MySQL基础篇--增删改查
一、DQL
1. 语法格式
1 select 2 [all|distinct] 3 <目标列的表达式1> [别名], 4 <目标列的表达式2> [别名]... 5 from <表名或视图名> [别名],<表名或视图名> [别名]... 6 [where<条件表达式>] 7 [group by <列名> 8 [having <条件表达式>]] 9 [order by <列名> [asc|desc]] 10 [limit <数字或者列表>];
简化:select *| 列名 from 表 where 条件
2. 简单查询
1 -- 1.查询所有的商品. 2 select * from product; 3 -- 2.查询商品名和商品价格. 4 select pname,price from product; 5 -- 3.别名查询.使用的关键字是as(as可以省略的). 6 -- 3.1表别名: 7 select * from product as p; 8 -- 3.2列别名: 9 select pname as pn from product; 10 -- 4.去掉重复值. 11 select distinct price from product; 12 -- 5.查询结果是表达式(运算查询):将所有商品的价格+10元进行显示. 13 select pname,price+10 from product;
3. 运算符
①算数运算符

②逻辑运算符
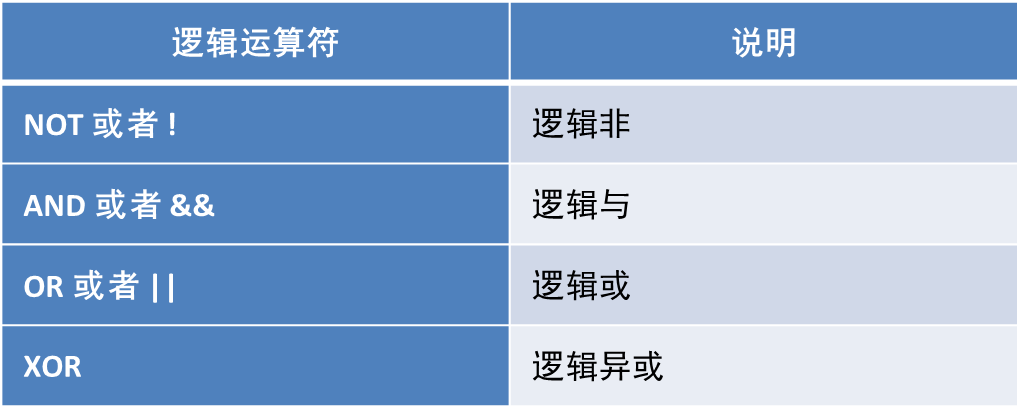
③比较运算符
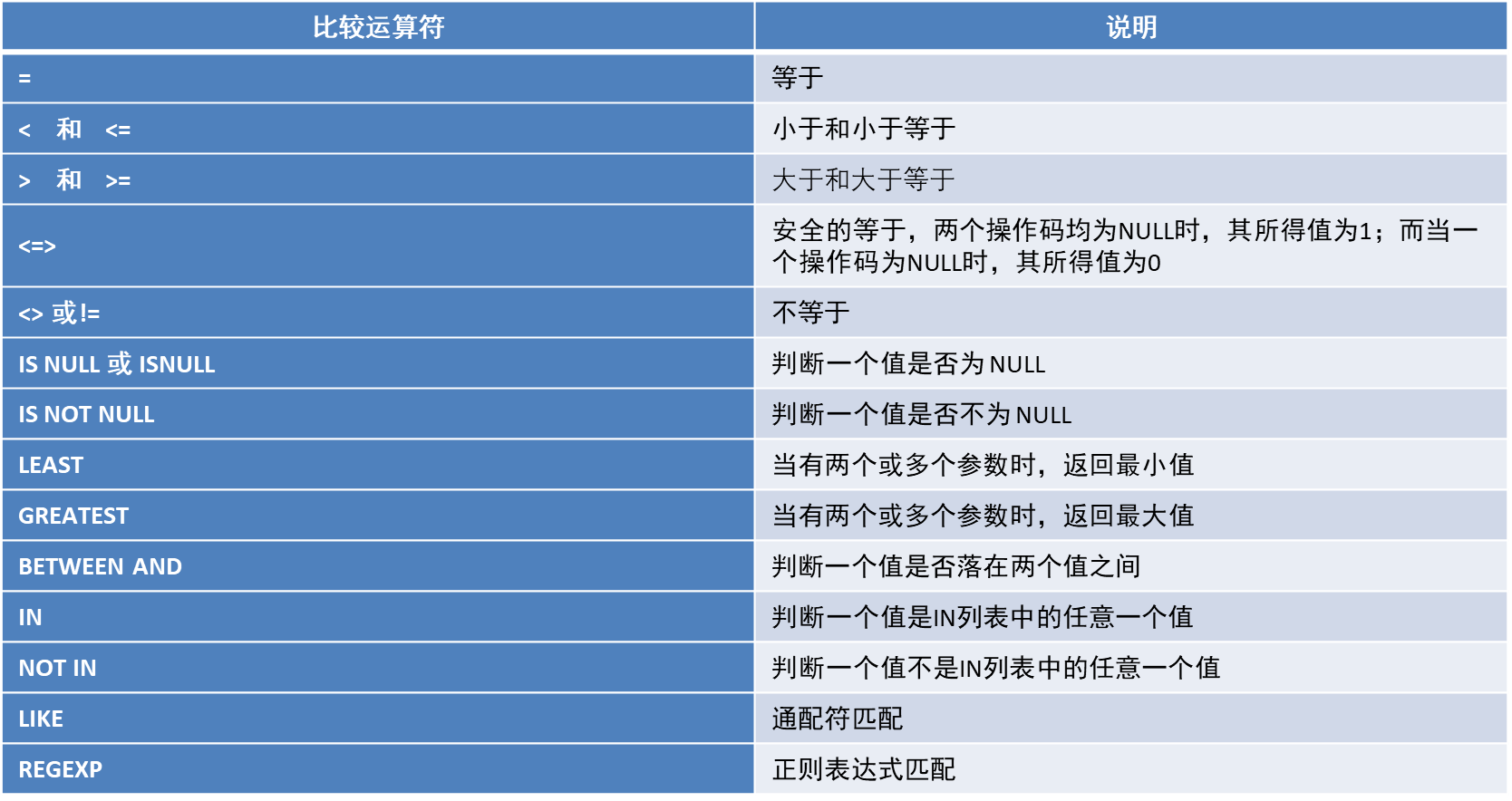
④位运算符
位运算符是在二进制数上进行计算的运算符。位运算会先将操作数变成二进制数,进行位运算。然后再将计算结果从二进制数变回十进制数。
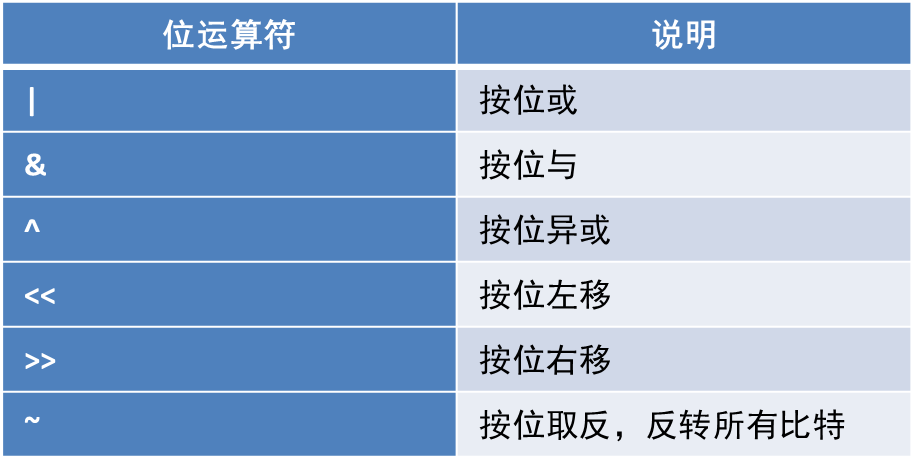
4. 运算查询
①算数操作
1 select 6 + 2; 2 select 6 - 2; 3 select 6 * 2; 4 select 6 / 2; 5 select 6 % 2; 6 7 -- 将每件商品的价格加10 8 select name,price + 10 as new_price from product; 9 -- 将所有商品的价格上调10% 10 select pname,price * 1.1 as new_price from product;
②条件查询
1 -- 查询商品名称为“海尔洗衣机”的商品所有信息: 2 select * from product where pname = '海尔洗衣机'; 3 4 -- 查询价格为800商品 5 select * from product where price = 800; 6 7 -- 查询价格不是800的所有商品 8 select * from product where price != 800; 9 select * from product where price <> 800; 10 select * from product where not(price = 800); 11 12 -- 查询商品价格大于60元的所有商品信息 13 select * from product where price > 60; 14 15 16 -- 查询商品价格在200到1000之间所有商品 17 select * from product where price >= 200 and price <=1000; 18 select * from product where price between 200 and 1000; 19 20 -- 查询商品价格是200或800的所有商品 21 select * from product where price = 200 or price = 800; 22 select * from product where price in (200,800); 23 24 -- 查询含有‘裤'字的所有商品 25 select * from product where pname like '%裤%'; 26 27 -- 查询以'海'开头的所有商品 28 select * from product where pname like '海%'; 29 30 -- 查询第二个字为'蔻'的所有商品 31 select * from product where pname like '_蔻%'; 32 33 -- 查询category_id为null的商品 34 select * from product where category_id is null; 35 36 -- 查询category_id不为null分类的商品 37 select * from product where category_id is not null;
1 -- 使用least求最小值 2 select least(10, 20, 30); -- 10 3 select least(10, null , 30); -- null 4 5 -- 使用greatest求最大值 6 select greatest(10, 20, 30); 7 select greatest(10, null, 30); -- null
③位运算
1 select 3&5; -- 位与 2 select 3|5; -- 位或 3 select 3^5; -- 位异或 4 select 3>>1; -- 位左移 5 select 3<<1; -- 位右移 6 select ~3; -- 位取反
5. 排序查询
1 select 2 字段名1,字段名2,…… 3 from 表名 4 order by 字段名1 [asc|desc],字段名2[asc|desc]……
特点:
- asc代表升序,desc代表降序,如果不写默认升序
- order by用于子句中可以支持单个字段,多个字段,表达式,函数,别名
- order by子句,放在查询语句的最后面。LIMIT子句除外
实现:
1 -- 1.使用价格排序(降序) 2 select * from product order by price desc; 3 -- 2.在价格排序(降序)的基础上,以分类排序(降序) 4 select * from product order by price desc,category_id asc; 5 -- 3.显示商品的价格(去重复),并排序(降序) 6 select distinct price from product order by price desc;
6. 聚合查询
之前的查询是横向查询,就是根据条件进行行判断。聚合查询是纵向查询,对一列值进行计算,然后返回一个单一的值。聚合函数会忽略空值。

1 -- 1 查询商品的总条数 2 select count(*) from product; 3 -- 2 查询价格大于200商品的总条数 4 select count(*) from product where price > 200; 5 -- 3 查询分类为'c001'的所有商品的总和 6 select sum(price) from product where category_id = 'c001'; 7 -- 4 查询商品的最大价格 8 select max(price) from product; 9 -- 5 查询商品的最小价格 10 select min(price) from product; 11 -- 6 查询分类为'c002'所有商品的平均价格 12 select avg(price) from product where category_id = 'c002';
聚合查询对null值的处理:
- 1)count函数对null值的处理,如果count函数的参数为星号(*),则统计所有记录的个数。而如果参数为某字段,不统计含null值的记录个数。
- 2)sum和avg函数对null值的处理这两个函数忽略null值的存在,就好象该条记录不存在一样。
- 3)max和min函数对null值的处理,max和min两个函数同样忽略null值的存在。
7. 分组查询
注意:如果要进行分组的话,则SELECT子句之后,只能出现分组的字段和统计函数,其他的字段不能出现。group by 不能和where一起使用
格式:
select 字段1,字段2… from 表名 group by 分组字段 [having 分组条件];
实现:
select category_id ,count(*) from product group by category_id having count(*) > 4;
8. 分页查询
格式:
1 -- 方式1-显示前n条 2 select 字段1,字段2... from 表明 limit n 3 -- 方式2-分页显示 4 select 字段1,字段2... from 表明 limit m,n 5 m: 整数,表示从第几条索引开始,计算方式 (当前页-1)*每页显示条数 6 n: 整数,表示查询多少条数据
实现:
-- 查询product表的前5条记录 select * from product limit 5 -- 从第4条开始显示,显示5条 select * from product limit 3,5
补充:Limit3,5 效果等同于 Limit 5,Offset3 Limit和Offset组合,Limit后面是要取的数量,Offset后面是跳过的数量
9. insert into select 语句
注意:要求目标表(插入数据的表)必须存在
格式:
1 insert into Table2(field1,field2,…) select value1,value2,… from Table1 或者: 2 insert into Table2 select * from Table1
10. select into from 语句
注意:要求目标表(插入数据的表)不存在,因为在插入时会自动创建,并将获取数据的表table1指定字段数据复制到插入数据的表table2。
格式:
SELECT vale1, value2 into Table2 from Table1
11. 正则表达式

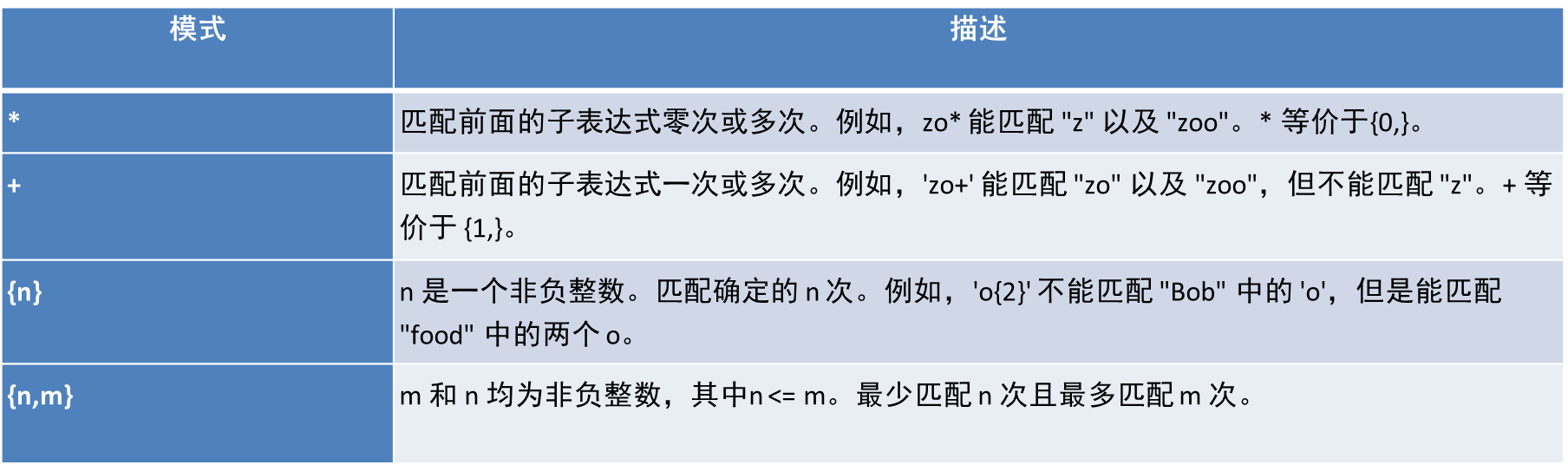
实现:
1 -- ^ 在字符串开始处进行匹配 2 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP '^a'; 3 4 -- $ 在字符串末尾开始匹配 5 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP 'a$'; 6 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP 'c$'; 7 8 -- . 匹配任意字符 9 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP '.b'; 10 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP '.c'; 11 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP 'a.'; 12 13 -- [...] 匹配括号内的任意单个字符 14 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP '[xyz]'; 15 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP '[xaz]'; 16 17 -- [^...] 注意^符合只有在[]内才是取反的意思,在别的地方都是表示开始处匹配 18 SELECT 'a' REGEXP '[^abc]'; 19 SELECT 'x' REGEXP '[^abc]'; 20 SELECT 'abc' REGEXP '[^a]'; 21 22 -- a* 匹配0个或多个a,包括空字符串。 可以作为占位符使用.有没有指定字符都可以匹配到数据 23 24 SELECT 'stab' REGEXP '.ta*b'; 25 SELECT 'stb' REGEXP '.ta*b'; 26 SELECT '' REGEXP 'a*'; 27 28 -- a+ 匹配1个或者多个a,但是不包括空字符 29 SELECT 'stab' REGEXP '.ta+b'; 30 SELECT 'stb' REGEXP '.ta+b'; 31 32 -- a? 匹配0个或者1个a 33 SELECT 'stb' REGEXP '.ta?b'; 34 SELECT 'stab' REGEXP '.ta?b'; 35 SELECT 'staab' REGEXP '.ta?b'; 36 37 -- a1|a2 匹配a1或者a2, 38 SELECT 'a' REGEXP 'a|b'; 39 SELECT 'b' REGEXP 'a|b'; 40 SELECT 'b' REGEXP '^(a|b)'; 41 SELECT 'a' REGEXP '^(a|b)'; 42 SELECT 'c' REGEXP '^(a|b)'; 43 44 -- a{m} 匹配m个a 45 46 SELECT 'auuuuc' REGEXP 'au{4}c'; 47 SELECT 'auuuuc' REGEXP 'au{3}c'; 48 49 -- a{m,n} 匹配m到n个a,包含m和n 50 51 SELECT 'auuuuc' REGEXP 'au{3,5}c'; 52 SELECT 'auuuuc' REGEXP 'au{4,5}c'; 53 SELECT 'auuuuc' REGEXP 'au{5,10}c'; 54 55 -- (abc) abc作为一个序列匹配,不用括号括起来都是用单个字符去匹配,如果要把多个字符作为一个整体去匹配就需要用到括号,所以括号适合上面的所有情况。 56 SELECT 'xababy' REGEXP 'x(abab)y'; 57 SELECT 'xababy' REGEXP 'x(ab)*y'; 58 SELECT 'xababy' REGEXP 'x(ab){1,2}y';
1. 查询时合并列
例1:计算两个科目分数之和
SELECT id ,name ,(math+english) FROM student;
这里是计算math和English这两个列合并后的值,适用于整型(Tinyint/ smallint/ mediumint/int/ bigint(M) unsigned zerofill)字段,用在文本字段没意义
例2:将姓名和住址合并为一列显示
SELECT score,CONCAT(`name`,`address`) FROM `result`
CONCAT函数将两个列拼接在一起
4. 查询时拼接字符串
CONACT()
Concat用来拼接字符串,SELECT CONCAT("My","S","Q","L");——>MYSQL。如果字符串中有一个为Null,则返回NULL。
CONCAT_WS(),SELECT CONCAT_WS(",","JAVA","C++","C");——>JAVA,C++,C。括号里第一个字符为分隔字符。
二、DDL
1. 对数据库的常用操作
查看所有数据库:show databases;
创建数据库:create database [if not exists] 数据库名称 [charset=utf8];
切换(选择要操作的数据库):use 数据库名称;
删除数据库:drop database [if not exists] 数据库名称;
修改数据库编码:alter database 数据库名称 character set utf8;
2. 数据类型
①数值类型

②日期类型

③字符串类型
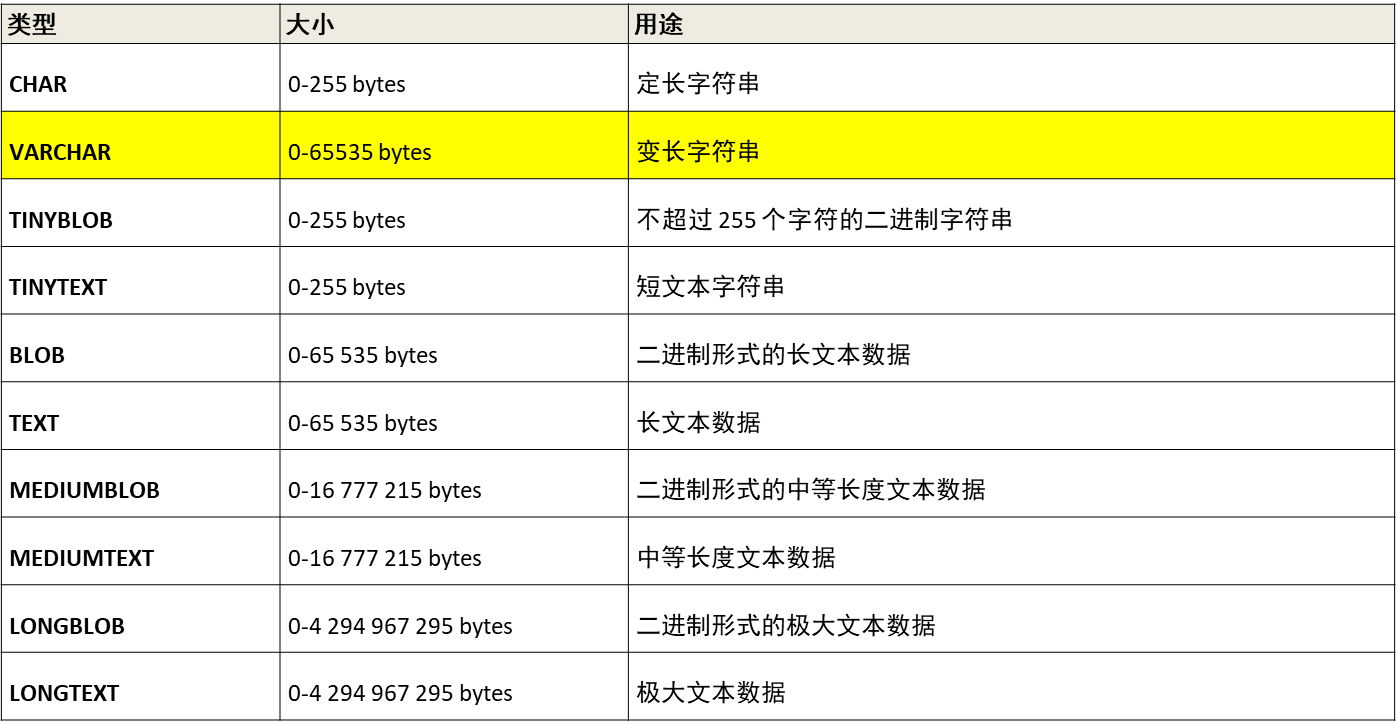
3. 对表结构的常用操作
①创建
create table [if not exists ] 表名(
字段名1 类型[(宽度)] [约束条件] [comment ‘字段说明’]
字段名2 类型[(宽度)] [约束条件] [comment ‘字段说明’]
...
);
②查看和删除
查看当前数据库的所有表名称:show tables;
查看指定某个表的创建语句:show create table 表名;
查看表结构:desc 表名;
删除表:drop table 表名;
③添加列
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型(长度) []约束;
④修改列名和类型
alter table 表名change 旧列名 类型(长度) 约束;
⑤删除列
alter table 表名 drop 列名
⑥修改表名
rename table 表名 to 新表名;
三、DML
1. 数据插入INSERT
插入指定列:insert into 表名 (列名1,列名3,...) values (值1,值3);
插入所有列:insert into 表名 values (值1,值2,...);
2. 数据修改UPDATE
update 表名 set 字段名=值;
update 表名 set 字段名=值 where 条件;
3. 数据删除DELETE
delete from 表名 [where 条件];
truncate table 表名 或者truncate 表名;
注意:delete和truncate不同,delete只是删除内容,而truncate类似于drop table,可以理解为将整个表删除后,再重建这个表。
四、约束constraint
约束就是表中数据的限制条件
1. 分类
①主键约束:primary key(PK)
主键约束是一个列或多个列的组合,其值能唯一的标识表中的每一行,方便在RDBMS中尽快的找到某一行
主键约束相当于唯一约束+非空约束,不允许重复也不允许为空
当创建注解约束时,系统默认会在所在列或所在列组合上建立对应的唯一索引
1)添加单列主键两种方式
----在添加字段同时指定主键
1 create table 表名( 2 3 字段名 数据类型 primary key 4 5 );
----在定义字段后再指定主键
1 create table 表名( 2 3 [constraint <约束名>] primary key [字段名]; 4 5 );
2)添加多列主键(联合主键)
联合主键:一张表的多个字段组成
注意:
1. 当主键是多个字段组成时,不能直接在字段名后面声明主键约束
2. 一张表只能有一个主键,所以联合主键也是一个主键
1 create table 表名( 2 primary key(字段1,字段2) 3 );
3)修改表时添加主键约束
alter table 表名 add primary key (字段列表)
4)删除主键约束
alter table 表名 drop primary key;
②非空约束:auto_increment
概念:MySQL 非空约束(not null)指字段的值不能为空。对于使用了非空约束的字段,如果用户在添加数据时没有指定值,数据库系统就会报错。
语法:
1 方式1:<字段名><数据类型> not null; 2 方式2:alter table 表名 modify 字段 类型 not null;
实现:
1 -- 方式1,创建表时指定 2 create table t_user6 ( 3 id int , 4 name varchar(20) not null, 5 address varchar(20) not null 6 ); 7 8 -- 方式2,创建表后指定 9 create table t_user7 ( 10 id int , 11 name varchar(20) , -- 指定非空约束 12 address varchar(20) -- 指定非空约束 13 ); 14 alter table t_user7 modify name varchar(20) not null; 15 alter table t_user7 modify address varchar(20) not null;
删除:
1 -- alter table 表名 modify 字段 类型 2 alter table t_user7 modify name varchar(20) ; 3 alter table t_user7 modify address varchar(20) ;
③外键约束:foreign key(FK)
④唯一约束:unique
概念:唯一约束(Unique Key)是指所有记录中字段的值不能重复出现。例如,为 id 字段加上唯一性约束后,每条记录的 id 值都是唯一的,不能出现重复的情况。
语法:
1 方式1:<字段名> <数据类型> unique 2 方式2: alter table 表名 add constraint 约束名 unique(列);
实现:
1 -- 方式1:创建表时指定 2 create table t_user8 ( 3 id int , 4 name varchar(20) , 5 phone_number varchar(20) unique -- 指定唯一约束 6 ); 7 8 -- 方式1:创建表后指定 9 create table t_user9 ( 10 id int , 11 name varchar(20) , 12 phone_number varchar(20) -- 指定唯一约束 13 ); 14 alter table t_user9 add constraint unique_ph unique(phone_number);
删除:
1 -- alter table <表名> drop index <唯一约束名>; 2 alter table t_user9 drop index unique_ph;
⑤自增长约束:default
语法:
字段名 数据类型 auto_increment
特点:
默认情况下,auto_increment的初始值是 1,每新增一条记录,字段值自动加 1。
一个表中只能有一个字段使用 auto_increment约束,且该字段必须有唯一索引,以避免序号重复(即为主键或主键的一部分)。
auto_increment约束的字段必须具备 NOT NULL 属性。
auto_increment约束的字段只能是整数类型(TINYINT、SMALLINT、INT、BIGINT 等。
auto_increment约束字段的最大值受该字段的数据类型约束,如果达到上限,auto_increment就会失效。
实现:
1 create table t_user1( 2 id int primary key auto_increment, 3 name varchar(20) 4 );
指定自增字段初始值:
如果第一条记录设置了该字段的初始值,那么新增加的记录就从这个初始值开始自增。例如,如果表中插入的第一条记录的 id 值设置为 5,那么再插入记录时,id 值就会从 5 开始往上增加
1 -- 方式1,创建表时指定 2 create table t_user2 ( 3 id int primary key auto_increment, 4 name varchar(20) 5 )auto_increment=100; 6 7 -- 方式2,创建表之后指定 8 create table t_user3 ( 9 id int primary key auto_increment, 10 name varchar(20) 11 ); 12 13 alter table t_user2 auto_increment=100;
⑥默认约束:default
概念:MySQL默认值约束用来指定某列的默认值
语法:
1 方式1: <字段名> <数据类型> default <默认值>; 2 方式2: alter table 表名 modify 列名 类型 default 默认值;
实现:
1 -- 方式1 2 create table t_user10 ( 3 id int , 4 name varchar(20) , 5 address varchar(20) default ‘北京’ -- 指定默认约束 6 ); 7 8 -- 方式2 9 -- alter table 表名 modify 列名 类型 default 默认值; 10 create table t_user11 ( 11 id int , 12 name varchar(20) , 13 address varchar(20) 14 ); 15 alter table t_user11 modify address varchar(20) default ‘北京’;
删除:
1 -- alter table <表名> modify column <字段名> <类型> default null; 2 3 alter table t_user11 modify column address varchar(20) default null;
⑦零填充约束:zerofill
概念:
1)插入数据时,当该字段的值的长度小于定义的长度时,会在该值的前面补上相应的0。
2)zerofill默认为int(10)。
3)当使用zerofill 时,默认会自动加unsigned(无符号)属性,使用unsigned属性后,数值范围是原值的2倍,例如,有符号为-128~+127,无符号为0~256。
实现:
1 create table t_user12 ( 2 id int zerofill , -- 零填充约束 3 name varchar(20) 4 );
删除:
1 alter table t_user12 modify id int;

