css40 CSS Counters
https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_counters.asp
CSS counters are "variables" maintained by CSS whose values can be incremented by CSS rules (to track how many times they are used). Counters let you adjust the appearance of content based on its placement in the document.
Automatic Numbering With Counters
CSS counters are like "variables". The variable values can be incremented by CSS rules (which will track how many times they are used).
To work with CSS counters we will use the following properties:
counter-reset- Creates or resets a countercounter-increment- Increments a counter valuecontent- Inserts generated contentcounter()orcounters()function - Adds the value of a counter to an element
To use a CSS counter, it must first be created with counter-reset.
The following example creates a counter for the page (in the body selector), then increments the counter value for each <h2> element and adds "Section <value of the counter>:" to the beginning of each <h2> element:
Example
body {
counter-reset: section;
}
h2::before {
counter-increment: section;
content: "Section " counter(section) ": ";
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
counter-reset: section;
}
h2::before {
counter-increment: section;
content: "Section " counter(section) ": ";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Using CSS Counters</h1>
<h2>HTML Tutorial</h2>
<h2>CSS Tutorial</h2>
<h2>JavaScript Tutorial</h2>
<h2>Python Tutorial</h2>
<h2>SQL Tutorial</h2>
</body>
</html>

Nesting Counters
The following example creates one counter for the page (section) and one counter for each <h1> element (subsection). The "section" counter will be counted for each <h1> element with "Section <value of the section counter>.", and the "subsection" counter will be counted for each <h2> element with "<value of the section counter>.<value of the subsection counter>":
Example
body {
counter-reset: section;
}
h1 {
counter-reset: subsection;
}
h1::before {
counter-increment:
section;
content: "Section " counter(section) ". ";
}
h2::before {
counter-increment: subsection;
content:
counter(section) "." counter(subsection) " ";
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {
counter-reset: section;
}
h1 {
counter-reset: subsection;
}
h1::before {
counter-increment: section;
content: "Section " counter(section) ". ";
}
h2::before {
counter-increment: subsection;
content: counter(section) "." counter(subsection) " ";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>HTML/CSS Tutorials</h1>
<h2>HTML</h2>
<h2>CSS</h2>
<h2>Bootstrap</h2>
<h2>W3.CSS</h2>
<h1>Scripting Tutorials</h1>
<h2>JavaScript</h2>
<h2>jQuery</h2>
<h2>React</h2>
<h1>Programming Tutorials</h1>
<h2>Python</h2>
<h2>Java</h2>
<h2>C++</h2>
</body>
</html>

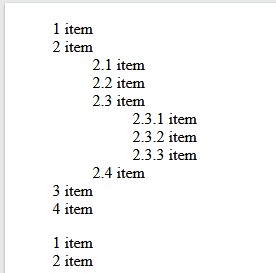
A counter can also be useful to make outlined lists because a new instance of a counter is automatically created in child elements. Here we use the counters() function to insert a string between different levels of nested counters:
Example
ol {
counter-reset: section;
list-style-type: none;
}
li::before {
counter-increment: section;
content: counters(section,".") " ";
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
ol {
counter-reset: section;
list-style-type: none;
}
li::before {
counter-increment: section;
content: counters(section,".") " ";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li>item</li>
<li>item
<ol>
<li>item</li>
<li>item</li>
<li>item
<ol>
<li>item</li>
<li>item</li>
<li>item</li>
</ol>
</li>
<li>item</li>
</ol>
</li>
<li>item</li>
<li>item</li>
</ol>
<ol>
<li>item</li>
<li>item</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>
CSS Counter Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| content | Used with the ::before and ::after pseudo-elements, to insert generated content |
| counter-increment | Increments one or more counter values |
| counter-reset | Creates or resets one or more counters |
| counter() | Returns the current value of the named counter |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号