第十二周学习总结
其他容器
1.JPanel
| 方法 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public JPanel | 构造 | 创建一个默认的JPanel对象,使用流布局管理 |
| public JPanel(LayoutManager layout) | 构造 | 创建应该指定流布局管理的JPanel对象 |
JPanel是Java图形化界面中最常使用的容器。
package.图形界面;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class JPanelDemo01{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame=newJFrame("Welcome TO MLDN"); //实例化窗体对象
JPanel pan=new JPanel(); //实例化JPanel对象
pan.add(new JLabel("标签-A"); //加入标签组件
pan.add(new JLabel("标签-B"); //加入标签组件
pan.add(new JLabel("标签-C"); //加入标签组件
pan.add(new JButton("按键-x")); //加入按钮组件
pan.add(new JButton("按键-y")); //加入按钮组件
pan.add(new JButton("按键-z")); //加入按钮组件
frame.add(pan); //将JPanel加入到窗体
frame.pack();
frame.setLocation(300,200);
frame.setVisible(true);
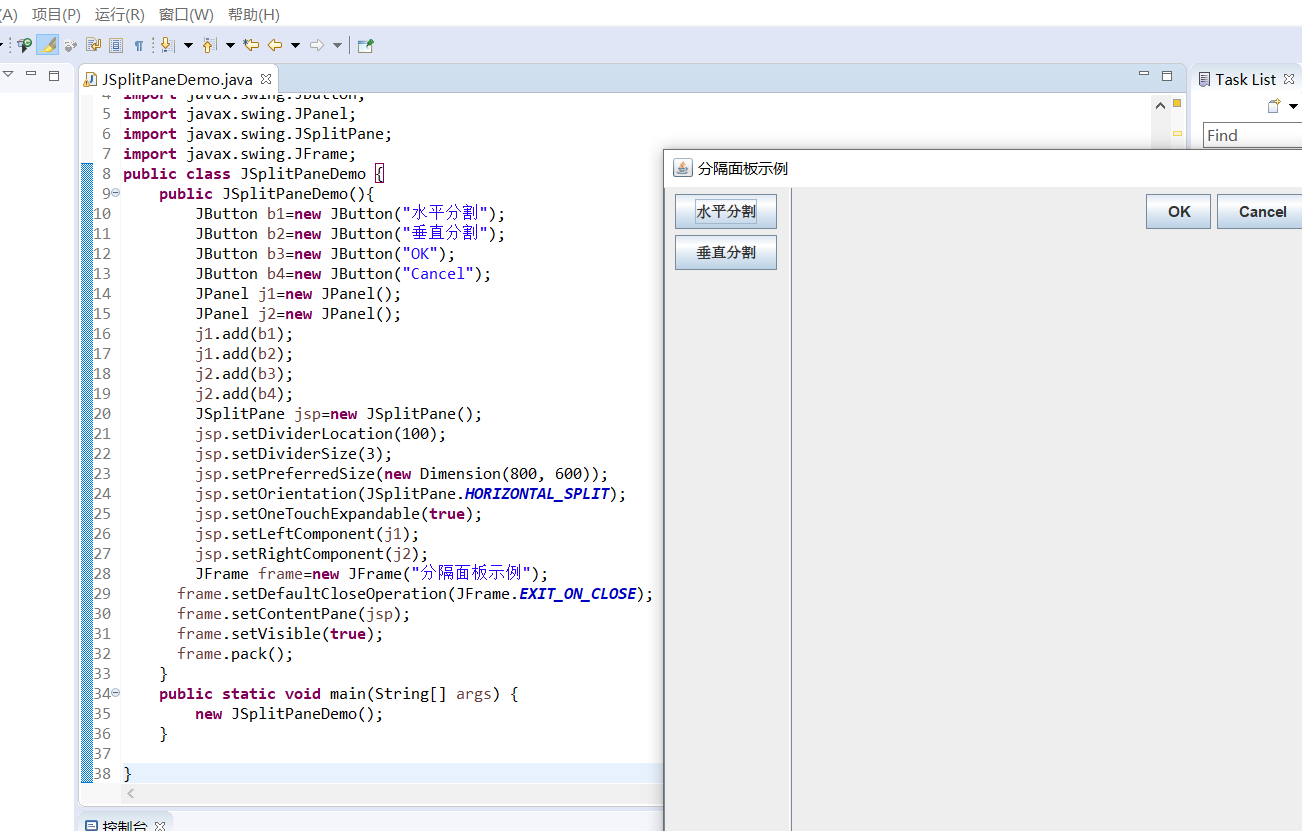
2.JSplitPane
JSplitPane主要功能是分割面吧,可以将应该窗体分割为两个子窗体,可以是水平排列也可以是垂直排列
| 方法及常量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public static final int HORIZONTAL_SPLIT | 常量 | 表示水平分割 |
| public static final int VERTICAL_SPLIT | 常量 | 表示垂直分割 |
| public JSplitPane(int newOrientation) | 构造 | 创建对象,并指明分割方式 |
| public JSplitPane(int newOrientation,boolean newContinuousLayout,Compoment NewLeftComponent,Compoment NewRightComponent) | 构造 | 创建对象、指明分割方式、分割条改变是否重绘图形以及两端的显示组件 |
| public void setDividerLocation(double proportionalLocation) | 普通 | 设置分割条的位置,按百分比 |
| public void setOneTouchExpandable(boolean NewValue) | 普通 | 设置是否提供快速展开/折叠的功能 |
| public void setDividerSize(int newSize) | 普通 | 设置分割条大小 |
package 图形界面;
import java.awt.Button;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JSplitPane;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class JSplitPaneDemo {
public JSplitPaneDemo(){
JButton b1=new JButton("水平分割");
JButton b2=new JButton("垂直分割");
JButton b3=new JButton("OK");
JButton b4=new JButton("Cancel");
JPanel j1=new JPanel();
JPanel j2=new JPanel();
j1.add(b1);
j1.add(b2);
j2.add(b3);
j2.add(b4);
JSplitPane jsp=new JSplitPane();
jsp.setDividerLocation(100);
jsp.setDividerSize(3);
jsp.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(800, 600));
jsp.setOrientation(JSplitPane.HORIZONTAL_SPLIT);
jsp.setOneTouchExpandable(true);
jsp.setLeftComponent(j1);
jsp.setRightComponent(j2);
JFrame frame=new JFrame("分隔面板示例");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setContentPane(jsp);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.pack();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new JSplitPaneDemo();
}
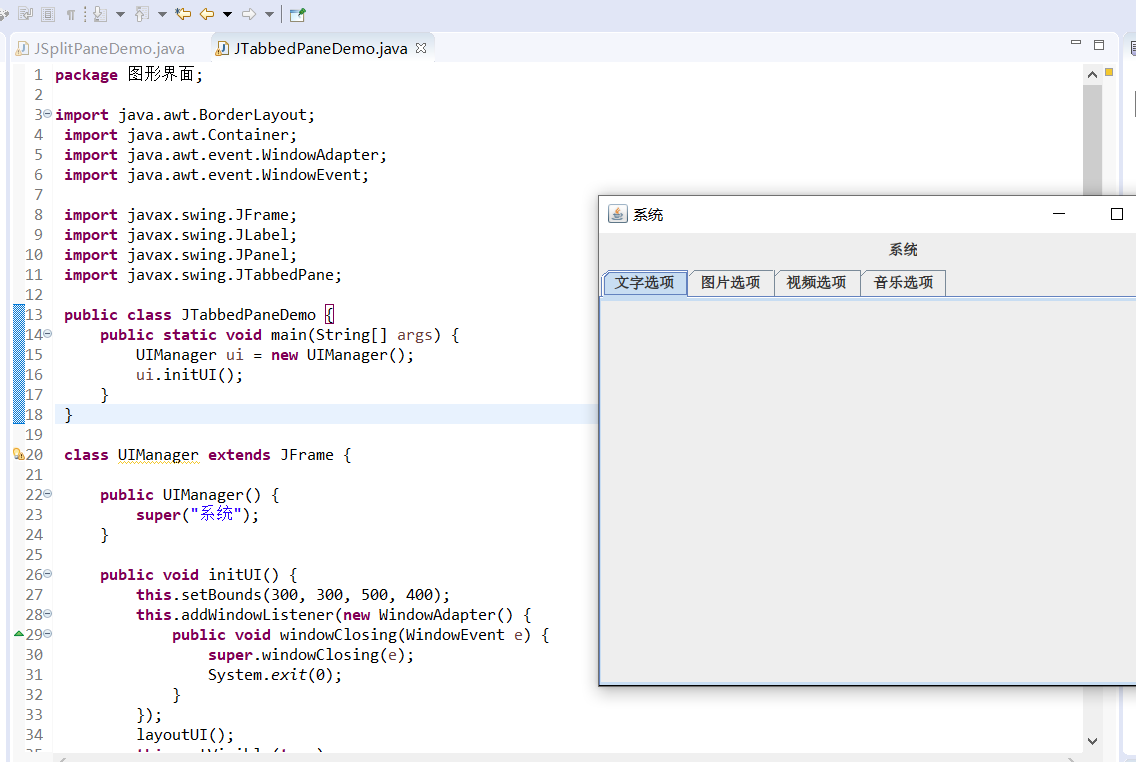
3.JTabbedPane
| 方法及常量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| static final int TOP | 常量 | 表示指向框顶部位置 |
| static final int BOTTOM | 常量 | 表示指向框底部位置 |
| static final int LEFT | 常量 | 表示指向框左部位置 |
| static final int RIGHT | 常量 | 表示指向框右部位置 |
| public JTabbedPane(int tabPlacement) | 构造 | 创建对象,并指定选项卡布局 |
| public void addTab(String title,Component component) | 普通 | 添加一个有标题,而没有图标的组件 |
| public void addTab(String title,Icon icon,Component component) | 普通 | 添加一个有标题,有图标的组件 |
| public void addTab(String title,Icon icon,Component component,String tip) | 普通 | 添加一个有标题,有图标,有提示信息的组件 |
package 图形界面;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTabbedPane;
public class JTabbedPaneDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UIManager ui = new UIManager();
ui.initUI();
}
}
class UIManager extends JFrame {
public UIManager() {
super("系统");
}
public void initUI() {
this.setBounds(300, 300, 500, 400);
this.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
super.windowClosing(e);
System.exit(0);
}
});
layoutUI();
this.setVisible(true);
}
private void layoutUI() {
// 对象实例化
JTabbedPane tab = new JTabbedPane(JTabbedPane.TOP);
// 容器
Container container = this.getLayeredPane();
// 对象化面板
JPanel combop = new JPanel();
JPanel p1 = new JPanel();
JPanel p2 = new JPanel();
JPanel p3 = new JPanel();
JPanel p4 = new JPanel();
tab.add(p1, "文字选项");
tab.add(p2, "图片选项");
tab.add(p3, "视频选项");
tab.add(p4, "音乐选项");
combop.add(new JLabel("系统"));
container.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
container.add(combop, BorderLayout.NORTH);
container.add(tab, BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
}
4.JScrollPane
JScrollPane 面板是带滚动条的面板,它也是一种容器,但是 JScrollPane 只能放置一个组件,并不可以使用布局管理器。如果需要在 JScrollPane 面板上放置多个组件,需要将多个组件放置在 JPanel 上,然后将 JPanel 面板作为一个整体组件添加在 JScrollPane 组件上。
public class JscrollPaneDemo extends JFrame{
private JPanel contentPane;
private JScrollPane scrollPane;
private JTextArea textArea;
public JscrollPaneDemo(){
contentPane=new JPanel();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5,5,5,5));
contentPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout(0,0));
this.setContentPane(contentPane);
scrollPane=new JScrollPane();
contentPane.add(scrollPane,BorderLayout.CENTER);
textArea=new JTextArea();
//scrollPane.add(textArea);
scrollPane.setViewportView(textArea);
this.setTitle("滚动面板使用");
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setBounds(100, 100, 250, 200);
this.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String []args){
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
JscrollPaneDemo example=new JscrollPaneDemo();
}
}
5.JDesktopPane与JInternalFrame
JDesktopPane规定了一个父窗体的基本形式而JInternalFrame规定了各个子窗体,JInternalFrame需要加入到JDesktopPane中
JDesktopPane:
| 方法及常量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public JDesktopPane() | 构造 | 创建一个JDesktopPane()对象 |
| public void setSelectedFrame(JInternalFrame f) | 普通 | 设置此JDesktopPane中当前活动的JInternalFrame |
JInternalFrame:
| 方法及常量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public JInternalFrame(String title) | 构造 | 创建不可以调整大小的、不可关闭的、不可最大化的、不可图标化的、具有指定标题的JInternalFrame |
| public JInternalFrame(String title,boolean resizable | 构造 | 创建不可关闭的、不可最大化的、不可图标化的、以及具有指定标题和可以调整大小的JInternalFrame |
| public JInternalFrame(String title,boolean resizable,boolean closable,boolean maximizable,boolean iconifiable | 构造 | 创建可调整、可关闭、可最大化、可图标化的JInternalFrame |
事件处理
事件和监听器
在Swing编程中,所有事件类都是EventObject的子类
public class EventObject extends Object implements Serializable{
public EventObject(Object source){ //构造一个发生事件的对象
{
public Object getSource(){ //返回一个事件对象
}
public String toString(){ //得到信息
}
}
窗体事件
WindowListener是专门处理窗体事件的监听接口
| 方法及常量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) | 普通 | 将窗口变为活动窗口时触发 |
| void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) | 普通 | 将窗口变为不活动窗口时触发 |
| void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) | 普通 | 将窗口政治关闭时触发 |
| void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) | 普通 | 将窗口关闭时触发 |
| void windowIconified(WindowEvent e) | 普通 | 窗口最小化时触发 |
| void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e) | 普通 | 窗口最小化恢复正常时触发 |
| void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) | 普通 | 窗口打开时触发 |
package 图形界面;
import java.awt.TextArea;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Test {
final static int x=100;
final static int y=50;
final static int width=500;
final static int height=300;
static TextArea text;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
text=new TextArea();
JFrame f = new JFrame();
f.add(text);
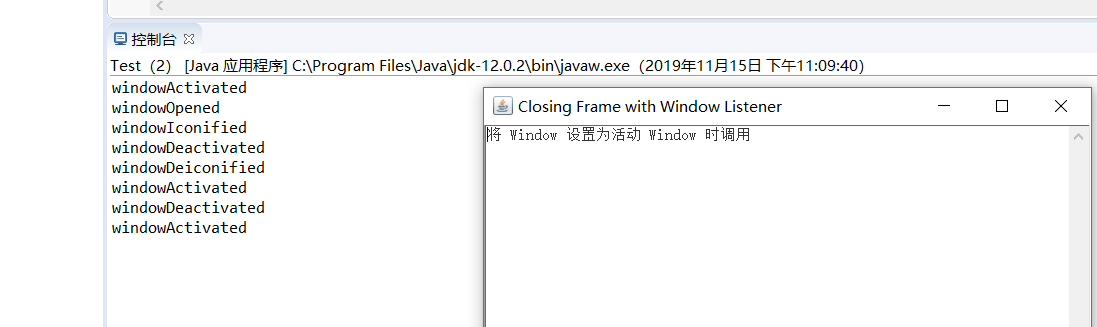
f.setTitle("Closing Frame with Window Listener");
f.setBounds(x,y,width,height);
f.addWindowListener(new MyWindowListener());
f.setVisible(true);
}
static class MyWindowListener extends WindowAdapter {
@Override
public void windowOpened(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowOpened");
text.setText("窗口首次变为可见时调用");
}
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowClosing");
text.setText("用户试图从窗口的系统菜单中关闭窗口时调用");
}
@Override
public void windowClosed(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowClosed");
text.setText("因对窗口调用 dispose 而将其关闭时调用");
}
@Override
public void windowIconified(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowIconified");
text.setText("窗口从正常状态变为最小化状态时调用");
}
@Override
public void windowDeiconified(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowDeiconified");
text.setText("窗口从最小化状态变为正常状态时调用");
}
@Override
public void windowActivated(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowActivated");
text.setText("将 Window 设置为活动 Window 时调用");
}
@Override
public void windowDeactivated(WindowEvent e) {
System.out.println("windowDeactivated");
text.setText("当 Window 不再是活动 Window 时调用");
}
}
}
监听适配器
因为上面的事件处理器存在如果只需要对一个窗口事件操作,其他操作不进行可以吗,那还要覆写那么多方法吗,因为如果一个类实现接口,则必须覆写里面的全部抽象方法
现在我们有了Adapter(适配器)类
用户只要继承了此类,就可以根据自己的需要覆写方法
ActionListener接口方法
| 方法及常量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) | 普通 | 发生操作时调用 |



