HTML 06 - Formatting
If you use a word processor, you must be familiar /fəˈmɪliə(r)/ with the ability to make text bold, italicized /ɪˈtælɪsaɪzd/, or underlined; these are just three of the ten options available to indicate how text can appear in HTML.
Bold Text 粗体,加粗
Any content enclosed within <b>...</b> element, is displayed in bold as shown in the example below −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Bold Text Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>The following word uses a <b>bold</b> typeface.</p>
</body>
</html>
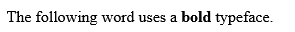
Italic /ɪˈtælɪk/ Text 斜体
Any content that is enclosed within <i>...</i> element is displayed in italicized /ɪˈtælɪsaɪzd/ as shown in the example below −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Italic Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>The following word uses a <i>italicized</i> typeface.</p> </body> </html>
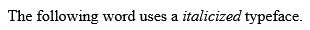
Underlined Text 下划线
Any content enclosed within <u>...</u> element, is displayed with underline as shown in the example below −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Underlined Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>The following word uses a <u>underlined</u> typeface.</p> </body> </html>

This will produce the output with an underline in the selected text.
Strike Text 中划线,删除线
Any content that is enclosed within <strike>...</strike> element is displayed with strikethrough 删除线, which is a thin line through the text as shown in the example below −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Strike Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>The following word uses a <strike>strikethrough</strike> typeface.</p> </body> </html>
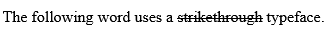
We can also use <s>...</s> element for the same.
Monospaced Font 等宽字体(相同宽度的字体)
The content enclosed within <tt>...</tt> element is written in monospaced font. Most of the fonts are known as variable-width fonts because different letters are of different widths (for example, the letter 'm' is wider than the letter 'i'). In a monospaced font, however, each letter has the same width.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Monospaced Font Example</title> </head> <body> <p>The following word uses a <tt>monospaced</tt> typeface.</p> </body> </html>
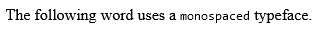
Superscript Text /ˈsuːpəskrɪpt; ˈsjuːpəskrɪpt/ 上标
The content enclosed within <sup>...</sup> element is written in superscript; the font size used is the same size as the characters surrounding it but is displayed at half the height of the surrounding characters, giving it a smaller and slightly raised appearance compared to the rest of the text.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Superscript Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>The following word uses a <sup>superscript</sup> typeface. </p> </body> </html>

Subscript Text /ˈsʌbskrɪpt/ 下标
The content of a <sub>...</sub> element is written in subscript; the font size used is the same as the characters surrounding it and is displayed half a character's height beneath the other characters. It is typically used for writing things like chemical formulas, where certain characters need to be displayed below the regular text line.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Subscript Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>The following word uses a <sub>subscript</sub> typeface. </p> </body> </html>

Inserted Text 插入(underlined,u)
Content that is enclosed within <ins>...</ins> element is displayed as inserted text. Below is an example for that −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Inserted Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>I want to drink <del>cola</del> <ins>wine</ins></p> </body> </html>
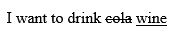
If you run the above example the word "cola" will be deleted and "wine" will be inserted.
Deleted Text 删除,strikethrough,strike
Content that is enclosed within <del>...</del> element, is displayed as deleted text. Below is an example for that −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Deleted Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>Hello welcome to <del>Madras</del> <ins>Chennai</ins></p> </body> </html>
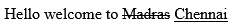
If you run the above example the word "Madras" will be deleted and "Chennai" will be inserted.
Larger Text 更大的
The content which is enclosed within <big>...</big> element is displayed one font size larger than the rest of the text surrounding it as shown below −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Larger Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>Hello Welcome to <big>Tutorialspoint</big>.</p> </body> </html>
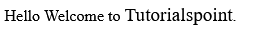
Since we have enclosed Tutorialspoint in the <big> tag it will be appeared in a larger font.
Smaller Text 更小的
The content which is enclosed within <small>...</small> element is displayed one font size smaller than the rest of the text surrounding it as shown below −
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Smaller Text Example</title> </head> <body> <p>Hello Welcome to <small>Tutorialspoint</small>.</p> </body> </html>
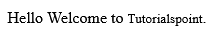
Since we have enclosed Tutorialspoint in the <small> tag it will be appeared in a smaller font.
Grouping Content 分组(group)
The <div> and <span> elements allow you to group together several elements to create sections or subsections of a page.
For example, you might want to put all of the footnotes on a page within a <div> element to indicate that all of the elements within that <div> element relate to the footnotes. You might then attach a style to this <div> element so that it appears using a special set of style rules.
div,p -- block element
span -- inline element
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Div Tag Example</title> </head> <body> <div id="menu" align="middle"> <a href="/index.htm">HOME</a> | <a href="/about/contact_us.htm">CONTACT</a> | <a href="/about/index.htm">ABOUT</a> </div> <div id="content" align="left" bgcolor="white"> <h5>Content Articles</h5> <p>Actual content goes here.....</p> </div> </body> </html>

The <span> element, on the other hand, can be used to group inline elements only. So, if you have a part of a sentence or paragraph which you want to group together, you could use the <span> element as follows
Example
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Span Tag Example</title> </head> <body> <p>This is the example of <span style="color:green">span tag</span> and the <span style="color:red">div tag</span> alongwith CSS</p> </body> </html>
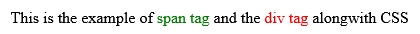


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号