SpringBoot08:MVC自动配置原理
MVC自动配置原理
官网阅读
在进行项目编写前,我们还需要知道一个东西,就是SpringBoot对我们的SpringMVC还做了哪些配置,包括如何扩展,如何定制。
只有把这些都搞清楚了,我们在之后使用才会更加得心应手。途径一:源码分析,途径二:官方文档!
Spring MVC Auto-configuration
// Spring Boot为Spring MVC提供了自动配置,它可以很好地与大多数应用程序一起工作。
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
// 自动配置在Spring默认设置的基础上添加了以下功能:
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
// 包含视图解析器
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
// 支持静态资源文件夹的路径,以及webjars
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars
// 自动注册了Converter:
// 转换器,这就是我们网页提交数据到后台自动封装成为对象的东西,比如把"1"字符串自动转换为int类型
// Formatter:【格式化器,比如页面给我们了一个2019-8-10,它会给我们自动格式化为Date对象】
Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
// HttpMessageConverters
// SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应信息的,比如我们要把一个User对象转换为JSON字符串,可以去看官网文档解释;
Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document).
// 定义错误代码生成规则的
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document).
// 首页定制
Static index.html support.
// 图标定制
Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document).
// 初始化数据绑定器:帮我们把请求数据绑定到JavaBean中!
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document).
/*
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化程序、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己
的@configuration类,类型为webmvcconfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义
实例,则可以声明WebMVCregistrationAdapter实例来提供此类组件。
*/
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration
(interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own
@Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide
custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
// 如果您想完全控制Spring MVC,可以添加自己的@Configuration,并用@EnableWebMvc进行注释。
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
我们来仔细对照,看一下它怎么实现的,它告诉我们SpringBoot已经帮我们自动配置好了SpringMVC,然后自动配置了哪些东西呢?
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 内容协商视图解析器
自动配置了ViewResolver,就是我们之前学习的SpringMVC的视图解析器;
即根据方法的返回值取得视图对象(View),然后由视图对象决定如何渲染(转发,重定向)。
我们去看看这里的源码:我们找到 WebMvcAutoConfiguration , 然后搜索ContentNegotiatingViewResolver。找到如下方法!
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean({ViewResolver.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
name = {"viewResolver"},
value = {ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class}
)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager((ContentNegotiationManager)beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
// ContentNegotiatingViewResolver使用所有其他视图解析器来定位视图,因此它应该具有较高的优先级
resolver.setOrder(-2147483648);
return resolver;
}
我们可以点进这类看看!找到对应的解析视图的代码;
@Override
@Nullable // 注解说明:@Nullable 即参数可为null
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
RequestAttributes attrs = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
Assert.state(attrs instanceof ServletRequestAttributes, "No current ServletRequestAttributes");
List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes = getMediaTypes(((ServletRequestAttributes) attrs).getRequest());
if (requestedMediaTypes != null) {
// 获取候选的视图对象
List<View> candidateViews = getCandidateViews(viewName, locale, requestedMediaTypes);
// 选择一个最适合的视图对象,然后把这个对象返回
View bestView = getBestView(candidateViews, requestedMediaTypes, attrs);
if (bestView != null) {
return bestView;
}
}
我们继续点进去看,他是怎么获得候选的视图的呢?
getCandidateViews中看到他是把所有的视图解析器拿来,进行while循环,挨个解析!
private List<View> getCandidateViews(String viewName, Locale locale, List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes)
throws Exception {
List<View> candidateViews = new ArrayList<>();
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
Assert.state(this.contentNegotiationManager != null, "No ContentNegotiationManager set");
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
candidateViews.add(view);
}
for (MediaType requestedMediaType : requestedMediaTypes) {
List<String> extensions = this.contentNegotiationManager.resolveFileExtensions(requestedMediaType);
for (String extension : extensions) {
String viewNameWithExtension = viewName + '.' + extension;
view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewNameWithExtension, locale);
if (view != null) {
candidateViews.add(view);
}
}
}
}
}
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultViews)) {
candidateViews.addAll(this.defaultViews);
}
return candidateViews;
}
所以得出结论:ContentNegotiatingViewResolver 这个视图解析器就是用来组合所有的视图解析器的
我们再去研究下它的组合逻辑,看到有个属性viewResolvers,看看它是在哪里进行赋值的!
@Override
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
// 这里它是从beanFactory工具中获取容器中的所有视图解析器
// ViewRescolver.class 把所有的视图解析器来组合的
Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), ViewResolver.class).values();
if (this.viewResolvers == null) {
this.viewResolvers = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.size());
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : matchingBeans) {
if (this != viewResolver) {
this.viewResolvers.add(viewResolver);
}
}
}
// ......
}
既然它是在容器中去找视图解析器,我们是否可以猜想,我们就可以去实现一个视图解析器了呢?
我们可以自己给容器中去添加一个视图解析器;这个类就会帮我们自动的将它组合进来;我们去实现一下
1、我们在我们的主程序中去写一个视图解析器来试试;
package com.edgar.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.View;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import java.util.Locale;
// 如果我们要扩展SpringMVC,官方建议我们这样去做!
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean //放到bean中
public ViewResolver myViewResolver(){
return new MyViewResolver();
}
//我们写一个静态内部类,视图解析器就需要实现ViewResolver接口
private static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver {
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String s, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}
2、怎么看我们自己写的视图解析器有没有起作用呢?
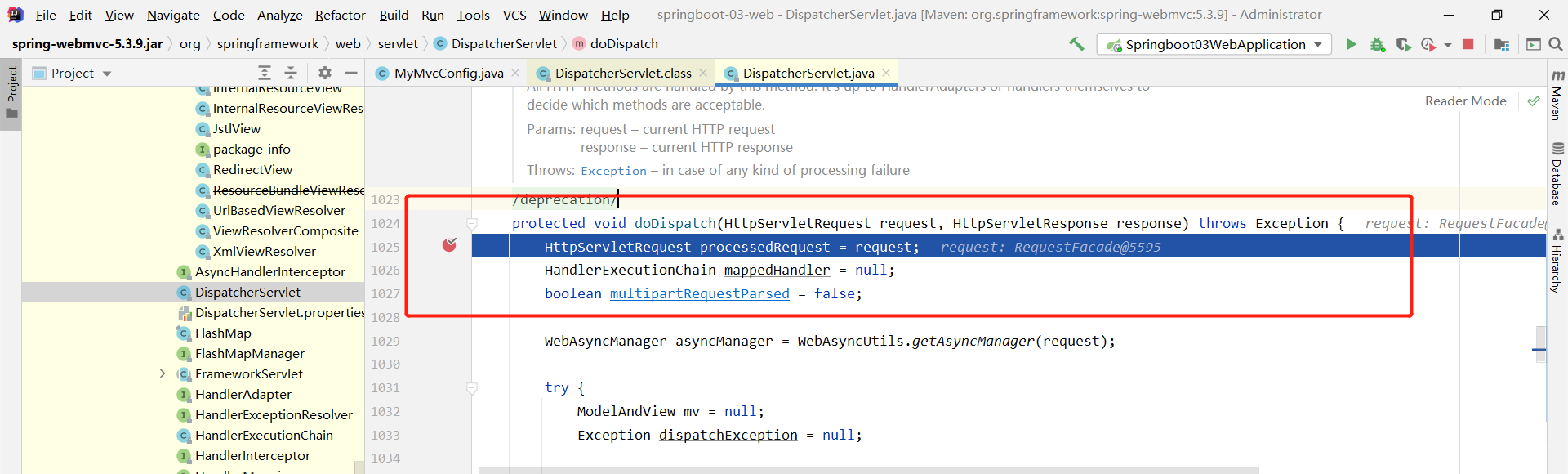
我们给 DispatcherServlet 中的 doDispatch方法 加个断点进行调试一下,因为所有的请求都会走到这个方法中
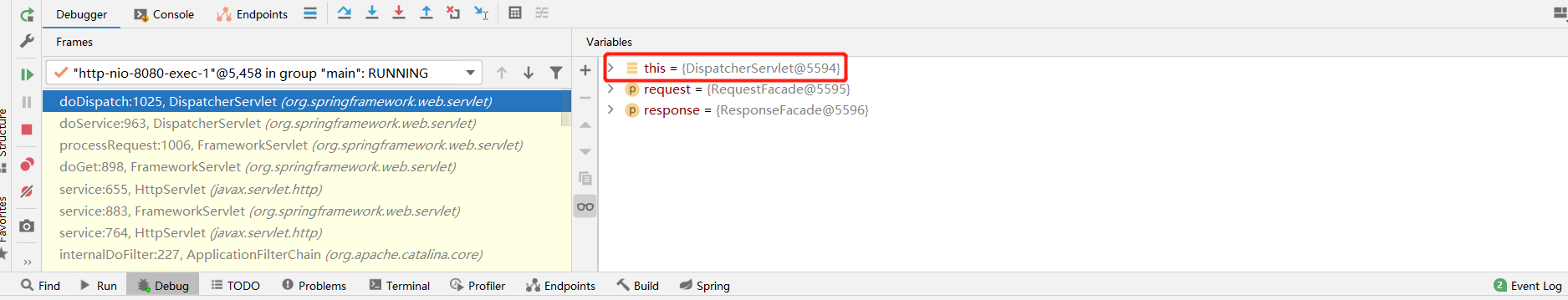
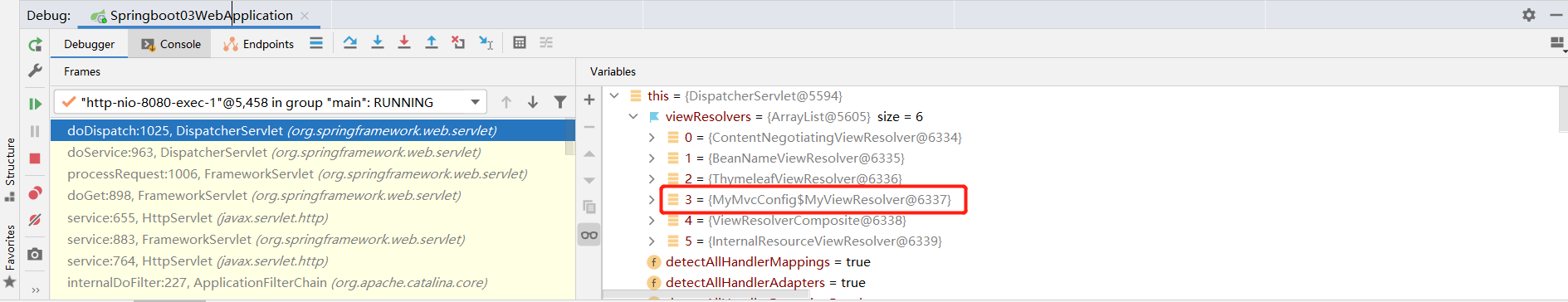
3、我们启动我们的项目,然后随便访问一个页面,看一下Debug信息;
找到this
找到视图解析器,我们看到我们自己定义的就在这里了;
所以说,我们如果想要使用自己定制化的东西,我们只需要给容器中添加这个组件就好了!剩下的事情SpringBoot就会帮我们做了!
转换器和格式化器
找到格式化转换器:
@Bean
public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() {
// 拿到配置文件中的格式化规则
Format format = this.mvcProperties.getFormat();
WebConversionService conversionService = new WebConversionService((new DateTimeFormatters()).dateFormat(format.getDate()).timeFormat(format.getTime()).dateTimeFormat(format.getDateTime()));
this.addFormatters(conversionService);
return conversionService;
}
点进去this.mvcProperties.getFormat():
public WebMvcProperties.Format getFormat() {
return this.format;
}
点击this.format,跳转至:
@ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "spring.mvc"
)
public class WebMvcProperties {
private final WebMvcProperties.Format format;
}
可以看到在我们的WebMvcProperties文件中,我们可以通过application.properties文件手动配置它!
如果配置了自己的格式化方式,就会注册到Bean中生效,我们可以在配置文件中配置日期格式化的规则:
# Date format to use, for example `dd/MM/yyyy`.
spring.mvc.format.date
# Date-time format to use, for example `yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss`.
spring.mvc.format.date-time
# Time format to use, for example `HH:mm:ss`.
spring.mvc.format.time
其余的就不一一举例了,大家可以下去多研究探讨即可!
修改SpringBoot的默认配置
这么多的自动配置,原理都是一样的,通过这个WebMVC的自动配置原理分析,我们要学会一种学习方式,通过源码探究,得出结论;这个结论一定是属于自己的,而且一通百通。
SpringBoot的底层,大量用到了这些设计细节思想,所以,没事需要多阅读源码!得出结论;
SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(如果用户自己配置@bean),如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有就用自动配置的;
如果有些组件可以存在多个,比如我们的视图解析器,就将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来!
扩展使用SpringMVC 官方文档如下:
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
我们要做的就是编写一个@Configuration注解类,并且类型要为WebMvcConfigurer,还不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解;我们去自己写一个;我们新建一个包叫config,写一个类MyMvcConfig;
// 因为类型要求为WebMvcConfigurer,所以我们实现其接口
// 可以使用自定义类扩展MVC的功能
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
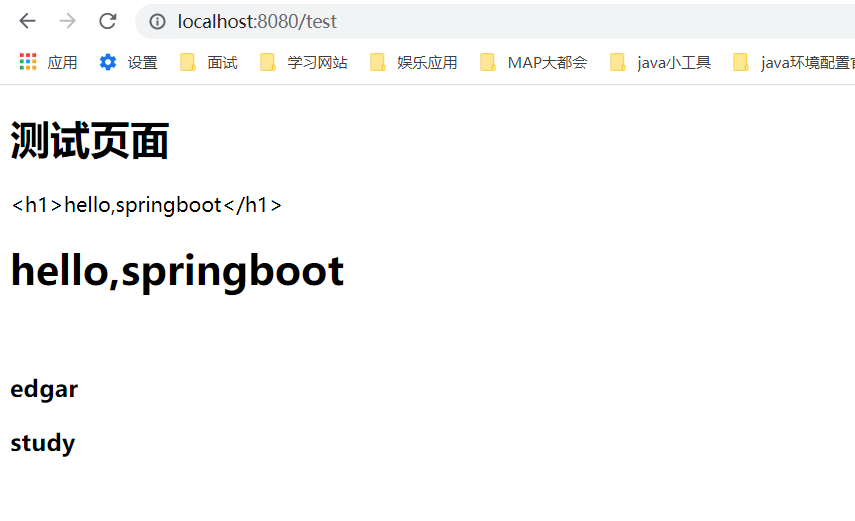
// 浏览器发送/test , 就会跳转到test页面;
registry.addViewController("/test").setViewName("test");
}
}
我们去浏览器访问一下:
确实也跳转过来了!所以说,我们要扩展SpringMVC,官方就推荐我们这么去使用,既保SpringBoot留所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置!
我们可以去分析一下原理:
1、WebMvcAutoConfiguration 是 SpringMVC的自动配置类,里面有一个类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
2、这个类上有一个注解,在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
3、我们点进EnableWebMvcConfiguration这个类看一下,它继承了一个父类:DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
这个父类中有这样一段代码:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
// 从容器中获取所有的webmvcConfigurer
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
// ......
}
所以得出结论:所有的WebMvcConfiguration都会被作用,不止Spring自己的配置类,我们自己的配置类当然也会被调用;
全面接管SpringMVC
官方文档:
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC
you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
全面接管即:SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己去配置!
只需在我们的配置类中要加一个@EnableWebMvc。
我们看下如果我们全面接管了SpringMVC了,我们之前SpringBoot给我们配置的静态资源映射一定会无效,我们可以去测试一下;
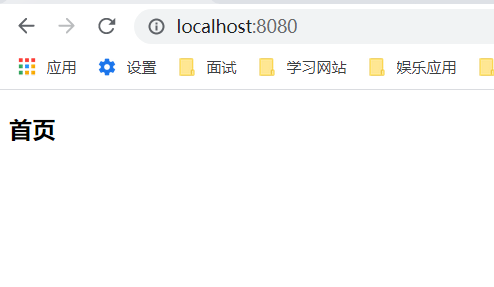
不加注解之前,访问首页:
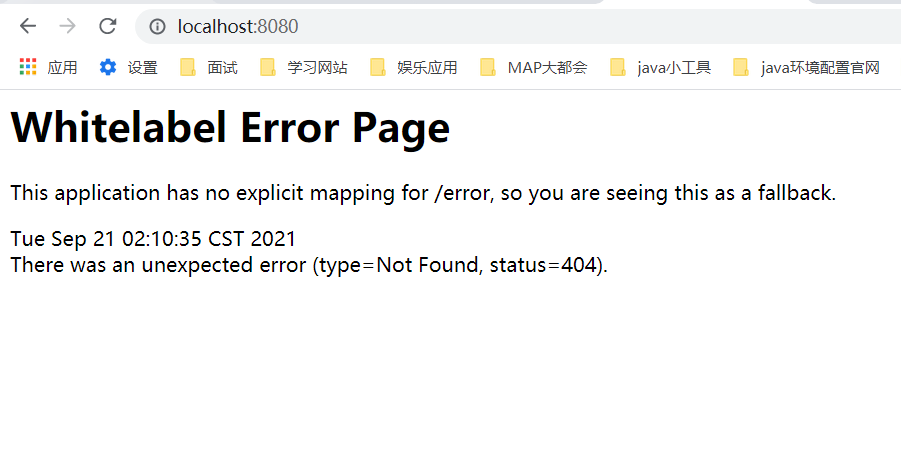
给配置类加上注解:@EnableWebMvc
我们发现所有的SpringMVC自动配置都失效了!回归到了最初的样子;
当然,我们开发中,不推荐使用全面接管SpringMVC
思考问题?为什么加了一个注解,自动配置就失效了!我们看下源码:
1、这里发现它是导入了一个类,我们可以继续进去看
@Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class})
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}
2、它继承了一个父类 WebMvcConfigurationSupport
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
// ......
}
3、我们来回顾一下Webmvc自动配置类
@Configuration(
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(
type = Type.SERVLET
)
@ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class})
// ConditionalOnMissingBean 当Spring容器中不存在WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class的bean才为true
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class})
@AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638)
@AutoConfigureAfter({DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class})
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
// ......
}
总结:
@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来了,而WebMvcAutoConfiguration自动配置类要生效需要Spring容器中不存在WebMvcConfigurationSupport的bean,


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号