C++版 - 剑指offer 面试题63:二叉搜索树的第k个结点(二叉树中序遍历的应用) 题解 编辑
面试题 63:二叉搜索树的第k个结点
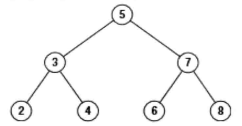
题目:给定一颗二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k大的结点。例如, 5 / \ 3 7 /\ /\ 2 4 6 8 (见下面的图1) 中,按结点数值大小顺序第三个结点的值为4。
图1:一个有7个结点的二叉搜索树,如果按结点数值大小顺序输出,则第3个结点的值是4
提交网址: http://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ef068f602dde4d28aab2b210e859150a?tpId=13&tqId=11215
分析:
对于二叉搜索树BST,在树中任取一棵子树,其节点值都满足:左结点的值 < 父节点的值 < 右结点的值,故如果按照中序遍历的顺序遍历一棵二叉搜索树BST,遍历序列的数值是递增序的。只需要用中序遍历算法遍历一棵二叉搜索树BST,就可以找出它的第k大结点。非递归中序遍历加上计数器即可解决。
6 / \ 3 8 / \ / \ 2 5 7 9
非递归实现 AC代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
struct TreeNode{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* KthNode(TreeNode* pRoot, unsigned int k)
{
TreeNode *p=pRoot;
TreeNode *resNode;
if(p==NULL || k==0) return NULL;
stack<TreeNode *> st;
unsigned int count=0;
while(!st.empty() || p != NULL)
{
if(p != NULL)
{
st.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
if(p == NULL)
{
p=st.top(); // 取当前节点
count++;
if(count==k) resNode=p;
st.pop();
p=p->right;
}
}
return resNode;
}
};
// 以下为测试
int main()
{
Solution sol;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(6);
root->left = new TreeNode(3);
root->left->left = new TreeNode(2);
root->left->right = new TreeNode(5);
root->right = new TreeNode(8);
root->right->left = new TreeNode(7);
root->right->right = new TreeNode(9);
TreeNode* p=sol.KthNode(root, 3);
printf("The value of Kth Node is: %d\n", p->val);
return 0;
}而提交同样作用的代码到牛客网OJ却报错了: control may reach end of non-void function [-Werror,-Wreturn-type, 本地在Visual Studio和Dev C++上都测试通过的...
意思好像是没有在函数最外层写统一的返回值,改了就AC了...
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* KthNode(TreeNode* pRoot, unsigned int k)
{
TreeNode *p=pRoot;
if(p==NULL || k==0) return NULL;
stack<TreeNode *> st;
unsigned int count=0;
while(!st.empty() || p != NULL)
{
if(p != NULL)
{
st.push(p);
p=p->left;
}
if(p == NULL)
{
p=st.top(); // 取当前节点
count++;
if(count==k) return p;
st.pop();
p=p->right;
}
}
}
}; 作者:极客玩家
出处:https://geekzl.com
版权声明:本文为博主原创或转载文章,欢迎转载,但转载文章之后必须在文章页面明显位置注明出处,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。如您有任何疑问或者授权方面的协商,请 .
如果,您希望更容易地发现我的新文章,不妨点击一下绿色通道的【关注我】,亦可微信搜索公众号「大白技术控」关注我。
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点击一下右下方的推荐按钮,您的推荐将是我写作的最大动力!版权声明:本文为博主原创或转载文章,欢迎转载,但转载文章之后必须在文章页面明显位置注明出处,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。如您有任何疑问或者授权方面的协商,请 .









【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?