--这篇算是杂记吧,套用了别人的俩个博客,是vs 连接mysql的方式,之前的帖子实现了python实现爬取股票和入库之后,准备用c++的代码实现分析
第一步是复习对sql数据库的最基本操作
第二步是单线程分析股票数据,选出自己理想的股票
第三步是多线程实现
第四步是加入前台界面
第五步是界面加入众多功能,可选日期范围,可选方案,先慢慢搞吧
每一步可能分好几篇帖子,记录自己的日常吧~
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <WinSock.h>
#include <mysql.h>
#pragma comment(lib,"wsock32.lib")
using namespace std;
MYSQL mysql;
MYSQL_FIELD *fd; //字段列数组
char field[32][32]; //存字段名二维数组
MYSQL_RES *res; //行的一个查询结果集
MYSQL_ROW column; //数据行的列
char query[150]; //查询语句
//函数声明
bool ConnectDatabase();
void FreeConnect();
bool QueryDatabase();
bool InsertData();
bool ModifyData();
bool DeleteData();
int main(int argc, char **argv){
ConnectDatabase();
QueryDatabase();
FreeConnect();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//连接数据库
bool ConnectDatabase(){
//Gets or initializes a MYSQL structure
mysql_init(&mysql);
// Connects to a MySQL server
const char host[] = "localhost";
const char user[] = "root";
const char passwd[] = "Test_123";
const char db[] = "test";
unsigned int port = 3306;
const char *unix_socket = NULL;
unsigned long client_flag = 0;
/*A MYSQL* connection handler if the connection was successful,
NULL if the connection was unsuccessful. For a successful connection,
the return value is the same as the value of the first parameter.*/
if (mysql_real_connect(&mysql, host, user, passwd, db, port, unix_socket, client_flag)){
printf("The connection was successful.\n");
return true;
}
else{
/*const char *mysql_error(MYSQL *mysql)
Returns the error message for the most recently invoked MySQL function
A null-terminated character string that describes the error.
An empty string if no error occurred.*/
printf("Error connecting to database:%s\n", mysql_error(&mysql));
return false;
}
}
//释放资源
/*void mysql_free_result(MYSQL_RES *result)
Frees the memory allocated for a result set by mysql_store_result(),
mysql_use_result(), mysql_list_dbs(), and so forth.When you are done
with a result set, you must free the memory it uses by calling mysql_free_result().
Do not attempt to access a result set after freeing it.*/
/*void mysql_close(MYSQL *mysql)
Closes a previously opened connection.mysql_close() also deallocates
the connection handler pointed to by mysql if the handler was allocated
automatically by mysql_init() or mysql_connect().*/
void FreeConnect(){
mysql_free_result(res);
mysql_close(&mysql);
}
//查询数据
bool QueryDatabase(){
//将数据格式化输出到字符串
sprintf_s(query, "select * from student");
//设置编码格式
mysql_query(&mysql, "set names gbk");
/*int mysql_query(MYSQL *mysql, const char *stmt_str)
Executes an SQL query specified as a null-terminated string
Executes the SQL statement pointed to by the null-terminated string stmt_str.
Normally, the string must consist of a single SQL statement without
a terminating semicolon (;). If multiple-statement execution has been enabled,
the string can contain several statements separated by semicolons.
Return Values:Zero for success. Nonzero if an error occurred.*/
if (mysql_query(&mysql, query)){
printf("Query failed (%s)\n", mysql_error(&mysql));
return false;
}
else{
printf("query success\n");
}
/*MYSQL_RES *mysql_store_result(MYSQL *mysql)
Retrieves a complete result set to the client
mysql_store_result() reads the entire result of a query to the client,
allocates a MYSQL_RES structure, and places the result into this structure.
mysql_store_result() returns a null pointer if the statement did not return
a result set(for example, if it was an INSERT statement). mysql_store_result()
also returns a null pointer if reading of the result set failed.
You can check whether an error occurred by checking whether mysql_error()
returns a nonempty string. Return Values:A MYSQL_RES result structure with
the results.NULL(0) if an error occurred.*/
res = mysql_store_result(&mysql);
if (!res){
printf("Couldn't get result from %s\n", mysql_error(&mysql));
return false;
}
/*my_ulonglong mysql_affected_rows(MYSQL *mysql)
It returns the number of rows changed, deleted,
or inserted by the last statement if it was an UPDATE, DELETE, or INSERT.
For SELECT statements, returns the number of rows in the result set.*/
printf("number of dataline returned: %d\n", mysql_affected_rows(&mysql));
/*MYSQL_FIELD *mysql_fetch_field(MYSQL_RES *result)
Returns the definition of one column of a result set as a MYSQL_FIELD structure.
Call this function repeatedly to retrieve information about all columns in the result set.*/
// 获取列数
int j = mysql_num_fields(res);
//存储字段信息
char *str_field[32];
//获取字段名
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++){
str_field[i] = mysql_fetch_field(res)->name;
}
//打印字段
for (int i = 0; i < j; i++)
printf("%10s\t", str_field[i]);
printf("\n");
//打印查询结果
//MYSQL_ROW mysql_fetch_row(MYSQL_RES *result)
//Fetches the next row from the result set
while (column = mysql_fetch_row(res)){
printf("%10s\t%10s\n", column[0], column[1]);
}
return true;
}
有很多准备条件,还有其他的操作数据库的方法,请具体参考下面的俩个帖子:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21095573/article/details/82824693
https://www.cnblogs.com/iwangzhengchao/p/10056075.html --快节奏的开发都是在借鉴别人的分享
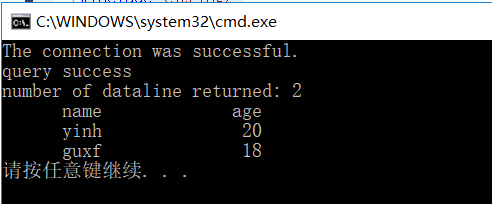
最终效果如下:
写代码的小熊猫 ~ :) 目前水平十分有限,慢慢提高吧,最近加班实在严重,估计会变成一个星期一俩更,学习不能停~



