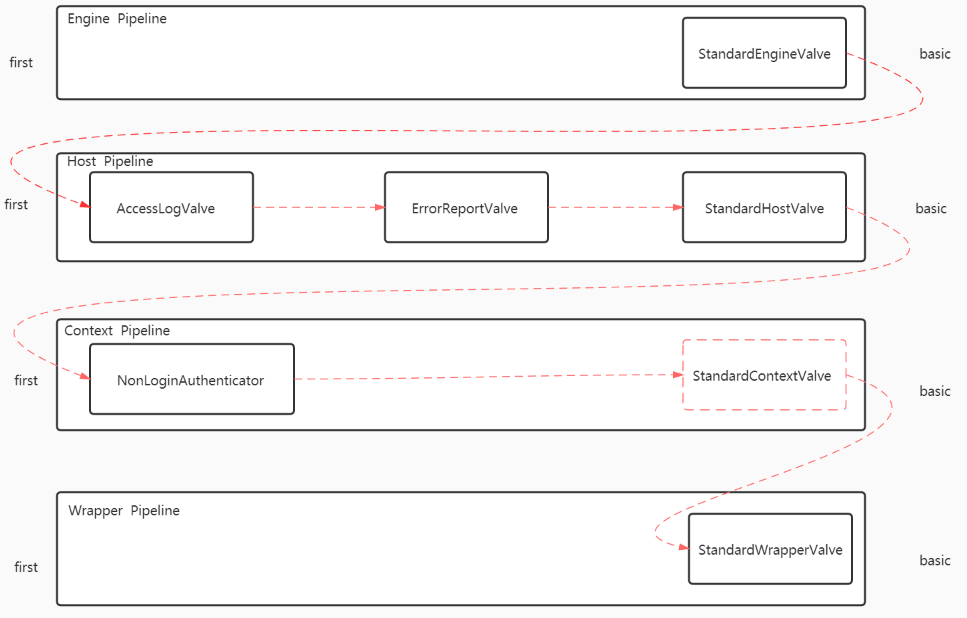
tomcat8.5.57源码阅读笔记5.1 - 管道
上一篇终于找到了调用管道方法的地方, 代码片段:
//org/apache/catalina/connector/CoyoteAdapter#service // Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific // request parameters 在 Map 中解析请求 postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response); if (postParseSuccess) { //check valves if we support async //getContainer() -> StandardEngine request.setAsyncSupported( connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); // Calling the container // 调用 StandardEngineValve#invoke(), 开始执行管道方法. (责任链模式) // 如果有多个 valve , 这里 getFirst() 拿到的就是 first valve, // 然后在 first valve中, 需要调用 getNext().invoke(request, response) 来传递 connector.getService() // --> StandardService .getContainer() // --> StandardEngine .getPipeline() // --> StandardPipeLine .getFirst() //获取优先级: first > basic .invoke(request, response); }
1. 从代码上看, 只获取了 first, 那说好的很多阀门呢? 带着疑问, 只能去看一下 StandardPipeLine 的阀门.
2. 默认情况下, 这里的getFirst() 获取到的是 StandardEngineValve, 其实他是 basic.
StandardPipeLine
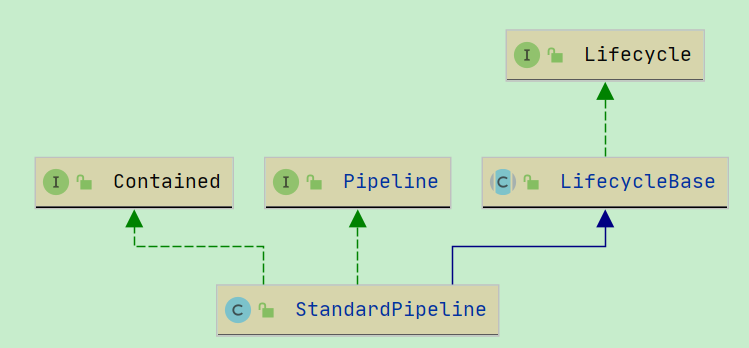
他有两个 阀门属性:
1. basic -- 末位阀门
2. first -- 首尾阀门
除此之外, 没找到任何阀门属性了. 没办法, 只能接着看看阀门
Valve
Valve 里面定义了两个方法:
1. public Valve getNext()
2. public void setNext(Valve valve)
看到这里, 总算明白了, 原来阀门本身, 也是一个指针, 指向了下一个阀门的位置. 使用阀门, 可以组成一个单向链表.
addValve()
明白了阀门是指针之后, 还需要知道, 增加阀门时的顺序, 所以必须看一下 addValve() 方法.
/** * 加入valve时, 会放到basic最近的位子上, 具体分两种情况: * 1. first为空, 则放在first上 : first -> basic * 2. first不为空, 则放在离basic最近的位子上 * first -> v1 -> v2 -> basic , 此时要插入 v3, 结果是: first -> v1 -> v2 -> v3 -> basic*/ @Override public void addValve(Valve valve) { // Validate that we can add this Valve if (valve instanceof Contained) ((Contained) valve).setContainer(this.container); // Start the new component if necessary if (getState().isAvailable()) { if (valve instanceof Lifecycle) { try { ((Lifecycle) valve).start(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { log.error(sm.getString("standardPipeline.valve.start"), e); } } } // Add this Valve to the set associated with this Pipeline if (first == null) { first = valve; valve.setNext(basic); } else { Valve current = first; while (current != null) { if (current.getNext() == basic) { current.setNext(valve); valve.setNext(basic); break; } current = current.getNext(); } } container.fireContainerEvent(Container.ADD_VALVE_EVENT, valve); }
初始状态下, first 是空的, 所有的阀门, 在新增的时候, 都是紧挨着basic的位置放的.
getFirst()
/** * 拿取优先级:(有头拿头, 没头拿尾) * 1. first存在, 则返回first * 2. first不存在, 则返回 basic * @return */ @Override public Valve getFirst() { if (first != null) { return first; } return basic; }
在获取的时候, 当 first 为空时, 直接获取 basic , 说明此时只有一个阀门
当first 不为空时, 则会拿取 first , 然后需要在 调用阀门的时候, 进行传递.
StandardEngineValve
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Select the Host to be used for this Request Host host = request.getHost(); if (host == null) { response.sendError (HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost", request.getServerName())); return; } if (request.isAsyncSupported()) { request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); } // Ask this Host to process this request //调用 StandardHostValve#invoke() 方法 host.getPipeline() //-->StandardPipeline .getFirst() //--> AccessLogValve --> ErrorReportValve --> StandardHostValve .invoke(request, response); }
StandardEngineValve 作为管道的 basic(末位) , 肩负着调用子节点的管道方法. 这里启动了 StandardHostValve
AccessLogValve
//org.apache.catalina.valves.AbstractAccessLogValve#invoke public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { if (tlsAttributeRequired) { // The log pattern uses TLS attributes. Ensure these are populated // before the request is processed because with NIO2 it is possible // for the connection to be closed (and the TLS info lost) before // the access log requests the TLS info. Requesting it now causes it // to be cached in the request. request.getAttribute(Globals.CERTIFICATES_ATTR); } if (cachedElements != null) { for (CachedElement element : cachedElements) { element.cache(request); } } getNext().invoke(request, response); }
ErrorReportValve
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Perform the request getNext().invoke(request, response); if (response.isCommitted()) { if (response.setErrorReported()) { // Error wasn't previously reported but we can't write an error // page because the response has already been committed. Attempt // to flush any data that is still to be written to the client. try { response.flushBuffer(); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); } // Close immediately to signal to the client that something went // wrong response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.CLOSE_NOW, request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION)); } return; } Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); // If an async request is in progress and is not going to end once this // container thread finishes, do not process any error page here. if (request.isAsync() && !request.isAsyncCompleting()) { return; } if (throwable != null && !response.isError()) { // Make sure that the necessary methods have been called on the // response. (It is possible a component may just have set the // Throwable. Tomcat won't do that but other components might.) // These are safe to call at this point as we know that the response // has not been committed. response.reset(); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); } // One way or another, response.sendError() will have been called before // execution reaches this point and suspended the response. Need to // reverse that so this valve can write to the response. response.setSuspended(false); try { report(request, response, throwable); } catch (Throwable tt) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt); } }
这里是先进行了传递, 然后根据后面执行的结果, 再进行一些错误处理.
StandardHostValve
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Select the Context to be used for this Request. context --> StandardContext Context context = request.getContext(); if (context == null) { return; } if (request.isAsyncSupported()) { request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); } boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync(); try { context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER); //fireRequestInitEvent 最终会调用 Servlet 监听器 ServletRequestListener#requestInitialized() if (!asyncAtStart && !context.fireRequestInitEvent(request.getRequest())) { // Don't fire listeners during async processing (the listener // fired for the request that called startAsync()). // If a request init listener throws an exception, the request // is aborted. return; } // Ask this Context to process this request. Requests that are // already in error must have been routed here to check for // application defined error pages so DO NOT forward them to the the // application for processing. try { if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) { //StandardContextValve#invoke() context.getPipeline() //-->StandardPipeline .getFirst() //--> NonLoginAuthenticator --> StandardContextValve .invoke(request, response); } } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); container.getLogger().error("Exception Processing " + request.getRequestURI(), t); // If a new error occurred while trying to report a previous // error allow the original error to be reported. if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) { request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, t); throwable(request, response, t); } } // Now that the request/response pair is back under container // control lift the suspension so that the error handling can // complete and/or the container can flush any remaining data response.setSuspended(false); Throwable t = (Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION); // Protect against NPEs if the context was destroyed during a // long running request. if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) { return; } // Look for (and render if found) an application level error page if (response.isErrorReportRequired()) { // If an error has occurred that prevents further I/O, don't waste time // producing an error report that will never be read AtomicBoolean result = new AtomicBoolean(false); response.getCoyoteResponse().action(ActionCode.IS_IO_ALLOWED, result); if (result.get()) { if (t != null) { throwable(request, response, t); } else { status(request, response); } } } if (!request.isAsync() && !asyncAtStart) {
//最终会调用 Servlet 监听器 ServletRequestListener#requestDestroyed() context.fireRequestDestroyEvent(request.getRequest()); } } finally { // Access a session (if present) to update last accessed time, based // on a strict interpretation of the specification if (ACCESS_SESSION) { request.getSession(false); } context.unbind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER); } }
StandardHostValve 作为末位valve, 同样的, 肩负着启动子节点的管道.
NonLoginAuthenticator
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Security checking request " + request.getMethod() + " " + request.getRequestURI()); } // Have we got a cached authenticated Principal to record? if (cache) { Principal principal = request.getUserPrincipal(); if (principal == null) { Session session = request.getSessionInternal(false); if (session != null) { principal = session.getPrincipal(); if (principal != null) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("We have cached auth type " + session.getAuthType() + " for principal " + principal); } request.setAuthType(session.getAuthType()); request.setUserPrincipal(principal); } } } } boolean authRequired = isContinuationRequired(request); Realm realm = this.context.getRealm(); // Is this request URI subject to a security constraint? SecurityConstraint[] constraints = realm.findSecurityConstraints(request, this.context); AuthConfigProvider jaspicProvider = getJaspicProvider(); if (jaspicProvider != null) { authRequired = true; } if (constraints == null && !context.getPreemptiveAuthentication() && !authRequired) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Not subject to any constraint"); } getNext().invoke(request, response); return; } // Make sure that constrained resources are not cached by web proxies // or browsers as caching can provide a security hole if (constraints != null && disableProxyCaching && !"POST".equalsIgnoreCase(request.getMethod())) { if (securePagesWithPragma) { // Note: These can cause problems with downloading files with IE response.setHeader("Pragma", "No-cache"); response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache"); } else { response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "private"); } response.setHeader("Expires", DATE_ONE); } if (constraints != null) { // Enforce any user data constraint for this security constraint if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Calling hasUserDataPermission()"); } if (!realm.hasUserDataPermission(request, response, constraints)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Failed hasUserDataPermission() test"); } /* * ASSERT: Authenticator already set the appropriate HTTP status * code, so we do not have to do anything special */ return; } } // Since authenticate modifies the response on failure, // we have to check for allow-from-all first. boolean hasAuthConstraint = false; if (constraints != null) { hasAuthConstraint = true; for (int i = 0; i < constraints.length && hasAuthConstraint; i++) { if (!constraints[i].getAuthConstraint()) { hasAuthConstraint = false; } else if (!constraints[i].getAllRoles() && !constraints[i].getAuthenticatedUsers()) { String[] roles = constraints[i].findAuthRoles(); if (roles == null || roles.length == 0) { hasAuthConstraint = false; } } } } if (!authRequired && hasAuthConstraint) { authRequired = true; } if (!authRequired && context.getPreemptiveAuthentication()) { authRequired = request.getCoyoteRequest().getMimeHeaders().getValue("authorization") != null; } if (!authRequired && context.getPreemptiveAuthentication() && HttpServletRequest.CLIENT_CERT_AUTH.equals(getAuthMethod())) { X509Certificate[] certs = getRequestCertificates(request); authRequired = certs != null && certs.length > 0; } JaspicState jaspicState = null; if ((authRequired || constraints != null) && allowCorsPreflightBypass(request)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("CORS Preflight request bypassing authentication"); } getNext().invoke(request, response); return; } if (authRequired) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Calling authenticate()"); } if (jaspicProvider != null) { jaspicState = getJaspicState(jaspicProvider, request, response, hasAuthConstraint); if (jaspicState == null) { return; } } if (jaspicProvider == null && !doAuthenticate(request, response) || jaspicProvider != null && !authenticateJaspic(request, response, jaspicState, false)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Failed authenticate() test"); } /* * ASSERT: Authenticator already set the appropriate HTTP status * code, so we do not have to do anything special */ return; } } if (constraints != null) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Calling accessControl()"); } if (!realm.hasResourcePermission(request, response, constraints, this.context)) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Failed accessControl() test"); } /* * ASSERT: AccessControl method has already set the appropriate * HTTP status code, so we do not have to do anything special */ return; } } // Any and all specified constraints have been satisfied if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Successfully passed all security constraints"); } getNext().invoke(request, response); if (jaspicProvider != null) { secureResponseJspic(request, response, jaspicState); } }
这个阀门是进行tomcat身份验证的.
StandardContextValve
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Disallow any direct access to resources under WEB-INF or META-INF MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB(); if ((requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/META-INF/", 0)) || (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/META-INF")) || (requestPathMB.startsWithIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF/", 0)) || (requestPathMB.equalsIgnoreCase("/WEB-INF"))) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); return; } // Select the Wrapper to be used for this Request Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper(); if (wrapper == null || wrapper.isUnavailable()) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND); return; } // Acknowledge the request try { response.sendAcknowledgement(); } catch (IOException ioe) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString( "standardContextValve.acknowledgeException"), ioe); request.setAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION, ioe); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); return; } if (request.isAsyncSupported()) { request.setAsyncSupported(wrapper.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported()); } //StandardWrapperValve#invoke() wrapper.getPipeline() //-->StandardPipeline .getFirst() //-->StandardWrapperValve .invoke(request, response); }
StandardWrapperValve
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException { // Initialize local variables we may need boolean unavailable = false; Throwable throwable = null; // This should be a Request attribute... long t1=System.currentTimeMillis(); //增加请求次数 CAS乐观锁的方式 requestCount.incrementAndGet(); StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer(); Servlet servlet = null; Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent(); // Check for the application being marked unavailable if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable")); unavailable = true; } // Check for the servlet being marked unavailable if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) { container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); long available = wrapper.getAvailable(); if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) { response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); } else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound", wrapper.getName())); } unavailable = true; } // Allocate a servlet instance to process this request try { if (!unavailable) { servlet = wrapper.allocate(); } } catch (UnavailableException e) { container.getLogger().error( sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e); long available = wrapper.getAvailable(); if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) { response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); } else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound", wrapper.getName())); } } catch (ServletException e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e)); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (Throwable e) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.allocateException", wrapper.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); servlet = null; } MessageBytes requestPathMB = request.getRequestPathMB(); DispatcherType dispatcherType = DispatcherType.REQUEST; if (request.getDispatcherType()==DispatcherType.ASYNC) dispatcherType = DispatcherType.ASYNC; request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_TYPE_ATTR,dispatcherType); request.setAttribute(Globals.DISPATCHER_REQUEST_PATH_ATTR, requestPathMB); // Create the filter chain for this request // 创建过滤器链 ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet); // Call the filter chain for this request // NOTE: This also calls the servlet's service() method try { if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) { // Swallow output if needed if (context.getSwallowOutput()) { try { SystemLogHandler.startCapture(); if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch(); } else { //执行过滤链 filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse()); } } finally { String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture(); if (log != null && log.length() > 0) { context.getLogger().info(log); } } } else { if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch(); } else {
//执行过滤器链方法, 最终会执行 Servlet 的 service 方法 filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse()); } } } } catch (ClientAbortException | CloseNowException e) { if (container.getLogger().isDebugEnabled()) { container.getLogger().debug(sm.getString( "standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e); } throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (IOException e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString( "standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (UnavailableException e) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString( "standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e); // throwable = e; // exception(request, response, e); wrapper.unavailable(e); long available = wrapper.getAvailable(); if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) { response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available); response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); } else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound", wrapper.getName())); } // Do not save exception in 'throwable', because we // do not want to do exception(request, response, e) processing } catch (ServletException e) { Throwable rootCause = StandardWrapper.getRootCause(e); if (!(rootCause instanceof ClientAbortException)) { container.getLogger().error(sm.getString( "standardWrapper.serviceExceptionRoot", wrapper.getName(), context.getName(), e.getMessage()), rootCause); } throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } catch (Throwable e) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); container.getLogger().error(sm.getString( "standardWrapper.serviceException", wrapper.getName(), context.getName()), e); throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } finally { // Release the filter chain (if any) for this request if (filterChain != null) { //释放过滤链资源 filterChain.release(); } // Deallocate the allocated servlet instance try { if (servlet != null) { //会受到 Servlet 池例中 wrapper.deallocate(servlet); } } catch (Throwable e) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.deallocateException", wrapper.getName()), e); if (throwable == null) { throwable = e; exception(request, response, e); } } // If this servlet has been marked permanently unavailable, // unload it and release this instance try { if ((servlet != null) && (wrapper.getAvailable() == Long.MAX_VALUE)) { wrapper.unload(); } } catch (Throwable e) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e); container.getLogger().error(sm.getString("standardWrapper.unloadException", wrapper.getName()), e); if (throwable == null) { exception(request, response, e); } } long t2=System.currentTimeMillis(); long time=t2-t1; processingTime += time; if( time > maxTime) maxTime=time; if( time < minTime) minTime=time; } }
总结