多线程笔记 - BIO
BIO
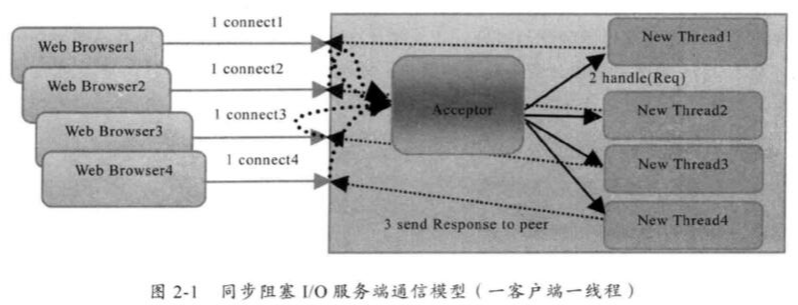
BIO 是一种同步阻塞模式, 只要有一个客户端接入, 服务器就会有一条线程与之对应, 进行通信.
以前的一种常用做法是, 服务器端起一条线程, 进行监听, 当监听到客户端接入后, 新起一条线程, 专门与客户端进行通信. 如果线程不够用了, 就不能建立连接了. 客户端只能等待.
同步说的其实是 一根筋, 只干一件事情, 比如执行io操作时, 也必须等待, 当 io 执行完后, 才可以继续执行后面的操作.
如果是异步的话, 执行io操作, 就可以交给其他程序执行, 主线程接着执行别的任务, 干别的事情. 当io执行完后, 通知我拿结果就行.
阻塞说的是, 我如果只有100个线程, 那就只能建立100个连接, 如果每个连接都满了, 其他的客户端就接不进来.
非阻塞可以理解为, 来者不拒. 就像服务大厅, 你来了, 领个号码(注册), 坐着等就行, 等叫号叫到你, 你就可以执行连接后续的逻辑. 对服务器来说, 你来了, 就接进来了, 不会拒绝你.
server:
public class Server implements Runnable { private Socket socket; public Server(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; } @Override public void run() { BufferedReader in = null; PrintWriter out = null; try { in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true); System.out.println("server : 客户端接入" + socket.toString()); while (true) { String msg = in.readLine(); if (msg == null) { break; } System.out.println("from client : " + msg); if (msg.equals("几点了")) { out.println(new DateTime(2020,1,1,1,1,1).toString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); } else{ out.println("没看懂..."); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (in != null) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (out != null) { out.close(); } if (this.socket != null) { try { this.socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { final ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(1234); try { System.out.println("服务器启动, 开始监听 1234 端口"); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println("监听到一个连接"); new Thread(new Server(socket)).start(); } finally { serverSocket.close(); } } }
ClientA:
public class ClientA { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //与服务器建立连接 Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 1234); BufferedReader in = null; PrintWriter out = null; try { in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true); out.println("几点了"); while (true) { String serverMsg = in.readLine(); if(serverMsg == null){ break; } System.out.println("from server : " + serverMsg); } } finally { if (in != null) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (out != null) { out.close(); } if (socket != null) { try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
测试:
clientA:
server:
参考:
Netty权威指南






