BeanFactory后置处理器 - ConfigurationClassPostProcessor - full / lite
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
首先看看他的类的关系:
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware { }
接着看:
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor { void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException; }
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor { void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; }
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中看到, spring 是先处理 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, 再处理的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor.
他刚好都实现了这两个接口.
按照spring 的执行顺序, 首先看 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry 方法
postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry
@Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry); if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry); } if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry); } this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId); processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry); }
看主要方法 processConfigBeanDefinitions
/** * Build and validate a configuration model based on the registry of * {@link Configuration} classes. */ public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { //定义一个list存放app 提供的bd(项目当中提供了@Compent) List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>(); //获取容器中注册的所有bd名字 //6个 String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); /** * Full * Lite */ for (String beanName : candidateNames) { BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.isFullConfigurationClass(beanDef) || ConfigurationClassUtils.isLiteConfigurationClass(beanDef)) { //果BeanDefinition中的configurationClass属性为full或者lite,则意味着已经处理过了,直接跳过 //这里需要结合下面的代码才能理解 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Bean definition has already been processed as a configuration class: " + beanDef); } } //判断是否是Configuration类,如果加了Configuration下面的这几个注解就不再判断了 // 还有 add(Component.class.getName()); // candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName()); // candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName()); // candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName()); //beanDef == startConfig else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { //BeanDefinitionHolder 也可以看成一个数据结构 configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName)); } } // Return immediately if no @Configuration classes were found if (configCandidates.isEmpty()) { return; } // 排序,根据order,不重要 // Sort by previously determined @Order value, if applicable configCandidates.sort((bd1, bd2) -> { int i1 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd1.getBeanDefinition()); int i2 = ConfigurationClassUtils.getOrder(bd2.getBeanDefinition()); return Integer.compare(i1, i2); }); // Detect any custom bean name generation strategy supplied through the enclosing application context SingletonBeanRegistry sbr = null; //如果BeanDefinitionRegistry是SingletonBeanRegistry子类的话, // 由于我们当前传入的是DefaultListableBeanFactory,是SingletonBeanRegistry 的子类 // 因此会将registry强转为SingletonBeanRegistry if (registry instanceof SingletonBeanRegistry) { sbr = (SingletonBeanRegistry) registry; if (!this.localBeanNameGeneratorSet) {//是否有自定义的 BeanNameGenerator generator = (BeanNameGenerator) sbr.getSingleton(CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR); //SingletonBeanRegistry中有id为 org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator //如果有则利用他的,否则则是spring默认的 if (generator != null) { this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator = generator; this.importBeanNameGenerator = generator; } } } if (this.environment == null) { this.environment = new StandardEnvironment(); } // Parse each @Configuration class //实例化ConfigurationClassParser 为了解析各个配置类 ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser( this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry); //实例化2个set,candidates用于将之前加入的configCandidates进行去重 //因为可能有多个配置类重复了 //alreadyParsed用于判断是否处理过 Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates); Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size()); do { parser.parse(candidates); parser.validate(); //map.keyset Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses()); configClasses.removeAll(alreadyParsed); // Read the model and create bean definitions based on its content if (this.reader == null) { this.reader = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader( registry, this.sourceExtractor, this.resourceLoader, this.environment, this.importBeanNameGenerator, parser.getImportRegistry()); } /** * 这里值得注意的是扫描出来的bean当中可能包含了特殊类 * 比如ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar那么也在这个方法里面处理 * 但是并不是包含在configClasses当中 * configClasses当中主要包含的是importSelector * 因为ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar在扫描出来的时候已经被添加到一个list当中去了 */ //将 bd 放到 map this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses); alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses); candidates.clear(); //由于我们这里进行了扫描,把扫描出来的BeanDefinition注册给了factory if (registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() > candidateNames.length) { String[] newCandidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames(); Set<String> oldCandidateNames = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(candidateNames)); Set<String> alreadyParsedClasses = new HashSet<>(); for (ConfigurationClass configurationClass : alreadyParsed) { alreadyParsedClasses.add(configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); } for (String candidateName : newCandidateNames) { if (!oldCandidateNames.contains(candidateName)) { BeanDefinition bd = registry.getBeanDefinition(candidateName); if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bd, this.metadataReaderFactory) && !alreadyParsedClasses.contains(bd.getBeanClassName())) { candidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(bd, candidateName)); } } } candidateNames = newCandidateNames; } } while (!candidates.isEmpty()); // Register the ImportRegistry as a bean in order to support ImportAware @Configuration classes if (sbr != null && !sbr.containsSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME)) { sbr.registerSingleton(IMPORT_REGISTRY_BEAN_NAME, parser.getImportRegistry()); } if (this.metadataReaderFactory instanceof CachingMetadataReaderFactory) { // Clear cache in externally provided MetadataReaderFactory; this is a no-op // for a shared cache since it'll be cleared by the ApplicationContext. ((CachingMetadataReaderFactory) this.metadataReaderFactory).clearCache(); } }
这个方法主要是对配置类进行解析, 例如前面篇幅中的 StartConfig.class
通过解析可能会得到的一批类的定义 BeanDefinition(ComponentScan , Import)
然后将这些 bd , 通过 loadBeanDefinitions 方法, 注册到spring容器中
checkConfigurationClassCandidate
这个方法也是蛮重要的.
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate( BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) { String className = beanDef.getBeanClassName(); if (className == null || beanDef.getFactoryMethodName() != null) { return false; } AnnotationMetadata metadata; if (beanDef instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition && className.equals(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata().getClassName())) { // Can reuse the pre-parsed metadata from the given BeanDefinition... //如果BeanDefinition 是 AnnotatedBeanDefinition的实例,并且className 和 BeanDefinition中 的元数据 的类名相同 // 则直接从BeanDefinition 获得Metadata metadata = ((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) beanDef).getMetadata(); } else if (beanDef instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).hasBeanClass()) { // Check already loaded Class if present... // since we possibly can't even load the class file for this Class. //如果BeanDefinition 是 AbstractBeanDefinition的实例,并且beanDef 有 beanClass 属性存在 //则实例化StandardAnnotationMetadata Class<?> beanClass = ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDef).getBeanClass(); metadata = new StandardAnnotationMetadata(beanClass, true); } else { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(className); metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata(); } catch (IOException ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not find class file for introspecting configuration annotations: " + className, ex); } return false; } } //判断当前这个bd中存在的类是不是加了@Configruation注解 //如果存在则spring认为他是一个全注解的类 if (isFullConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { //如果存在Configuration 注解,则为BeanDefinition 设置configurationClass属性为full beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_FULL); } //判断是否加了以下注解,摘录isLiteConfigurationCandidate的源码 // candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName()); // candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName()); // candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName()); // candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName()); //如果不存在Configuration注解,spring则认为是一个部分注解类 else if (isLiteConfigurationCandidate(metadata)) { beanDef.setAttribute(CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, CONFIGURATION_CLASS_LITE); } else { return false; } // It's a full or lite configuration candidate... Let's determine the order value, if any. Integer order = getOrder(metadata); if (order != null) { beanDef.setAttribute(ORDER_ATTRIBUTE, order); } return true; }
这里有两个重要的方法:
1. isFullConfigurationCandidate
这个方法, 是判断配置类上面, 有没有直接或者间接的加 @Configuration 注解,
如果加了这个注解, 则设置属性 CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE = full
public static boolean isFullConfigurationCandidate(AnnotationMetadata metadata) { return metadata.isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName()); }
直接的方式很好理解, 就是
@Configuration public class StartConfig {}
间接的方式, 其实就是 配置类上没有加 Configuration, 但是它上面加了其他的注解, 并且这个注解中有 Configuration, 如:
@Configuration public @interface EnableIndex {} @EnableIndex public class StartConfig {}
2.isLiteConfigurationCandidate
这个方法相对复杂一点. 注意到前面的源码是 if ... else if ...
所以, 如果上面那个方法满足了, 是不会进这个方法的. 能进这个方法, 则说明, 配置类上, 根本就没有 @Configuration 配置类.
这里会先检测配置类中, 是否有 @Component / @ComponentScan / @Import / @ImportResource
如果都没有, 则会去检测配置类中的方法上, 是否有@Bean
如果能满足以上的条件, 则设置属性 CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE = lite
private static final Set<String> candidateIndicators = new HashSet<>(8); static { candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName()); candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName()); candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName()); candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName()); } public static boolean isLiteConfigurationCandidate(AnnotationMetadata metadata) { // Do not consider an interface or an annotation... if (metadata.isInterface()) { return false; } // Any of the typical annotations found? for (String indicator : candidateIndicators) { if (metadata.isAnnotated(indicator)) { return true; } } // Finally, let's look for @Bean methods... try { return metadata.hasAnnotatedMethods(Bean.class.getName()); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Failed to introspect @Bean methods on class [" + metadata.getClassName() + "]: " + ex); } return false; } }
费这么多代码, 得到结果, 设置属性 CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE = full / lite, 到底有什么意义呢?
先做两个小测试, 一个是配置类上有 @Configuration 注解, 另一个是配置类上, 没有 @Configuration 注解.
1. 没有注解的
public class IndexDao1 { public IndexDao1() { System.out.println("IndexDao1 -- constructor"); } } public class IndexDao2 { public IndexDao2() { System.out.println("IndexDao2 -- constructor"); } }
//@Configuration public class StartConfig { @Bean public IndexDao1 indexDao1(){ return new IndexDao1(); } @Bean public IndexDao2 indexDao2(){ indexDao1(); return new IndexDao2(); } }
通过上面的代码, 发现 indexDao2() 方法里面调用了 IndexDao1()方法, 那么理论上, IndexDao1 是不是会被创建两遍呢?
通过运行
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext acac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(StartConfig.class); IndexDao1 bean1 = acac.getBean(IndexDao1.class); IndexDao2 bean2 = acac.getBean(IndexDao2.class); }
这段测试代码, 我发现, IndexDao1 确实被创建了两遍

2. 有@Configuration注解的
代码还是上面那段代码, 只是在 StartConfig 上面加一个 @Configuration
运行测试代码
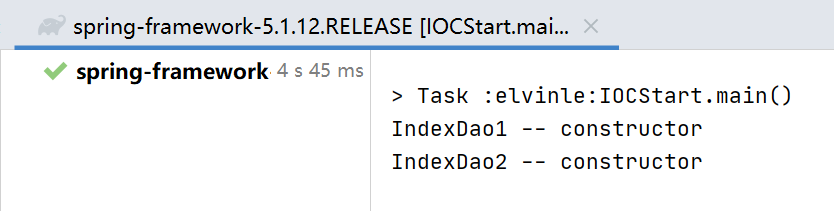
则会发现 IndexDao1 只被创建了一次.
这里的一次和两次, 和这个 full / lite 有什么关系呢?
代码还没到, 暂时不揭晓谜底了, 到后面执行
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory
的时候, 再来揭晓谜底吧.
parser.parse
这个方法内容比较多, 不考虑 xml 的情况, 这里主要是处理 ComponentScan 和 Import 的.
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) { //根据BeanDefinition 的类型 做不同的处理,一般都会调用ConfigurationClassParser#parse 进行解析 for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) { BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition(); try { if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { //解析注解对象,并且把解析出来的bd放到map,但是这里的 bd 指的是普通的 //何谓不普通的呢?比如@Bean 和各种beanFactoryPostProcessor得到的bean不在这里put //但是 是这里解析,只是不put而已 parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName()); } else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) { parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName()); } else { parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex); } } //处理延迟加载的importSelect?为什么要延迟加载,估计就是为了延迟吧 this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process(); }
parse 方法内部, 会去调用 org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#processConfigurationClass 方法
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException { if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) { return; } // 处理Imported 的情况 //就是当前这个注解类有没有被别的类import ConfigurationClass existingClass = this.configurationClasses.get(configClass); if (existingClass != null) { if (configClass.isImported()) { if (existingClass.isImported()) { existingClass.mergeImportedBy(configClass); } // Otherwise ignore new imported config class; existing non-imported class overrides it. return; } else { // Explicit bean definition found, probably replacing an import. // Let's remove the old one and go with the new one. this.configurationClasses.remove(configClass); this.knownSuperclasses.values().removeIf(configClass::equals); } } // Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy. SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass); do { sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass); } while (sourceClass != null); //一个map,用来存放扫描出来的bean(注意这里的bean不是对象,仅仅bean的信息,因为还没到实例化这一步) this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass); }
在这个方法中, 将配置类封装成了 SourceClass,
然后调用
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassParser#doProcessConfigurationClass 方法.
doProcessConfigurationClass 就是要解析的重点方法.
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException { if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) { // Recursively process any member (nested) classes first //处理内部类, 正常情况下, 我们不会用这个来配置, 所以不用重点关注 processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass); } // Process any @PropertySource annotations for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class, org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) { if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) { processPropertySource(propertySource); } else { logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment"); } } // Process any @ComponentScan annotations Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class); if (!componentScans.isEmpty() && !this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) { for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) { // The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately //扫描普通类 //这里扫描出来所有 @Component //并且把扫描的出来的普通bean放到 map 当中 Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions = this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); // Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed //检查扫描出来的类当中是否还有configuration for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) { BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); if (bdCand == null) { bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition(); } //检查扫描出来的类中, 是否还有加载了 @Configuration 的类, 如果有, 则接着递归处理 if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } } }
// Process any @Import annotations // 处理@Import imports 3种情况 // ImportSelector 将类的字符串数组返回给spring, 这些类的创建过程, 完全由 spring 去解析创建, 经典示例: @EnableCaching // 普通类 普通类会解析成 db, 放到 Map<ConfigurationClass, ConfigurationClass> configurationClasses 中,
// 等待parse方法执行完后, 注册到 spring 容器中, 由 spring 去创建 // ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 用户创建(或扫描创建) bd, 然后将这些bd注册到容器中, 由spring去创建, 经典示例: mybatis //这里和内部递归调用时候的情况不同 /** * 这里处理的import是需要判断我们的类当中时候有@Import注解 * 如果有这把@Import当中的值拿出来,是一个类 * 比如@Import(xxxxx.class),那么这里便把xxxxx传进去进行解析 * 在解析的过程中如果发觉是一个importSelector那么就回调selector的方法 * 返回一个字符串(类名),通过这个字符串得到一个类 * 继而在递归调用本方法来处理这个类 * * 判断一组类是不是imports(3种import) */ processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), true); // Process any @ImportResource annotations AnnotationAttributes importResource = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class); if (importResource != null) { String[] resources = importResource.getStringArray("locations"); Class<? extends BeanDefinitionReader> readerClass = importResource.getClass("reader"); for (String resource : resources) { String resolvedResource = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(resource); configClass.addImportedResource(resolvedResource, readerClass); } } // Process individual @Bean methods Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass); for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) { configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass)); } // Process default methods on interfaces processInterfaces(configClass, sourceClass); // Process superclass, if any if (sourceClass.getMetadata().hasSuperClass()) { String superclass = sourceClass.getMetadata().getSuperClassName(); if (superclass != null && !superclass.startsWith("java") && !this.knownSuperclasses.containsKey(superclass)) { this.knownSuperclasses.put(superclass, configClass); // Superclass found, return its annotation metadata and recurse return sourceClass.getSuperClass(); } } // No superclass -> processing is complete return null; }
这里的代码比较复杂, 就不再这一篇解析了, 不然篇幅太长了, 我自己都不想看了.(汗)






