结对项目之词频统计——增强功能
1、基本信息
1.1、本次作业的地址:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/ntu/Embedded_Application/homework/2300
1.2 、项目 Git地址:https://gitee.com/ntucs/PairProg.git
1.3、结对成员:唐庆阳 1613072009 戴俊明 1613072010
2、项目分析
2.1、程序运行模块(方法、函数)介绍
任务1、接口封装 —— 将基本功能封装成(类或独立模块)
我们将作业四中写的韩式封装成一个WordCount类,在主函数中直接调用这个类就能实现原来的功能。(与原本函数几乎一样的函数,具体代码以省略)
class WordCount: def __init__(self, i, o, s='stop_words.txt', m=1, n=10): """初始化""" self.i = i self.o = o self.output = None self.s = s self.m = m self.n = n def process_file(self): """读取文本文件""" def process_buffer(self, text_string): """当只统计单词时(num == 1),生成<str,int>形式的键值对, 当统计短语时,生成字典套字典的形式,具体参考sample.json文件""" def process_wordgroupcount(self, text_string): """对词组进行统计,num为自促所包含的单词数目""" @staticmethod def get_dict_value(word_freq, keys): """如果keys为字符串,返回word_freq字典中以keys为键的值。 如果keys为列表,则使用eval()函数进行字符串拼接,深度查找word_freq字典中以keys为键的值。""" @staticmethod def format_dict(word_freq): """对统计短语的情况生成的复杂字典进行格式化,格式化后的形式为<str,int>""" def output_result(self, word_freq): """输出单词个数到输出文件""" def calculation(self): """主要流程封装""" output = open(self.o, 'w+') self.output = output buffer = self.process_file() word_freq = self.process_buffer(buffer) if self.m != 1: word_freq = self.process_wordgroupcount(buffer) word_freq = self.format_dict(word_freq) self.output_result(word_freq) self.output.close()
主函数测试:
if __name__ == "__main__": import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('--i', '-i', type=str, default='Gone_with_the_wind.txt', help="读取文件路径") parser.add_argument('--o', '-o', type=str, default='result.txt', help="输出文件路径") parser.add_argument('--s', '-s', type=str, default='stop_words.txt', help="停词表路径") parser.add_argument('--m', '-m', type=int, default=2, help="输出的单个词组长度") parser.add_argument('--n', '-n', type=int, default=10, help="输出频率前n个的单词和词组数量") args = parser.parse_args() word_count = WordCount(args.i, args.o, args.s, args.m, args.n) word_count.calculation()
任务2、增加新功能
我们在任务一的基础上增加了新的功能,我们增加参数的数量,便可以实现。
def __init__(self, i, o, s='stop_words.txt', m=1, n=10): self.i = i self.o = o self.output = None self.s = s self.m = m self.n = n
这是WordCount类的构造函数,接下来是我们对命令行参数的处理。
parser.add_argument('--i', '-i', type=str, default='Gone_with_the_wind.txt', help="读取文件路径") parser.add_argument('--o', '-o', type=str, default='result.txt', help="输出文件路径") parser.add_argument('--s', '-s', type=str, default='stop_words.txt', help="停词表路径") parser.add_argument('--m', '-m', type=int, default=2, help="输出的单个词组长度") parser.add_argument('--n', '-n', type=int, default=10, help="输出频率前n个的单词和词组数量")
每一个参数都有对应的默认值,这让我们能够随意添加或省略之中的每一个参数。
2.2、运行截图
Pycharm运行截图:

cmd运行截图:
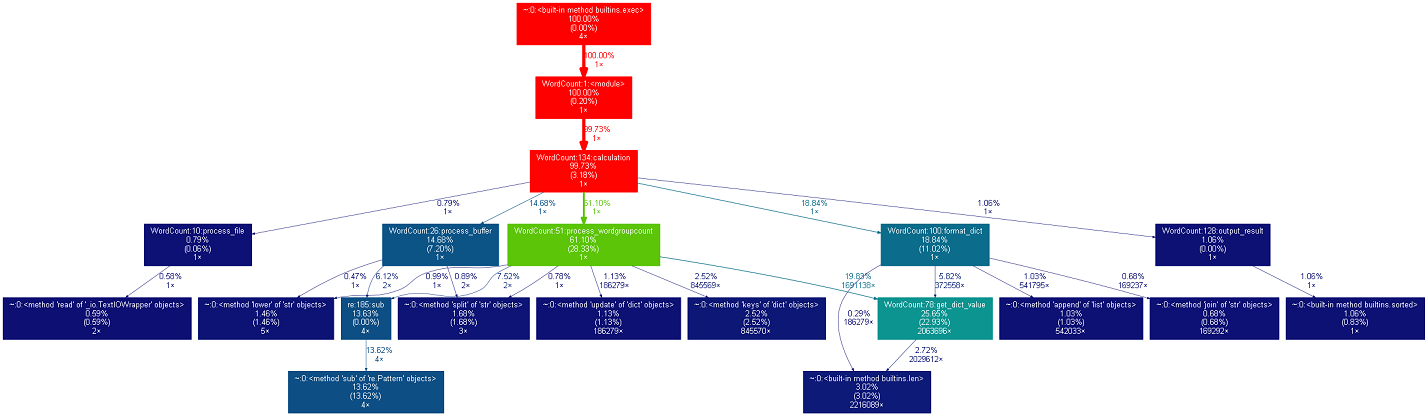
3、性能分析
本次代码与作业四其实没什么不同,性能上面并没有什么大的突破。
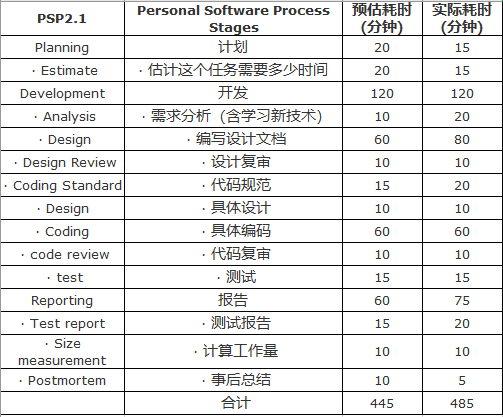
4、PSP表格
5、事后分析与总结
5.1、简述结对编程时,针对某个问题的讨论决策过程:
这个其实没啥过程,无论是封装成类,还是命令行传参,我们的意见一直都是一致的。
5.2、评价对方:
唐庆阳对戴俊明的评价:有代码洁癖,对代码的格式、命名规范很重视。
戴俊明对唐庆阳的评价:经常有新的点子,并且在一定程度上对如今的代码结构有一定的优化。
5.3、评价整个过程:
两人分工完成,一个进行封装,一个进行测试,分工明确,效率也很高。
5.4、结对编程照片:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号