第九周课程总结&实验报告(七)
第九周课程总结
取得设置线程名称
在Thread类中,可以通过 getName() 方法取得线程的名称,通过 setNmae()方法设置线程的名称
class MyThread implements Runnable{ //实现Runnable接口
public void run(){ //覆写接口中的run()方法
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){ //循环输出3次
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"运行,i="+i); //取得当前线程的名称
}
}
};
public class ThreadNameDemo{
public static void main(String args[]){
MyThread my =new MyThread(); //定义Runnable子类对象
new Thread(my).start(); //系统自动设置线程名称
new Thread(my,"线程-A").start(); //手工设置线程名称
new Thread(my,"线程-B").start();
new Thread(my).start();
new Thread(my).start();
}
}
由上可知,在Thread类中必然存在一个static类型的属性,用于为线程自动命名
判断线程是否启动
因为线程通过Thread类之中的start()方法通知CPU这个线程已经准备好启动,然后就等待分配CPU资源,运行此线程。在Java中可以使用isAlive()方法来测试线程是否已经启动而且还在运行
线程的强制运行
可以使用join()方法让一个线程强制运行。在线程强制运行期间 其他线程无法运行,必须等待此线程完成之后才可以继续执行
线程的休眠
可以直接使用Thread.sleep()方法即可实现
中断线程
当一个线程运行时,另外一个线程可以直接通过interrupt()方法,中断其运行状态
线程的优先级
在Java线程操作中,哪个线程优先级高就有可能先被执行 所以可以使用 setPriority() 方法可以设置一个线程的优先级
| 定义 | 描述 | 表示的常量 |
|---|---|---|
| public static final int MIN_PRIORITY | 最低优先级 | 1 |
| public static final int NORM_PRIORITY | 中等优先级,是线程的默认优先级 | 5 |
| public static final int MAX_PRIORITY | 最高优先级 | 10 |
线程的礼让
使用yield()方法可以将一个线程的操作暂时让给其他线程执行
Java IO
操作文件的类-----File
File类的构造方法
public File(String pathname) →实例化File类的时候,必须设置好路径
| 序号 | 方法或常量 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | public static final String pathSeparator | 常量 | 表示路径的分隔符(windows 是:";") |
| 2 | public final String separator | 常量 | 表示路径的分隔符(windows 是:"") |
| 3 | public File(String pathname) | 构造 | 创建File类对象,传入完整路径 |
| 4 | public File(File parent,String child) | 构造 | 根据指定的父路径创建子文件 |
| 5 | public boolean createNewFile() throws IOException | 普通 | 创建新文件 |
| 6 | public boolean delete() | 普通 | 删除文件 |
| 7 | public boolean exists() | 普通 | 判断文件是否存在 |
| 8 | public boolean isDirectory() | 普通 | 判断给定的路径是否是一个目录 |
| 9 | public long length() | 普通 | 返回文件的大小 |
| 10 | public String[] list() | 普通 | 列出指定目录的全部内容,只是列出了名称 |
| 11 | public File[] listFiles() | 普通 | 列出指定目录的全部内容,会列出路径 |
| 12 | public boolean mkdir() | 普通 | 创建一个目录 |
| 13 | public boolean mkdirs() | 普通 | 创建多级目录 |
| 14 | public boolean renameTo(File dest) | 普通 | 为已有的文件重新命名 |
| 15 | public long lastModified | 普通 | 取得文件的最后一次修改日期时间 |
| 16 | public File getParentFile() | 普通 | 取得当前路径的父路径 |
可以使用list()方法列出一个目录中的全部内容
实验报告(七)
实验任务详情:
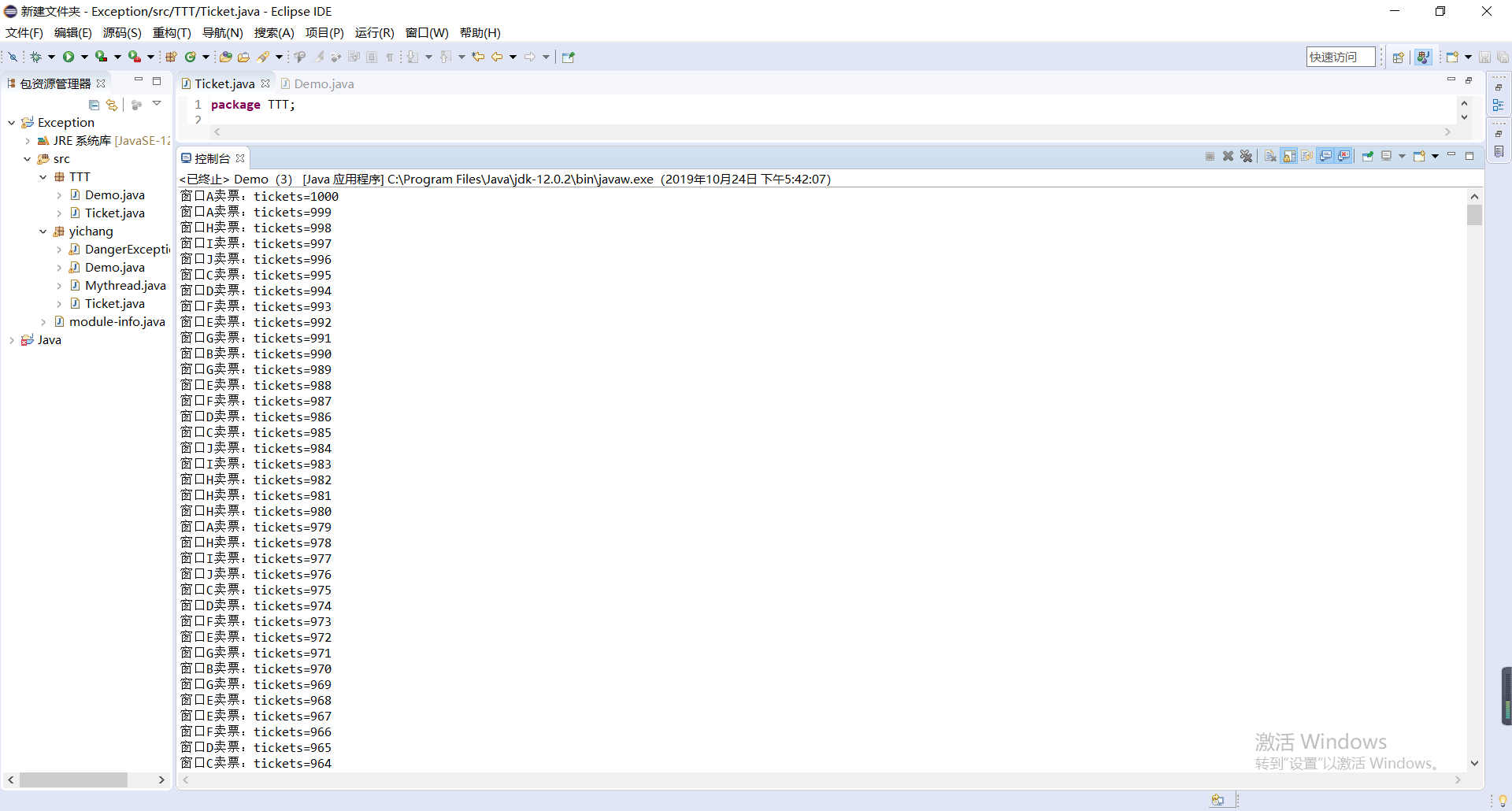
完成火车站售票程序的模拟。
要求:
(1)总票数1000张;
(2)10个窗口同时开始卖票;
(3)卖票过程延时1秒钟;
(4)不能出现一票多卖或卖出负数号票的情况。
源代码
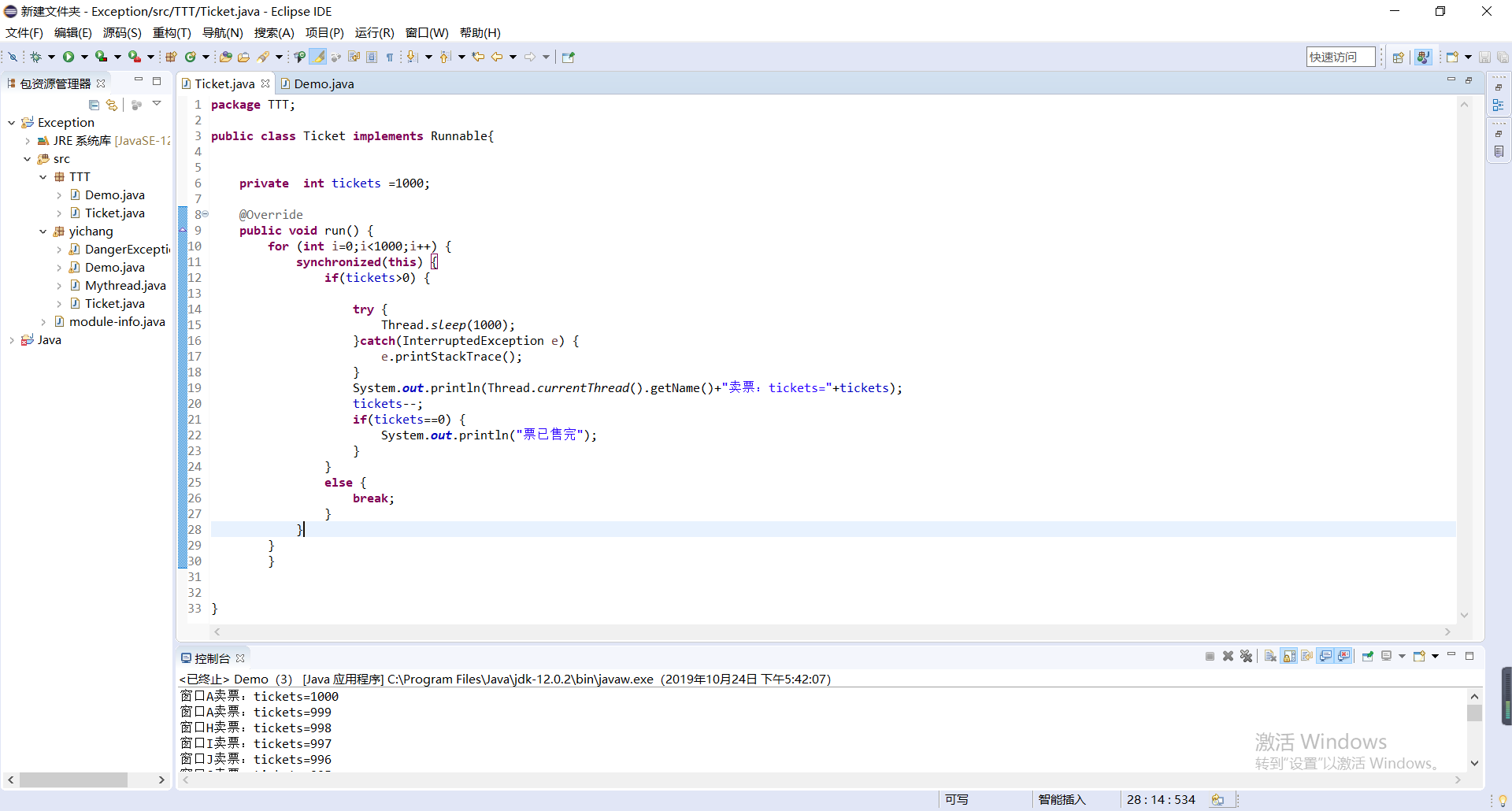
package TTT;
public class Ticket implements Runnable{
private int tickets =1000;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<1000;i++) {
synchronized(this) {
if(tickets>0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖票:tickets="+tickets);
tickets--;
if(tickets==0) {
System.out.println("票已售完");
}
}
else {
break;
}
}
}
}
};
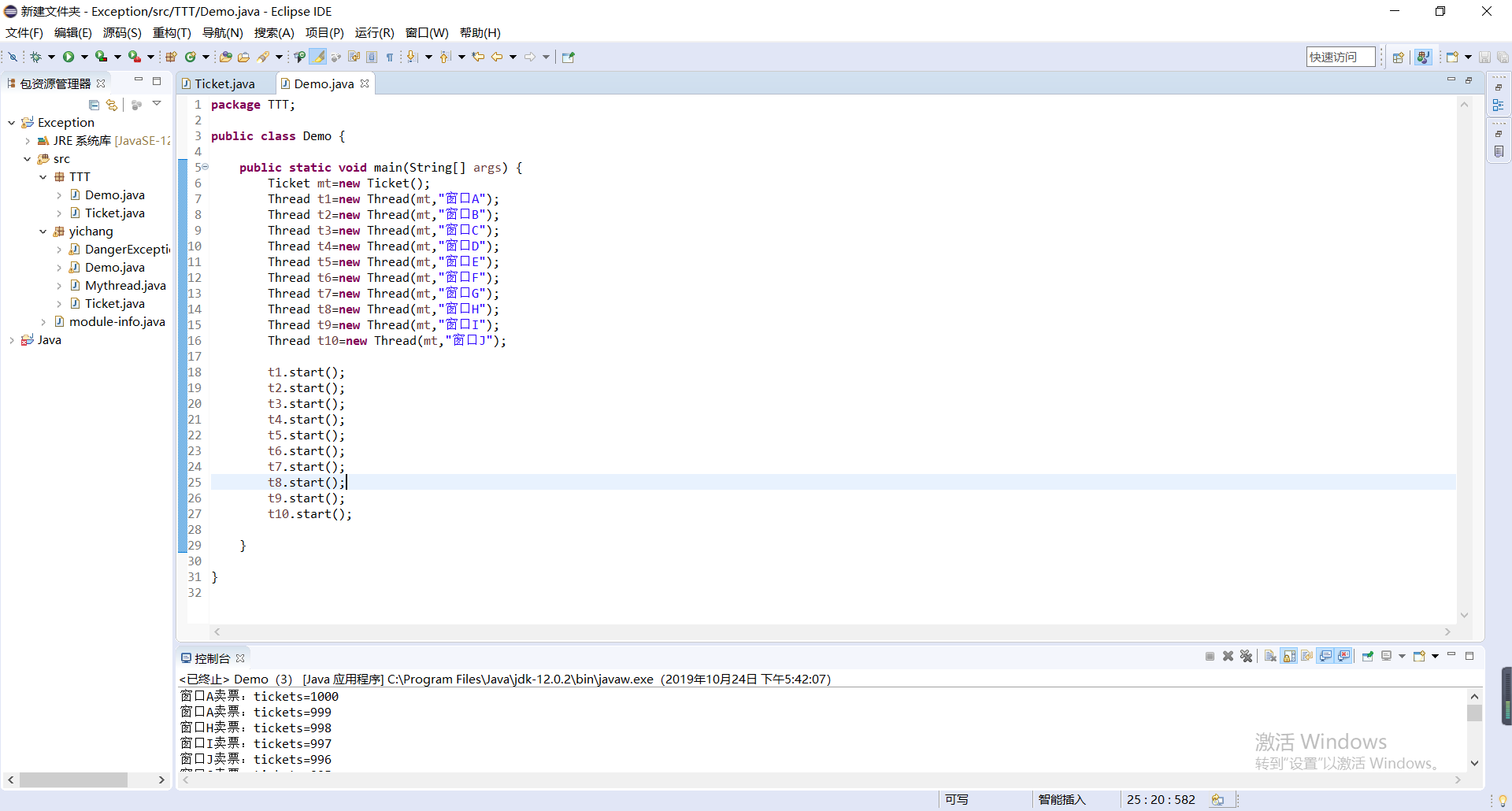
package TTT;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket mt=new Ticket();
Thread t1=new Thread(mt,"窗口A");
Thread t2=new Thread(mt,"窗口B");
Thread t3=new Thread(mt,"窗口C");
Thread t4=new Thread(mt,"窗口D");
Thread t5=new Thread(mt,"窗口E");
Thread t6=new Thread(mt,"窗口F");
Thread t7=new Thread(mt,"窗口G");
Thread t8=new Thread(mt,"窗口H");
Thread t9=new Thread(mt,"窗口I");
Thread t10=new Thread(mt,"窗口J");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
t6.start();
t7.start();
t8.start();
t9.start();
t10.start();
}
}
截图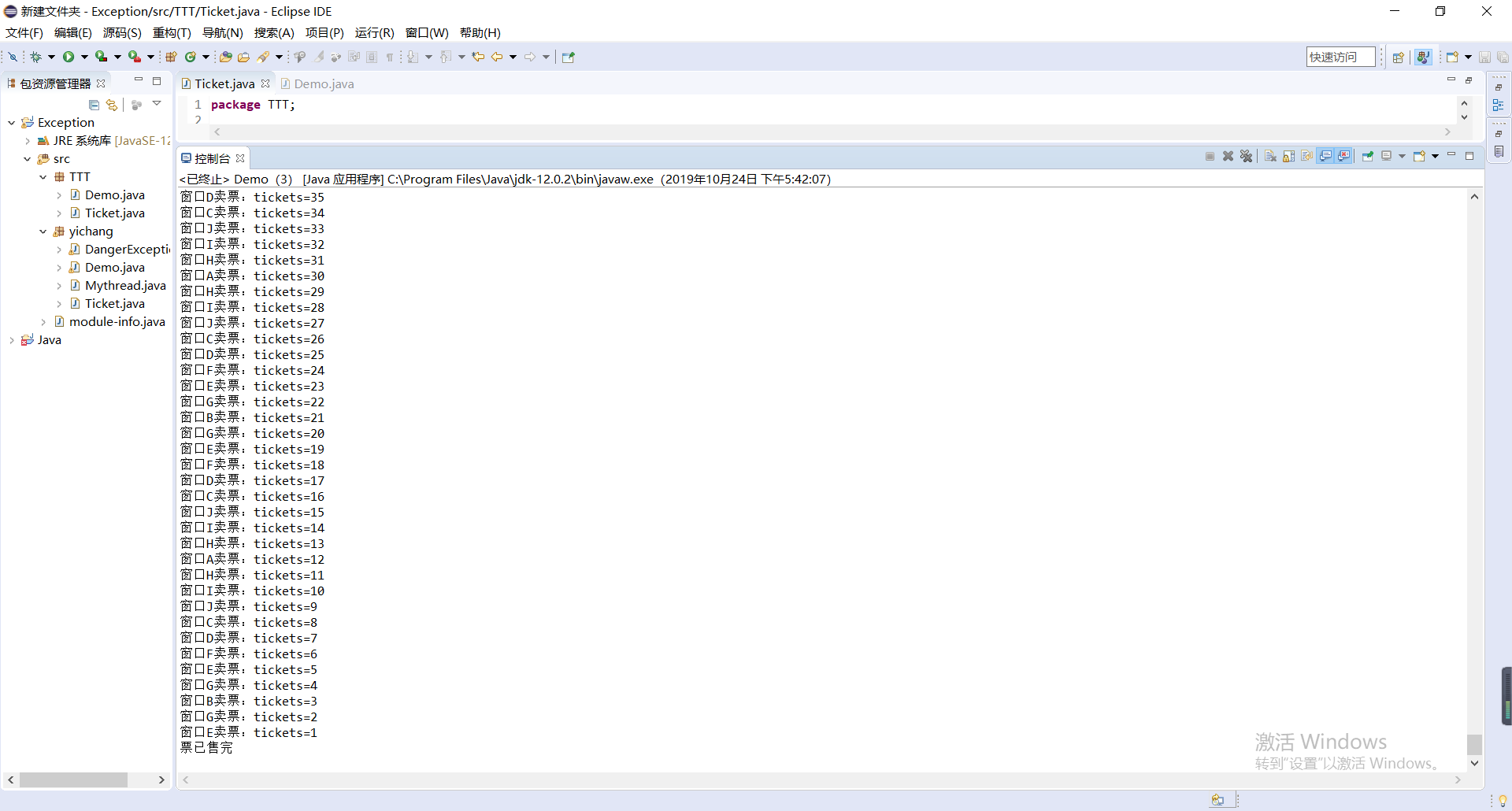


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号