDefaultTopicQueueNums(), data.getReadQueueNums());
data.setReadQueueNums(queueNums);
data.setWriteQueueNums(queueNums);
}
}
} else {
topicRouteData = this.mQClientAPIImpl.getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, 1000 * 3);
}
这里分为直接从 NameServer 获取和获取 default topic 后对其元信息进行继承。
关于 ReadQueue 和 WriteQueue
可读 Queue 代表消费者可以读取的 Queue,可写 Queue 代表生产者可以写入的 Queue。
将它们进行分离的主要是为了方便的动态调整 Queue 的大小
其中 getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer 主要是 Netty 使用 RPC 获取 Topic,具体内容在其他章看看
在获取了路由信息后,就开始对其进行检查更改的项目
if (topicRouteData != null) {
// 检查路由信息是否发生改变
TopicRouteData old = this.topicRouteTable.get(topic);
boolean changed = topicRouteDataIsChange(old, topicRouteData);
if (!changed) {
changed = this.isNeedUpdateTopicRouteInfo(topic);
} else {
log.info("the topic[{}] route info changed, old[{}] ,new[{}]", topic, old, topicRouteData);
}
// 发生改变则进行更改
if (changed) {
TopicRouteData cloneTopicRouteData = topicRouteData.cloneTopicRouteData();
// 更新路由地址
for (BrokerData bd : topicRouteData.getBrokerDatas()) {
this.brokerAddrTable.put(bd.getBrokerName(), bd.getBrokerAddrs());
}
// Update Pub info
{
TopicPublishInfo publishInfo = topicRouteData2TopicPublishInfo(topic, topicRouteData);
publishInfo.setHaveTopicRouterInfo(true);
Iterator<Entry<String, MQProducerInner>> it = this.producerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, MQProducerInner> entry = it.next();
MQProducerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
// 在这,被新建的Topic放入了本地生产者表
impl.updateTopicPublishInfo(topic, publishInfo);
}
}
}
// Update sub info
{
Set<MessageQueue> subscribeInfo = topicRouteData2TopicSubscribeInfo(topic, topicRouteData);
Iterator<Entry<String, MQConsumerInner>> it = this.consumerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, MQConsumerInner> entry = it.next();
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
impl.updateTopicSubscribeInfo(topic, subscribeInfo);
}
}
}
log.info("topicRouteTable.put. Topic = {}, TopicRouteData[{}]", topic, cloneTopicRouteData);
// 重新放入
this.topicRouteTable.put(topic, cloneTopicRouteData);
return true;
}
} else {
log.warn("updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer, getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer return null, Topic: {}. [{}]", topic, this.clientId);
}
如果是 default topic 的话,就会在这一步放入本地。
这是因为,在 Broker 中,如果开启了自动创建 Topic 的选项,便会创建一个和 default 同名(default 的默认名称为 TBW102)的 Topic,并以这个 Topic 来创建新的 Topic ,但若没有开启,则会因为找不到 TopicName 而返回错误。
DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendDefaultImpl
我们再回到发送方法来,在获取到要发送的 Topic 的元信息后,就可以开始发送了
boolean callTimeout = false;
MessageQueue mq = null;
Exception exception = null;
SendResult sendResult = null;
// 最多发送timesTotal次
int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC ? 1 + this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1;
int times = 0;
String[] brokersSent = new String[timesTotal];
for (; times < timesTotal; times++) {
String lastBrokerName = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName();
// 选择一个Queue
MessageQueue mqSelected = this.selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName);
if (mqSelected != null) {
/* pass */
} else {
break;
}
}
在这里,Producer 会根据发送类型来选择发送次数,同步会选择默认的重试次数加一,而异步和oneway则只会尝试一次
在发送流程中,首先需要选择 Topic 中的 Queue
MQFaultStrategy#selectOneMessageQueue
从类名可以看出,这个类主要实现故障退避功能,同时使用轮询的方式来选择 Queue
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) {
// 故障退避: 当要发送的Broker在上一次发送中延迟了较久的时间或发送失败,会进行一段时间的退避
if (this.sendLatencyFaultEnable) {
try {
// 首先,增加线程本地的轮询计数
int index = tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().incrementAndGet();
for (int i = 0; i < tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size(); i++) {
int pos = Math.abs(index++) % tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().size();
if (pos < 0)
pos = 0;
MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.getMessageQueueList().get(pos);
// 如果可用(不需要进行退避),则直接使用
if (latencyFaultTolerance.isAvailable(mq.getBrokerName()))
return mq;
}
// 在所有Broker都需要退避的情况下,即没有最优解,选择次优
final String notBestBroker = latencyFaultTolerance.pickOneAtLeast();
int writeQueueNums = tpInfo.getQueueIdByBroker(notBestBroker);
if (writeQueueNums > 0) {
final MessageQueue mq = tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
if (notBestBroker != null) {
mq.setBrokerName(notBestBroker);
mq.setQueueId(tpInfo.getSendWhichQueue().incrementAndGet() % writeQueueNums);
}
return mq;
} else {
// 如果可写 Queue 已经为零,说明已经不在了
latencyFaultTolerance.remove(notBestBroker);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Error occurred when selecting message queue", e);
}
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue();
}
// 如果没有开启开关,则选择一个不是上一次发送的Broker来发送
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName);
}
大多数内容直接看代码就能理解,所以我们主要看下 pickOneAtLeast 方法
LatencyFaultToleranceImpl#pickOneAtLeast
这个方法用于在所有 Broker 都需要"故障退避"的时候,选择一个可能最好的
public String pickOneAtLeast() {
final Enumeration<FaultItem> elements = this.faultItemTable.elements();
List<FaultItem> tmpList = new LinkedList<FaultItem>();
while (elements.hasMoreElements()) {
final FaultItem faultItem = elements.nextElement();
tmpList.add(faultItem);
}
if (!tmpList.isEmpty()) {
Collections.shuffle(tmpList);
Collections.sort(tmpList);
final int half = tmpList.size() / 2;
if (half <= 0) {
return tmpList.get(0).getName();
} else {
final int i = this.whichItemWorst.incrementAndGet() % half;
return tmpList.get(i).getName();
}
}
return null;
}
这个方法主要的策略是:
对当前的处于"故障退避"状态的 Broker 使用洗牌算法(这有啥意义...),然后进行排序,然后选择所有元素的前半段使用轮询策略
排序方案:是否可用 > 上次响应时间(短>长)(发生网络分区的时候会相同)> 未来可用时间点(近>远)
DefaultMQProducerImpl#sendDefaultImpl
选择完 Queue 后,就要进行实际的发送了
mq = mqSelected;
brokersSent[times] = mq.getBrokerName();
try {
beginTimestampPrev = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (times > 0) {
// 在重新发送期间使用命名空间重置主题
msg.setTopic(this.defaultMQProducer.withNamespace(msg.getTopic()));
}
// 消耗时间的度量
long costTime = beginTimestampPrev - beginTimestampFirst;
if (timeout < costTime) {
callTimeout = true;
break;
}
// 发送MSG
sendResult = this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, timeout - costTime);
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 更新故障退避功能
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false);
// 根据发送方式选择返回结果
switch (communicationMode) {
case ASYNC:
return null;
case ONEWAY:
return null;
case SYNC:
if (sendResult.getSendStatus() != SendStatus.SEND_OK) {
if (this.defaultMQProducer.isRetryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK()) {
continue;
}
}
return sendResult;
default:
break;
}
} catch (XXX e) {
/* 这里删除了一堆Expection catch, 它们都主要做了更新"故障退避", 然后抛出 */
}
可以看出,实际的发送方法是 sendKernelImpl
private SendResult sendKernelImpl(final Message msg,
final MessageQueue mq,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo,
final long timeout) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
String brokerAddr = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInPublish(mq.getBrokerName());
if (null == brokerAddr) {
// 不在内存中,尝试获取或创建
tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(mq.getTopic());
brokerAddr = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInPublish(mq.getBrokerName());
}
SendMessageContext context = null;
if (brokerAddr != null) {
// 是否使用vip,broker有两个端口共同服务
brokerAddr = MixAll.brokerVIPChannel(this.defaultMQProducer.isSendMessageWithVIPChannel(), brokerAddr);
byte[] prevBody = msg.getBody();
try {
// 对于MessageBatch,生成过程中已经设置了ID
if (!(msg instanceof MessageBatch)) {
MessageClientIDSetter.setUniqID(msg);
}
// 将实例名设置为命名空间
boolean topicWithNamespace = false;
if (null != this.mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().getNamespace()) {
msg.setInstanceId(this.mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().getNamespace());
topicWithNamespace = true;
}
// 是否为压缩消息
int sysFlag = 0;
boolean msgBodyCompressed = false;
if (this.tryToCompressMessage(msg)) {
sysFlag |= MessageSysFlag.COMPRESSED_FLAG;
msgBodyCompressed = true;
}
final String tranMsg = msg.getProperty(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TRANSACTION_PREPARED);
if (tranMsg != null && Boolean.parseBoolean(tranMsg)) {
sysFlag |= MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_PREPARED_TYPE;
}
// 发送消息的校验钩子
if (hasCheckForbiddenHook()) {
CheckForbiddenContext checkForbiddenContext = new CheckForbiddenContext();
checkForbiddenContext.setNameSrvAddr(this.defaultMQProducer.getNamesrvAddr());
checkForbiddenContext.setGroup(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup());
checkForbiddenContext.setCommunicationMode(communicationMode);
checkForbiddenContext.setBrokerAddr(brokerAddr);
checkForbiddenContext.setMessage(msg);
checkForbiddenContext.setMq(mq);
checkForbiddenContext.setUnitMode(this.isUnitMode());
this.executeCheckForbiddenHook(checkForbiddenContext);
}
// 发送消息前的钩子
if (this.hasSendMessageHook()) {
context = new SendMessageContext();
context.setProducer(this);
context.setProducerGroup(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup());
context.setCommunicationMode(communicationMode);
context.setBornHost(this.defaultMQProducer.getClientIP());
context.setBrokerAddr(brokerAddr);
context.setMessage(msg);
context.setMq(mq);
context.setNamespace(this.defaultMQProducer.getNamespace());
String isTrans = msg.getProperty(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TRANSACTION_PREPARED);
if (isTrans != null && isTrans.equals("true")) {
context.setMsgType(MessageType.Trans_Msg_Half);
}
if (msg.getProperty("__STARTDELIVERTIME") != null || msg.getProperty(MessageConst.PROPERTY_DELAY_TIME_LEVEL) != null) {
context.setMsgType(MessageType.Delay_Msg);
}
this.executeSendMessageHookBefore(context);
}
// 组装消息头
SendMessageRequestHeader requestHeader = new SendMessageRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setProducerGroup(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup());
requestHeader.setTopic(msg.getTopic());
requestHeader.setDefaultTopic(this.defaultMQProducer.getCreateTopicKey());
requestHeader.setDefaultTopicQueueNums(this.defaultMQProducer.getDefaultTopicQueueNums());
requestHeader.setQueueId(mq.getQueueId());
requestHeader.setSysFlag(sysFlag);
requestHeader.setBornTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
requestHeader.setFlag(msg.getFlag());
requestHeader.setProperties(MessageDecoder.messageProperties2String(msg.getProperties()));
requestHeader.setReconsumeTimes(0);
requestHeader.setUnitMode(this.isUnitMode());
requestHeader.setBatch(msg instanceof MessageBatch);
// 发往重发Topic的消息
if (requestHeader.getTopic().startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
String reconsumeTimes = MessageAccessor.getReconsumeTime(msg);
if (reconsumeTimes != null) {
requestHeader.setReconsumeTimes(Integer.valueOf(reconsumeTimes));
MessageAccessor.clearProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_RECONSUME_TIME);
}
String maxReconsumeTimes = MessageAccessor.getMaxReconsumeTimes(msg);
if (maxReconsumeTimes != null) {
requestHeader.setMaxReconsumeTimes(Integer.valueOf(maxReconsumeTimes));
MessageAccessor.clearProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_MAX_RECONSUME_TIMES);
}
}
SendResult sendResult = null;
switch (communicationMode) {
case ASYNC:
Message tmpMessage = msg;
boolean messageCloned = false;
if (msgBodyCompressed) {
//If msg body was compressed, msgbody should be reset using prevBody.
//Clone new message using commpressed message body and recover origin massage.
//Fix bug:https://github.com/apache/rocketmq-externals/issues/66
tmpMessage = MessageAccessor.cloneMessage(msg);
messageCloned = true;
msg.setBody(prevBody);
}
// 从命名空间中解包
if (topicWithNamespace) {
if (!messageCloned) {
tmpMessage = MessageAccessor.cloneMessage(msg);
messageCloned = true;
}
msg.setTopic(NamespaceUtil.withoutNamespace(msg.getTopic(), this.defaultMQProducer.getNamespace()));
}
// 超时检查
long costTimeAsync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeout < costTimeAsync) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendKernelImpl call timeout");
}
// 发送异步消息
sendResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage(
brokerAddr,
mq.getBrokerName(),
tmpMessage,
requestHeader,
timeout - costTimeAsync,
communicationMode,
sendCallback,
topicPublishInfo,
this.mQClientFactory,
this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed(),
context,
this);
break;
case ONEWAY:
case SYNC:
long costTimeSync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeout < costTimeSync) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendKernelImpl call timeout");
}
sendResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage(
brokerAddr,
mq.getBrokerName(),
msg,
requestHeader,
timeout - costTimeSync,
communicationMode,
context,
this);
break;
default:
assert false;
break;
}
// 发送消息后的钩子
if (this.hasSendMessageHook()) {
context.setSendResult(sendResult);
this.executeSendMessageHookAfter(context);
}
return sendResult;
} catch (RemotingException e) {
if (this.hasSendMessageHook()) {
context.setException(e);
this.executeSendMessageHookAfter(context);
}
throw e;
} catch (MQBrokerException e) {
if (this.hasSendMessageHook()) {
context.setException(e);
this.executeSendMessageHookAfter(context);
}
throw e;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (this.hasSendMessageHook()) {
context.setException(e);
this.executeSendMessageHookAfter(context);
}
throw e;
} finally {
msg.setBody(prevBody);
msg.setTopic(NamespaceUtil.withoutNamespace(msg.getTopic(), this.defaultMQProducer.getNamespace()));
}
}
throw new MQClientException("The broker[" + mq.getBrokerName() + "] not exist", null);
}
这个方法干了不少脏活,不过发送的具体实现还是通过 MQClientAPIImpl.sendMessage 来实现。
send 发送流程
-
检查消息
-
从消息的目的 TopicName 中获取元信息;若获取不到 Topic,则抛异常
2.1 从本地获取,没有则从 NameServer 获取
2.1.1 从 NameServer 获取 Topic 元信息,没有则直接返回
2.1.2 更新获取的 Topic 的路由信息
2.2 将获取的 Topic 直接返回,若 NameServer 也没,则进行创建
2.2.1 获取默认 Topic;获取失败直接返回
2.2.2 继承该 Topic 的信息来进行更改以作为新 Topic
-
从 Topic 中选择 Queue
3.1 排除掉在故障退避的 Broker 后,将下一个 Broker 所在的 Queue 返回
3.2 所有 Broker 都需要退避下,选择次优 Broker
-
发送消息;失败则退回第三步
4.1 Vip 检查
4.2 消息类型检查
4.3 调用钩子
4.4 组装消息头
4.5 发送消息
-
更新故障退避信息
-
根据发送方式返回结果

