logic
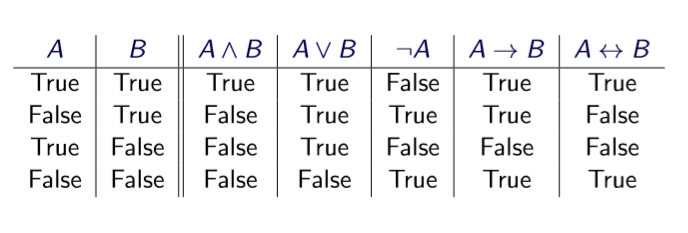
1. proposition是一个声明性描述,只有T或F
2. proposition通过logical connectives成为larger proposition,故而logical connectives是一个operations

although=and=but=nevertheless
3. Compound propositions复合命题的正确性取决于子命题
4. Vacuous truth
A → B If A (premise) then B (conclusion)
只有premise成立但是conclusion不成立时才是False
5. # X={}
Every x∈X is odd(True)
Every x∈X is even(True)
6. A proposition is:
a tautology if it is always true,
a contradiction if it is always false,
a contingency if it is neither a tautology or a contradiction,
satsfiable if it is not a contradiction.
7. Logical equivalence
e.g. A=¬(¬A)
8. valid
An argument is valid if the conclusions are true whenever all the premises are true. Thus: if we believe the premises, we should also believe the conclusion
9. Syntax is how things are written:
Semantics is what things mean
“Rabbit” and “Bunny” are syntactically different, but semantically the same.
10. well-formed-formulas


p∧¬T没有()不符合
(p∧q∧r)三个用一个()不符合
通俗习惯有:
a) 无歧义时省略括号,e.g. p∧q
b) ¬ binds more tightly than ∧ and ∨, which bind more tightly than → and ↔ (e.g. p∧q → r instead of ((p∧q) → r)
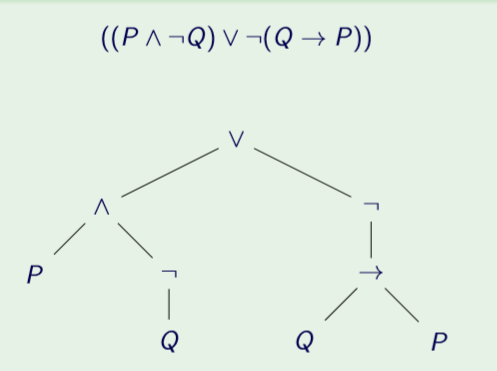
11. Parse trees
The structure of well-formed formulas (and other grammar-defined syntaxes) can be shown with a parse tree


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号