SpringBoot中使用注解@RequestParam与 @RequestBody
在SpringBoot项目中,使用 @RequestParam和 @RequestBody解析http请求中的参数:
@RequestParam 用于 url查询字符串、form-data、和 x-www-form-urlencoded参数格式解析。
@RequestBody 用于application/json 参数格式解析。
@RequestParam可以很方便的解析参数较少的请求,并且易于对参数校验。@RequestBody 适用于参数较多的请求,解析时需要提供实体类,由jackson自动反序列化成对应的Java实体类对象。 对比一下二者在解析GET、POST 请求方式上的区别。
1、@RequestParam 解析GET请求
先定义一个controller,并规定传入name和id两个参数,请求方式为get,分别打印出参数url,查询字符串参数、编码方式、请求方式。
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test (@RequestParam("name") String name, @RequestParam("id") int id, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
logger.info("请求url {}", httpServletRequest.getRequestURI());
logger.info("查询字符串参数 {}",httpServletRequest.getQueryString());
logger.info("参数编码方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getContentType());
logger.info("请求方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getMethod());
logger.info("name {}",name);
logger.info("id {}",id);
return "ok";
}
使用postman请求,分别使用查询字符串、放入body的form-data和x-www-form-urlencoded 格式进行请求:
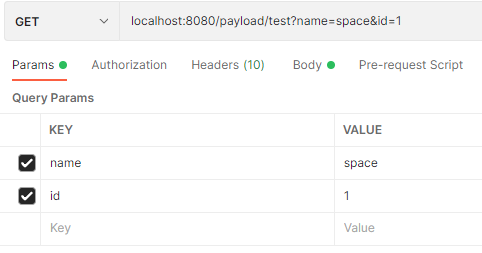
查询字符串
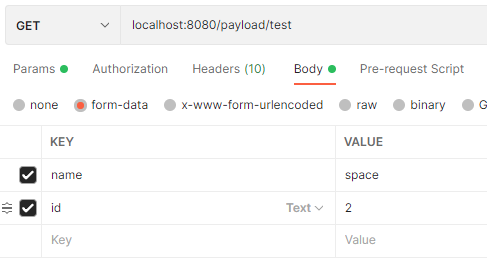
form-data
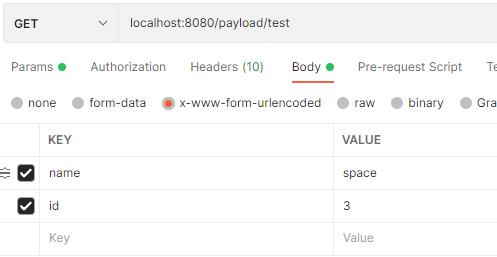
x-www-form-urlencoded
响应如下:
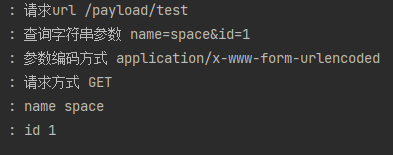
查询字符串参数解析:
form-data参数解析
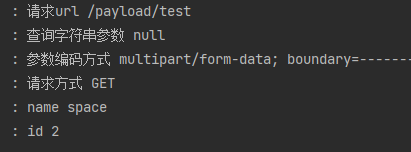
x-www-form-urlencoded参数解析
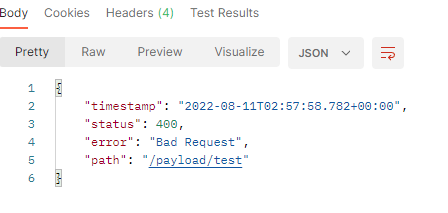
可以看到使用@RequestParam注解对于 GET 类型的请求,前端传递的查询字符串、form-data 的参数均能正确解析, 但无法解析 x-www-form-urlencoded 参数格式。
2、@RequestParam 解析POST请求
重新定义一个controller。
@PostMapping("text")
public String text(@RequestParam("name") String name, @RequestParam("id") int id, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
logger.info("请求url {}", httpServletRequest.getRequestURI());
logger.info("查询字符串参数 {}",httpServletRequest.getQueryString());
logger.info("参数编码方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getContentType());
logger.info("请求方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getMethod());
logger.info("name {}",name);
logger.info("id {}",id);
return "ok";
}
依次使用查询字符串、放入body使用form-data格式、和 x-www-form-urlencoded参数格式请求。
查询字符串
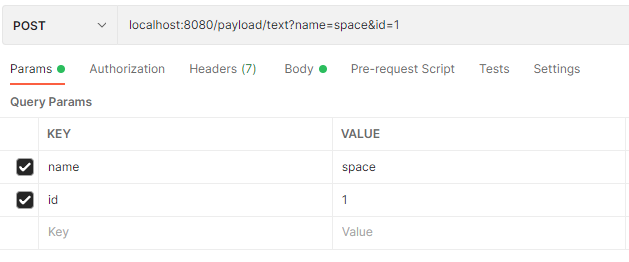
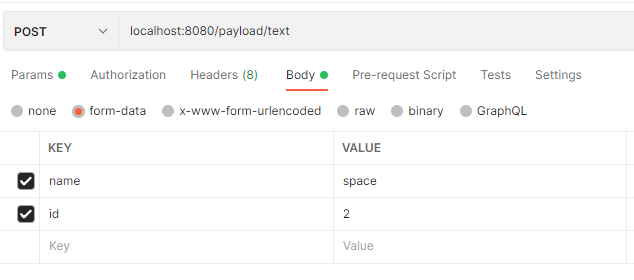
form-data
x-www-form-urlencoded
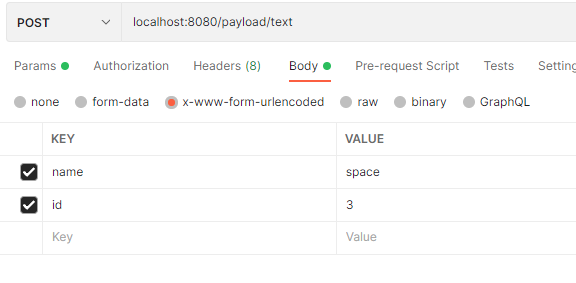
解析如下:
查询字符串参数解析:
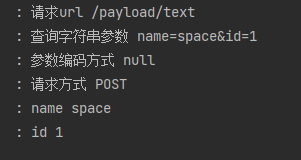
form-data参数解析
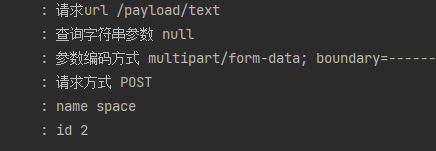
x-www-form-urlencoded参数解析
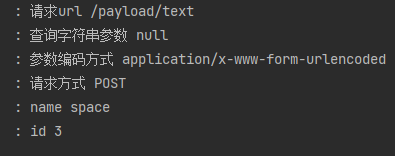
可以看到使用@RequestParam注解对于 POST 类型的请求,前端传递的查询字符串、form-data、 x-www-form-urlencoded 的类型参数均能正确解析。
3、@RequestBody 注解
@RequestBody注解可以解析 body体的 application/json编码方式的请求参数,且GET、POST方式均可以解析。
@GetMapping("signGet")
public String signin(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
logger.info("请求url {}", httpServletRequest.getRequestURI());
logger.info("查询字符串参数 {}",httpServletRequest.getQueryString());
logger.info("参数编码方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getContentType());
logger.info("请求方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getMethod());
logger.info("name {}",user.name);
logger.info("id {}",user.id);
return "ok";
}
@PostMapping("signPost")
public String signout(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
logger.info("请求url {}", httpServletRequest.getRequestURI());
logger.info("查询字符串参数 {}",httpServletRequest.getQueryString());
logger.info("参数编码方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getContentType());
logger.info("请求方式 {}", httpServletRequest.getMethod());
logger.info("name {}",user.name);
logger.info("id {}",user.id);
return "ok";
}
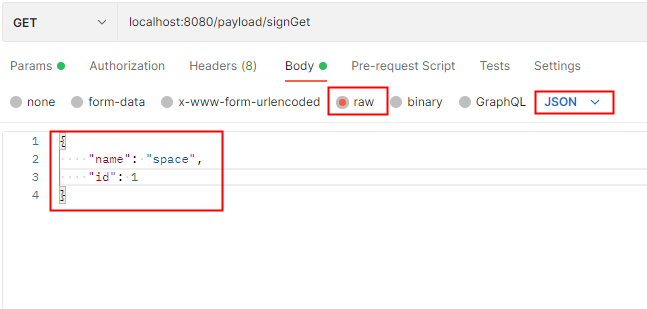
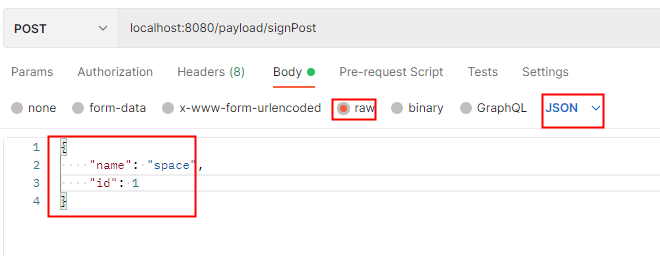
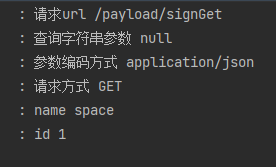
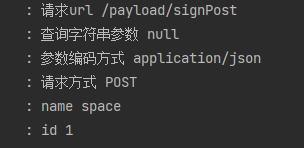
由于springboot内置了Jackson,自动将参数解析并组装到实体类里面。以上结果运行在spring boot 2.7 并使用spring boot默认配置测试。
有关get请求是否可以有body体的问题,可以参阅 HTTP GET 请求可以有 body 吗?


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号