BSON
BSON是二进制JSON,是一个二进制编码的文档序列。类似JSON,BSON支持嵌套的文档和数组。BSON除支持基础的JSON类型外还支持扩展类型,如Date和BinData。
BSON [bee · sahn], short for Binary JSON, is a binary-encoded serialization of JSON-like documents. Like JSON, BSON supports the embedding of documents and arrays within other documents and arrays. BSON also contains extensions that allow representation of data types that are not part of the JSON spec. For example, BSON has a Date type and a BinData type.
BSON是一种二进制格式,零个或多个排序的键值对存储在一个实体中,称实体为一个文档。
BSON is a binary format in which zero or more ordered key/value pairs are stored as a single entity. We call this entity a document.
BSON目前主要应用于MongoDB中,是mongodb的数据存储格式。
数据类型
基础类型
byte,int32,int64,uint64,double,decimal128
|
byte |
1 byte (8-bits) |
|
int32 |
4 bytes (32-bit signed integer, two's complement) |
|
int64 |
8 bytes (64-bit signed integer, two's complement) |
|
uint64 |
8 bytes (64-bit unsigned integer) |
|
double |
8 bytes (64-bit IEEE 754-2008 binary floating point) |
|
decimal128 |
16 bytes (128-bit IEEE 754-2008 decimal floating point) |
注:每种基础类型必须以小端(little-endian)方式序列化。
Non-terminals
注:引用的字符串应该用C语法解析,如"\x01"代表一个字节(00000001)。
注:*代表重复的次数。*2代表重复两次。

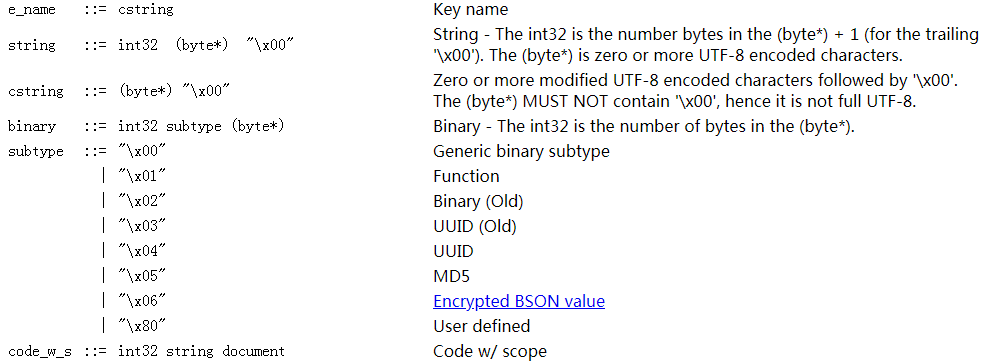
注:Array - The document for an array is a normal BSON document with integer values for the keys, starting with 0 and continuing sequentially. For example, the array ['red', 'blue'] would be encoded as the document {'0': 'red', '1': 'blue'}. The keys must be in ascending numerical order.
示例1:
{"hello": "world"} "\x16\x00\x00\x00\x02hello\x00\x06\x00\x00\x00world\x00\x00"
"\x16\x00\x00\x00":文档的长度,这里用小端表示,即文档的长度是22个字节
第5个字节:\x02 :元素的类型,即"world"的类型是string,string类型 = 长度 + 内容 + '\0',注意,这里指的是"world"的类型。
hello\x00 : 元素的名字,以"\0"结尾,在这里,元素的名字是hello。注意元素的名字是CString类型,不是String类型。即元素的名字是没有长度信息的。
x06\x00\x00\x00 : string类型的长度
world\x00 : string的内容和结尾的'\0'
最后一个"\x00" : 文档的结尾
示例2:
{"BSON": ["awesome", 5.05, 1986]}
"1\x00\x00\x00\x04BSON\x00&\x00\x00\x00\x020\x00\x08\x00\x00\x00awesome\x00\x011\x00333333\x14@\x102\x00\xc2\x07\x00\x00\x00\x00"
1\x00\x00\x00 : 文档的长度
第5个字节\x04 : 元素的类型,\x04,即数组类型
BSON\x00 : 元素的名字,以"\0"结尾,在这里,元素的名字是BSON
&\x00\x00\x00 : 数组即一个子文档,子文档的长度,这里子文档实际上是{"0":"awesome","1":5.05,"2":1986}
\x02 : 元素的类型,即"awesome"的类型是string
0\x00 : 即"0"'\0',即元素的名字是"0",字符串以'\0'结尾
\x08\x00\x00\x00awesome\x00 : 长度 + "awesome" + '\0'
\x01 : 元素的类型,即5.05的类型是Floating point
1\x00 : 即"1"'\0',即元素的名字是"1"
333333\x14@ : 即5.05
\x10 : 元素的类型,即1986的类型是32-bit Integer
2\x00 : 即"2"'\0',即元素的名字是"2"
\xc2\x07\x00\x00 : 即1986
\x00 : 子文档,即数组的结尾
\x00 : 文档的结尾
Go驱动
一般mongodb的Go驱动都实现了bson的支持,下面以gopkg.in/mgo.v2/bson为例说明。
文档参考:https://godoc.org/gopkg.in/mgo.v2/bson,常用Marshal/Unmarshal/type M。
type M map[string]interface{}
M is a convenient alias for a map[string]interface{} map, useful for dealing with BSON in a native way. For instance:
bson.M{"a": 1, "b": true}
There's no special handling for this type in addition to what's done anyway for an equivalent map type. Elements in the map will be dumped in an undefined ordered.
package main import ( "fmt" "gopkg.in/mgo.v2/bson" ) type Person struct { Name string Phone string ",omitempty" } func main() { data, err := bson.Marshal(&Person{Name:"Bob"}) if err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Printf("%q", data) }
//type Reading struct {
// Created int64 `bson:"created" json:"created"`
// Modified int64 `bson:"modified" json:"modified"`
// Origin int64 `bson:"origin" json:"origin"`
// Uuid string `bson:"uuid" json:"uuid"`
// Pushed int64 `bson:"pushed" json:"pushed"`
// Device string `bson:"device" json:"device"`
// Name string `bson:"name" json:"name"`
// Value string `bson:"value" json:"value"`
//}
// date := next.AddDate(0, 0, 0-days)
// t := date.UnixNano() / 1e6
// selector := bson.M{"origin": bson.M{"$lte": t}}
// info, err := configCol.RemoveAll(selector)
与JSON比较
与JSON相比,BSON着眼于提高存储和扫描效率。BSON文档中的大型元素以长度字段为前缀以便于扫描。在某些情况下,由于长度前缀和显式数组索引的存在,BSON使用的空间会多于JSON。
BSON主要会实现以下三点目标:
(1)更快的遍历速度
对JSON格式来说,太大的JSON结构会导致数据遍历非常慢。在JSON中,要跳过一个文档进行数据读取,需要对此文档进行扫描才行,需要进行麻烦的数据结构匹配,比如括号的匹配,而BSON对JSON的一大改进就是,它会将JSON的每一个元素的长度存在元素的头部,这样你只需要读取到元素长度就能直接seek到指定的点上进行读取了。
(2)操作更简易
对JSON来说,数据存储是无类型的,比如你要修改基本一个值,从9到10,由于从一个字符变成了两个,所以可能其后面的所有内容都需要往后移一位才可以。而使用BSON,你可以指定这个列为数字列,那么无论数字从9长到10还是100,我们都只是在存储数字的那一位上进行修改,不会导致数据总长变大。当然,在MongoDB中,如果数字从整形增大到长整型,还是会导致数据总长变大的。
(3)增加了额外的数据类型
JSON是一个很方便的数据交换格式,但是其类型比较有限。BSON在其基础上增加了“byte array”数据类型。这使得二进制的存储不再需要先base64转换后再存成JSON。大大减少了计算开销和数据大小。
但是,在有的时候,BSON相对JSON来说也并没有空间上的优势,比如对{“field”:7},在JSON的存储上7只使用了一个字节,而如果用BSON,那就是至少4个字节(32位)
综上所述:
数据结构: json是像字符串一样存储的,bson是按结构存储的(像数组或者说struct)
存储空间:bson>json
操作速度:bson>json。比如,遍历查找:json需要扫字符串,而bson可以直接定位
修改: json也要大动大移,bson就不需要。
参考:
1. http://bsonspec.org/ 官网
2. http://bsonspec.org/spec.html
3. https://blog.csdn.net/z69183787/article/details/26709505


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号