代码题(15)— 环形链表
1、141. 环形链表
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return false; ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head; while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) return true; } return false; } };
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return false; ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head->next->next; while(slow != fast) { if(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } else return false; } return true; } };
2、142. 环形链表 II
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
方法一:(最简单)
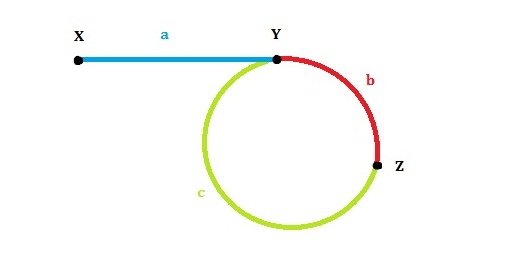
设:链表头是X,环的第一个节点是Y,slow和fast第一次的交点是Z。各段的长度分别是a,b,c,如图所示。环的长度是L。
第一次相遇时slow走过的距离:a+b,fast走过的距离:a+b+c+b。
因为fast的速度是slow的两倍,所以fast走的距离是slow的两倍,有 2(a+b) = a+b+c+b,可以得到a=c(这个结论很重要!)。
我们发现L=b+c=a+b,也就是说,从一开始到二者第一次相遇,循环的次数就等于环的长度。
步骤:(1)慢指针走一步,快指针走两步,找到二者相遇的节点,此时慢指针走过的长度就是环的长度;(2)让其中一个指针指向头节点,二者再一起每次走一步,相遇点即环的入口节点。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return nullptr; ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head; while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if(slow == fast) break; } // 此处要判断指针是否为空,即该链表是否有环 if(fast == nullptr || fast->next == nullptr) return nullptr; slow = head; while(slow != fast) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; } return slow; } };
方法二:
步骤:(1)判断链表是否有环;(2)求环的长度;(3)环的入口,一个指针不走,一个走环的长度步,之后两个一起每次走一步,直到二者相遇,该节点就是环的入口。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) { if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return nullptr; ListNode* slow = head; ListNode* fast = head->next->next; while(slow != fast) { if(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } else return nullptr; } fast = fast->next; int num = 1; while(slow != fast) { num++; fast = fast->next; } fast = head; for(int i=0;i<num;++i) fast = fast->next; slow = head; while(fast != slow) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; } return slow; } };


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号