ht-5 treemap特性
(1)TreeMap类通过使用红黑树实现Map接口
(2)TreeMap提供按排序顺序存储键值对的有效手段,同时允许快速检索
(3)不同于散列映射,树映射保证它的元素按键的自然顺序升序排列
(4)TreeMap构造方法:
TreeMap()
TreeMap(Comparator comp)
TreeMap(Map m)
TreeMap(SortedMap sm)
(5)TreeMap实现SortedMap并且扩展AbstractMap,它本身并没有定义其他方法
JDK中对treemap的定义如下:
public class TreeMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements SortedMap<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
SortedMap 接口的基于红黑树的实现。此类保证了映射按照升序顺序排列关键字,根据使用的构造方法不同,可能会按照键的类的自然顺序 进行排序(参见 Comparable),或者按照创建时所提供的比较器进行排序。
treemap构造方法

TreeMap的key存储引用类型数据,需要满足一定条件:
要么引用类型实现Comparable接口,要么在构建TreeMap对象时,为该TreeMap容器提供实现Comparator接口的比较器对象
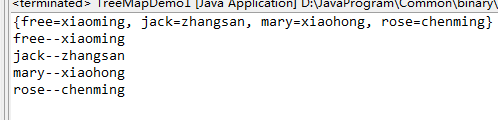
1 package com.iotek.treemap; 2 3 import java.util.Map.Entry; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 import java.util.TreeMap; 6 7 public class TreeMapDemo1 { 8 9 /** 10 * @param args 11 */ 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 TreeMap<String, String> tmap = new TreeMap<String, String>(); 14 tmap.put("jack", "zhangsan"); 15 tmap.put("mary", "xiaohong"); 16 tmap.put("rose", "xiaozhang"); 17 tmap.put("free", "xiaoming"); 18 tmap.put("rose", "chenming"); 19 System.out.println(tmap); 20 // 输出结果是,第三个put进去的键值对被重名的后添加的键对应的键值对替换了,键是唯一的 21 Set<Entry<String, String>> entrys = tmap.entrySet(); 22 /* 23 * 用entrySet()方法返回map容器中的entry对象,然后用foreach来遍历键值对, 24 * 用一个Entry类型的引用变量entry,调用entry的getKey 和getValue方法 25 */ 26 for (Entry<String, String> entry : entrys) { 27 System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--" + entry.getValue()); 28 } 29 30 } 31 32 }
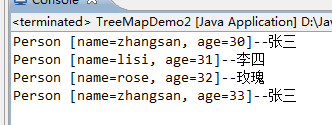
1 package com.iotek.treemap; 2 3 import java.util.Map.Entry; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 import java.util.TreeMap; 6 7 public class TreeMapDemo2 { 8 9 /** 10 * @param args 11 */ 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 TreeMap<Person, String> pdata = new TreeMap<Person, String>(); 14 // 构造一个新的空映射,该映射根据给定的比较器进行排序 15 pdata.put(new Person("zhangsan", 30), "张三"); 16 pdata.put(new Person("lisi", 31), "李四"); 17 pdata.put(new Person("rose", 32), "玫瑰"); 18 pdata.put(new Person("zhangsan", 33), "张三"); 19 Set<Entry<Person, String>> entrys = pdata.entrySet(); 20 for (Entry<Person, String> entry : entrys) { 21 System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--" + entry.getValue()); 22 } 23 // 如果Person类不实现Comparable接口,会报错。因为默认对象作为键名时,不会实现Comparable接口 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 class Person implements Comparable<Person> { 29 private String name; 30 private int age; 31 32 public Person(String name, int age) { 33 super(); 34 this.name = name; 35 this.age = age; 36 } 37 38 public String getName() { 39 return name; 40 } 41 42 public void setName(String name) { 43 this.name = name; 44 } 45 46 public int getAge() { 47 return age; 48 } 49 50 public void setAge(int age) { 51 this.age = age; 52 } 53 54 @Override 55 public int compareTo(Person o) { //按age的自然顺序进行升序排序 56 if (this.age - o.getAge() > 0) { // 如果当前Person对象的age比形参的Person对象的age大,则返回1 57 // 如果o1的age大于o2的age,就放在二叉树节点的右边 58 return 1; 59 } else if (this.age - o.getAge() < 0) { 60 return -1; 61 } 62 return 0; 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public String toString() { 67 return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 68 } 69 70 }
结果:按照年龄升序排序:
按照名字和age排序:
1 package com.iotek.treemap; 2 3 import java.util.Comparator; 4 import java.util.Map.Entry; 5 import java.util.Set; 6 import java.util.TreeMap; 7 8 public class TreeMapDemo3 { 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 // TreeMap的构造方法:TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> c)/ 12 // 构造一个新的空映射,该映射根据给定的比较器进行排序 13 TreeMap<Person1, String> pdata = new TreeMap<Person1, String>( 14 new Comparator<Person1>() { 15 @Override 16 public int compare(Person1 o1, Person1 o2) { 17 if (o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) > 0) { 18 /* o1.getName()得到的是字符串,调用其 compareTo()方法,该方法按字符串的自然顺序进行排序(字符串比较大小) */ 19 return 1; 20 } else if (o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()) < 0) { 21 return -1; 22 } else { // 当名字相同时,再按照年龄来比较 23 return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 }); 28 29 pdata.put(new Person1("zhangsan", 30), "张三"); 30 pdata.put(new Person1("lisi", 31), "李四"); 31 pdata.put(new Person1("rose", 32), "玫瑰"); 32 pdata.put(new Person1("zhangsan", 33), "张三"); 33 Set<Entry<Person1, String>> entrys = pdata.entrySet(); 34 for (Entry<Person1, String> entry : entrys) { 35 System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--" + entry.getValue()); 36 } 37 38 } 39 40 } 41 42 /* 43 * 按字符串的自然顺序进行排序(字符串比较大小):String类的方法 int 44 * compareTo(String anotherString) 按字典顺序比较两个字符串。 45 * anotherString - 要比较的 String。 返回:如果参数字符串等于此字符串, 则返回 0 46 * 值; 如果按字典顺序此字符串小于字符串参数,则返回一个小于 0 的值;如果按字典顺序此字符串 47 * 大于字符串参数, 则返回一个大于 0 的值。 48 */ 49 /* o1.getName()得到的是字符串,调用其 compareTo()方法 */ 50 51 class Person1 { 52 private String name; 53 private int age; 54 55 public Person1(String name, int age) { 56 super(); 57 this.name = name; 58 this.age = age; 59 } 60 61 public String getName() { 62 return name; 63 } 64 65 public void setName(String name) { 66 this.name = name; 67 } 68 69 public int getAge() { 70 return age; 71 } 72 73 public void setAge(int age) { 74 this.age = age; 75 } 76 77 @Override 78 public String toString() { 79 return "Person1 [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 80 } 81 82 }
结果如下:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号