pybedtools 安装和使用 难用且坑多,一定要检查结果
REF https://daler.github.io/pybedtools/search.html?q=cat
示例数据:
# more /python3.8/site-packages/pybedtools/test/data/a.bed
chr1 1 100 feature1 0 +
chr1 100 200 feature2 0 +
chr1 150 500 feature3 0 -
chr1 900 950 feature4 0 +
more /python3.8/site-packages/pybedtools/test/data/b.bed
chr1 155 200 feature5 0 -
chr1 800 901 feature6 0 +
a = pybedtools.example_bedtool('a.bed')
b = pybedtools.example_bedtool('b.bed')
a_and_b = a.intersect(b)
(a - b).head()
通过pip 安装
pip install pybedtools
由文件创建BedTool对象
test = pybedtools.BedTool('test.bed')
pybedtools.BedTool( ).sort().merge()
查看前几行数据
>>> a.head()
chr1 1 100 feature1 0 +
chr1 100 200 feature2 0 +hg38_windows.head()
有时head() 可以显示数据,有时不能显示数据。
通过把bedtool保存为bed文件,然后再load,这样就可以用 head()。
intersect 取交集,
不同参数结果输出不同的区域,A和B是输入的两个BED文件。不输入参数输出结果为两个BED文件的交集,-wa保留和b文件有重叠的全部A文件区域,-v 输出结果为-wa的补集,即B中没有A重叠的区域。可以用图表示为:
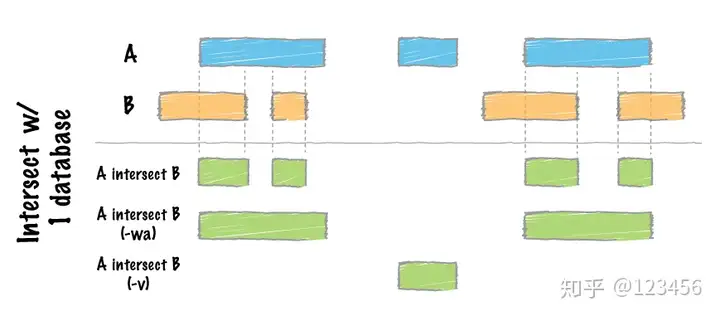
a = pybedtools.example_bedtool('a.bed')
b = pybedtools.example_bedtool('b.bed')
a_and_b = a.intersect(b)
filter
BedTool.filter() 可以对BedTool 对象进行过滤。传递一个函数,其接收的第一个参数是一个Interval. 返回True/False来进行过滤。
a = pybedtools.example_bedtool('a.bed')
b = a.filter(lambda x: len(x) > 100)
print(b)
# chr1 150 500 feature3 0 -
bed= BedTool(bedfile)
filtered = bed.filter(lambda a: a.name in snp_list)bed = bed.filter(lambda r: r.chrom == chrom)
iltered_ref = full_ref.filter(lambda gtf: gtf[2] == args.feature)self.bedtool.filter(lambda x : x[0] == 'chr' + str(int(chrnum))).saveas()
saveas
bed.saveas('/Users/huan/bed/test_w100.bed')
sort
第一列升序排序(按照字符;染色体号),第二列按照数字排序(起始位置);
bedtools merge requires that you presort your data by chromosome and then by start position (e.g., sort -k1,1 -k2,2n in.bed > in.sorted.bed for BED files).
这个命令这样写也许看的更清楚些: sort -k 1,1 -k 2,2n input.bed > input_sorted.bed
主要有两个参数 -n 和 -k;
其中 -n 的意思是按照数值大小排序。(-n 参数在 2,2 后面, 它仅对第二列有效)
其中 -k 的意思是指定排序的列(域),比如说 -k 1,1 表示仅仅对第一列有效, -k 2,2n 表示仅仅对第二列按照数字排序
其中 -t 的意思是指定行分隔符, 这里应该是 -t $'\t', 因为默认的也是, 所以可以省略。
cat
串联(串接)各个区段(比如: 1-100, 101-200, cat串联为 1-200; 1-150,100-200,串接为 1-200)。
Concatenate interval files together.
Concatenates two BedTool objects (or an object and a file) and does an optional post-merge of the features.
postmerge=True by default; use postmerge=False if you want to keep features separate.
force_truncate=False by default; force_truncate=True to truncate all files to chrom, start, stop.
When force_truncate=False and postmerge=False, the output will contain the smallest number of fields observed across all inputs. This maintains compatibility with BEDTools programs, which assume constant number of fields in all lines of a file.
Other kwargs are sent to BedTool.merge() (and assuming that postmerge=True).
a = pybedtools.example_bedtool('a.bed') b = pybedtools.example_bedtool('b.bed') print(a.cat(b)) chr1 1 500 chr1 800 950 print(a.cat(*[b,b], postmerge=False)) chr1 1 100 feature1 0 + chr1 100 200 feature2 0 + chr1 150 500 feature3 0 - chr1 900 950 feature4 0 + chr1 155 200 feature5 0 - chr1 800 901 feature6 0 + chr1 155 200 feature5 0 - chr1 800 901 feature6 0 +
REF: https://daler.github.io/pybedtools/autodocs/pybedtools.bedtool.BedTool.cat.html
https://daler.github.io/pybedtools/autodocs/pybedtools.bedtool.BedTool.cat.html
each
BedTool.each()也是将函数应用于每个Interval, 但主要是对Interval进行修改。
slop
Add requested base pairs of "slop" to each feature. 给每个feature添加指定的base paire。
REF: https://bedtools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/content/tools/slop.html
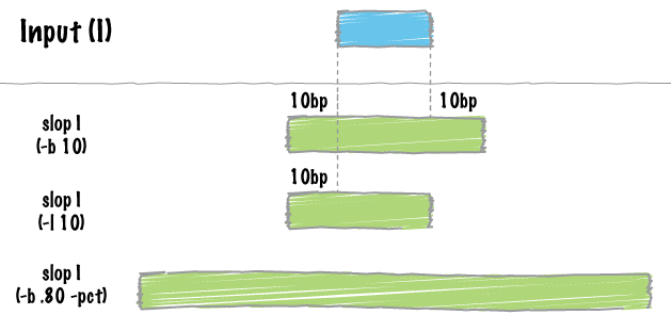

-b 10 , both 两侧加10个碱基长度
-l 10, left 左侧加10个碱基
-b 80 both两侧加80个碱基
Usage and option summary
Usage:
bedtools slop [OPTIONS] -i <BED/GFF/VCF> -g <GENOME> [-b or (-l and -r)]
(or):
slopBed [OPTIONS] -i <BED/GFF/VCF> -g <GENOME> [-b or (-l and -r)]
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -b | Increase the BED/GFF/VCF entry by the same number base pairs in each direction. Integer. |
| -l | The number of base pairs to subtract from the start coordinate. Integer. |
| -r | The number of base pairs to add to the end coordinate. Integer. |
| -s | Define -l and -r based on strand. For example. if used, -l 500 for a negative-stranded feature, it will add 500 bp to the end coordinate. |
| -pct | Define -l and -r as a fraction of the feature’s length. E.g. if used on a 1000bp feature, -l 0.50, will add 500 bp “upstream”. Default = false. |
| -header | Print the header from the input file prior to results. |
Notes:
(1) Starts will be set to 0 if options would force it below 0.
(2) Ends will be set to the chromosome length if requested slop would
force it above the max chrom length.
(3) The genome file should tab delimited and structured as follows:
<chromName><TAB><chromSize>
For example, Human (hg19):
chr1 249250621
chr2 243199373
...
chr18**gl000207**random 4262
Tips:
One can use the UCSC Genome Browser's MySQL database to extract
chromosome sizes. For example, H. sapiens:
mysql --user=genome --host=genome-mysql.cse.ucsc.edu -A -e \
"select chrom, size from hg19.chromInfo" > hg19.genome
Default behavior
By default, bedtools slop will either add a fixed number of bases in each direction (-b) or an asymmetric number of bases in each direction with -l and -r.
$ cat A.bed
chr1 5 100
chr1 800 980
$ cat my.genome
chr1 1000
$ bedtools slop -i A.bed -g my.genome -b 5
chr1 0 105
chr1 795 985
$ bedtools slop -i A.bed -g my.genome -l 2 -r 3
chr1 3 103
chr1 798 983
However, if the requested number of bases exceeds the boundaries of the chromosome, bedtools slop will “clip” the feature accordingly.
$ cat A.bed
chr1 5 100
chr1 800 980
$ cat my.genome
chr1 1000
$ bedtools slop -i A.bed -g my.genome -b 5000
chr1 0 1000
chr1 0 1000
-s Resizing features according to strand
bedtools slop will optionally increase the size of a feature based on strand.
For example:
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200 a1 1 +
chr1 100 200 a2 2 -
$ cat my.genome
chr1 1000
$ bedtools slop -i A.bed -g my.genome -l 50 -r 80 -s
chr1 50 280 a1 1 +
chr1 20 250 a2 2 -
-pct Resizing features by a given fraction
bedtools slop will optionally increase the size of a feature by a user-specific fraction.
For example:
$ cat A.bed
chr1 100 200 a1 1 +
$ bedtools slop -i A.bed -g my.genome -b 0.5 -pct
chr1 50 250 a1 1 +
$ bedtools slop -i a.bed -l 0.5 -r 0.0 -pct -g my.genome
chr1 50 200 a1 1 +
-header Print the header for the A file before reporting results.
By default, if your A file has a header, it is ignored when reporting results. This option will instead tell bedtools to first print the header for the A file prior to reporting results.
pybedtools window_maker
把整个输入的genome都划分为一个个window,用户要指定window大小,默认按照step=window size滑动窗口。
There are two alternatives for supplying a genome. Use g="genome.filename" if you have a genome’s chrom sizes saved as a file. This is the what BEDTools expects when using it from the command line. Alternatively, use the genome="assembly.name" (for example, genome="hg19") to use chrom sizes for that assembly without having to manage a separate file. The genome argument triggers a call pybedtools.chromsizes, so see that method for more details.
REF https://daler.github.io/pybedtools/autodocs/pybedtools.bedtool.BedTool.window_maker.html
Tool: bedtools makewindows Version: v2.30.0 Summary: Makes adjacent or sliding windows across a genome or BED file. Usage: bedtools makewindows [OPTIONS] [-g <genome> OR -b <bed>] [ -w <window**size> OR -n <number of windows> ] Input Options: -g <genome> Genome file size (see notes below). Windows will be created for each chromosome in the file. -b <bed> BED file (with chrom,start,end fields). Windows will be created for each interval in the file. Windows Output Options: -w <window**size> Divide each input interval (either a chromosome or a BED interval) to fixed-sized windows (i.e. same number of nucleotide in each window). Can be combined with -s <step**size> -s <step**size> Step size: i.e., how many base pairs to step before creating a new window. Used to create "sliding" windows. - Defaults to window size (non-sliding windows). -n <number**of**windows> Divide each input interval (either a chromosome or a BED interval) to fixed number of windows (i.e. same number of windows, with varying window sizes). -reverse Reverse numbering of windows in the output, i.e. report windows in decreasing order ID Naming Options: -i src|winnum|srcwinnum The default output is 3 columns: chrom, start, end . With this option, a name column will be added. "-i src" - use the source interval's name. "-i winnum" - use the window number as the ID (e.g. 1,2,3,4...). "-i srcwinnum" - use the source interval's name with the window number. See below for usage examples. Notes: (1) The genome file should tab delimited and structured as follows: <chromName><TAB><chromSize> For example, Human (hg19): chr1 249250621 chr2 243199373 ... chr18**gl000207**random 4262 Tips: One can use the UCSC Genome Browser's MySQL database to extract chromosome sizes. For example, H. sapiens: mysql --user=genome --host=genome-mysql.cse.ucsc.edu -A -e \ "select chrom, size from hg19.chromInfo" > hg19.genome Examples: # Divide the human genome into windows of 1MB: $ bedtools makewindows -g hg19.txt -w 1000000 chr1 0 1000000 chr1 1000000 2000000 chr1 2000000 3000000 chr1 3000000 4000000 chr1 4000000 5000000 ... # Divide the human genome into sliding (=overlapping) windows of 1MB, with 500KB overlap: $ bedtools makewindows -g hg19.txt -w 1000000 -s 500000 chr1 0 1000000 chr1 500000 1500000 chr1 1000000 2000000 chr1 1500000 2500000 chr1 2000000 3000000 ... # Divide each chromosome in human genome to 1000 windows of equal size: $ bedtools makewindows -g hg19.txt -n 1000 chr1 0 249251 chr1 249251 498502 chr1 498502 747753 chr1 747753 997004 chr1 997004 1246255 ... # Divide each interval in the given BED file into 10 equal-sized windows: $ cat input.bed chr5 60000 70000 chr5 73000 90000 chr5 100000 101000 $ bedtools makewindows -b input.bed -n 10 chr5 60000 61000 chr5 61000 62000 chr5 62000 63000 chr5 63000 64000 chr5 64000 65000 ... # Add a name column, based on the window number: $ cat input.bed chr5 60000 70000 AAA chr5 73000 90000 BBB chr5 100000 101000 CCC $ bedtools makewindows -b input.bed -n 3 -i winnum chr5 60000 63334 1 chr5 63334 66668 2 chr5 66668 70000 3 chr5 73000 78667 1 chr5 78667 84334 2 chr5 84334 90000 3 chr5 100000 100334 1 chr5 100334 100668 2 chr5 100668 101000 3 ... # Reverse window numbers: $ cat input.bed chr5 60000 70000 AAA chr5 73000 90000 BBB chr5 100000 101000 CCC $ bedtools makewindows -b input.bed -n 3 -i winnum -reverse chr5 60000 63334 3 chr5 63334 66668 2 chr5 66668 70000 1 chr5 73000 78667 3 chr5 78667 84334 2 chr5 84334 90000 1 chr5 100000 100334 3 chr5 100334 100668 2 chr5 100668 101000 1 ... # Add a name column, based on the source ID + window number: $ cat input.bed chr5 60000 70000 AAA chr5 73000 90000 BBB chr5 100000 101000 CCC $ bedtools makewindows -b input.bed -n 3 -i srcwinnum chr5 60000 63334 AAA**1 chr5 63334 66668 AAA**2 chr5 66668 70000 AAA**3 chr5 73000 78667 BBB**1 chr5 78667 84334 BBB**2 chr5 84334 90000 BBB**3 chr5 100000 100334 CCC**1 chr5 100334 100668 CCC**2 chr5 100668 101000 CCC**3 ...
window_maker 示例:
w = BedTool.window_maker(BedTool(), b=bedtool, w=windowWidth, s=step)
features = pybedtools.BedTool().window_maker( genome='hg19', w=windowsize)
features = pybedtools.BedTool()\
.window_maker(genome='hg19', w=WINDOWSIZE)\
.filter(lambda x: x.chrom == 'chr19')
pybedtools.BedTool().window_maker(genome="hg38", w=args.window_size)
pybedtools.BedTool().window_maker(w=params["parallel_window_size"],
b=pybedtools.BedTool(variant_regions)).saveas(tx_out_file)
windows = window.window_maker(genome='hg19', w=args.window_size, s=args.step_size)
Usage
1 2 3 |
bedtools_makewindows(cmd = "--help")
R_bedtools_makewindows(b, g = NA_character_, w, s, n)
do_bedtools_makewindows(b, g = NA_character_, w, s, n)
|
Arguments
cmd |
String of bedtools command line arguments, as they would be entered at the shell. There are a few incompatibilities between the docopt parser and the bedtools style. See argument parsing. |
b |
Path to a BAM/BED/GFF/VCF/etc file, a BED stream, a file object, or a ranged data structure, such as a GRanges. Use |
g |
A genome file, identifier or Seqinfo object that defines the order and size of the sequences. Specifying this generates windows over the genome. Exclusive with |
w |
Window size, exclusive with |
s |
Step size (generates sliding windows). |
n |
Number of windows, exclusive with |
https://rdrr.io/bioc/HelloRanges/man/bedtools_makewindows.html
merge() 合并坐标区间
x1 = a.intersect(b, u=True)
x2 = x1.merge()注意:合并之前必须先排序sort。
将一个BED文件中所有的重叠区域和相邻merge为一个大的区域,可以将结果转换为其他格式的数据,可以通过参数设置相距多远的两个区域,可以取他们的并集:
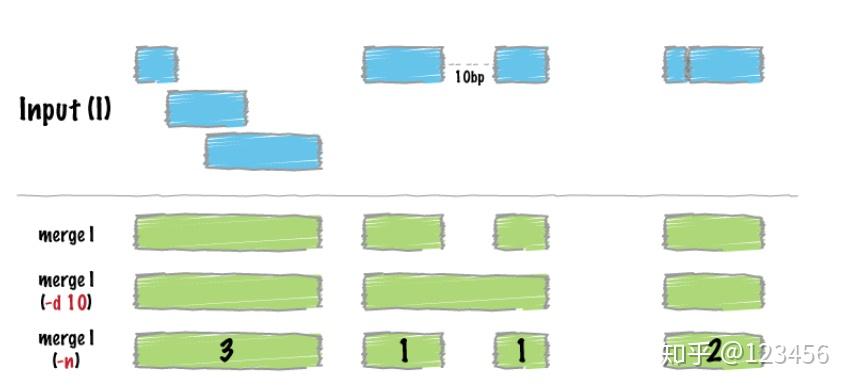
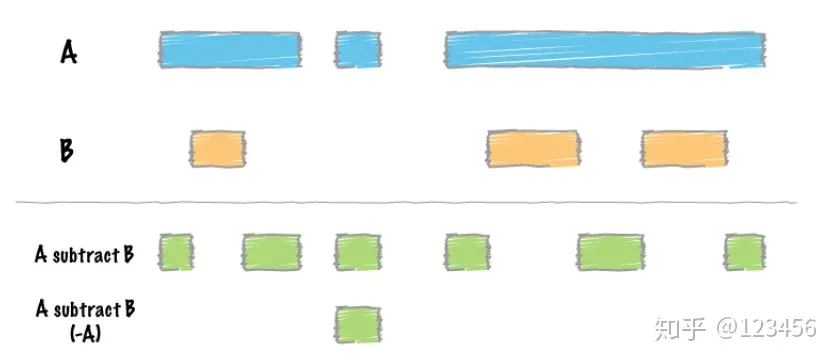
差集运算,用A中的区域减去B中的区域,通过参数-A可以实现有重叠区域的全部剔除:
pybedtools.BedTool( "HaHa.bed").sort().merge(c=5, o="mean")
Original BEDTools help::
Tool: bedtools merge (aka mergeBed)
Version: v2.30.0
Summary: Merges overlapping BED/GFF/VCF entries into a single interval.
Usage: bedtools merge [OPTIONS] -i <bed/gff/vcf>
Options:
-s Force strandedness. That is, only merge features
that are on the same strand.
- By default, merging is done without respect to strand.
-S Force merge for one specific strand only.
Follow with + or - to force merge from only
the forward or reverse strand, respectively.
- By default, merging is done without respect to strand.
-d Maximum distance between features allowed for features
to be merged.
- Def. 0. That is, overlapping & book-ended features are merged.
- (INTEGER)
- Note: negative values enforce the number of b.p. required for overlap.
-c Specify columns from the B file to map onto intervals in A.
Default: 5.
Multiple columns can be specified in a comma-delimited list.
-o Specify the operation that should be applied to -c.
Valid operations:
sum, min, max, absmin, absmax,
mean, median, mode, antimode
stdev, sstdev
collapse (i.e., print a delimited list 