SqlSession与SqlSessionFactory到底是什么关系?
1. SqlSession和SqlSessionFactory的接口定义
SqlSession:
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
<T> T selectOne(String var1);
<T> T selectOne(String var1, Object var2);
<E> List<E> selectList(String var1);
<E> List<E> selectList(String var1, Object var2);
<E> List<E> selectList(String var1, Object var2, RowBounds var3);
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String var1, String var2);
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String var1, Object var2, String var3);
<K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String var1, Object var2, String var3, RowBounds var4);
void select(String var1, Object var2, ResultHandler var3);
void select(String var1, ResultHandler var2);
void select(String var1, Object var2, RowBounds var3, ResultHandler var4);
int insert(String var1);
int insert(String var1, Object var2);
int update(String var1);
int update(String var1, Object var2);
int delete(String var1);
int delete(String var1, Object var2);
void commit();
void commit(boolean var1);
void rollback();
void rollback(boolean var1);
List<BatchResult> flushStatements();
void close();
void clearCache();
Configuration getConfiguration();
<T> T getMapper(Class<T> var1);
Connection getConnection();
}SqlSession,数据库的C、R、U、D及事务处理接口,你懂的。
SqlSessionFactory:
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSession openSession();
SqlSession openSession(boolean var1);
SqlSession openSession(Connection var1);
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel var1);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType var1);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType var1, boolean var2);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType var1, TransactionIsolationLevel var2);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType var1, Connection var2);
Configuration getConfiguration();
}不解释,你懂的。
2. SqlSession和SqlSessionFactory的类结构图
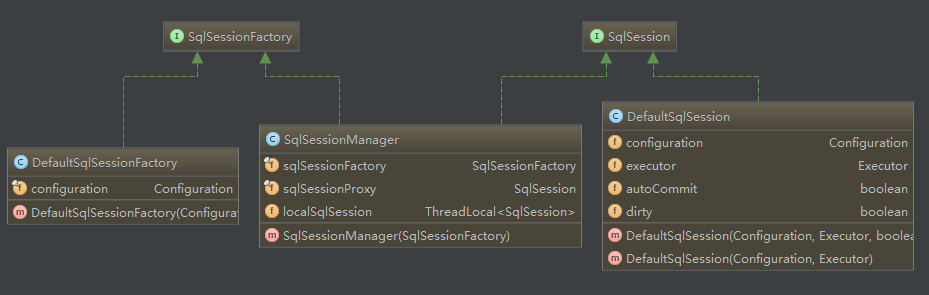
(Made In Intellij Idea IDE)
SqlSession实现类:DefaultSqlSession和SqlSessionManager
SqlSessionFactory实现类:DefaultSqlSessionFactory和SqlSessionManager
3. DefaultSqlSession和DefaultSqlSessionFactory源码分析
org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.java部分源码:
private Configuration configuration;
private Executor executor;
@Override
public void select(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}总结:似乎一切的一切,都是从配置对象Configuration中取出材料来,委托给执行器Executor去处理。
org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java部分源码:
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
//...创建一个DefaultSqlSession并返回,这里出现了那个贯穿Mybatis执行流程的Executor接口,非常重要的接口,后续会对其进行仔细分析。
4. SqlSessionManager源码分析(重点)
SqlSessionManager同时实现了SqlSession和SqlSessionFactory接口。
org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionManager.java部分源码。
public class SqlSessionManager implements SqlSessionFactory, SqlSession {
private final SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
// proxy
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
// 保持线程局部变量SqlSession的地方
private ThreadLocal<SqlSession> localSqlSession = new ThreadLocal<SqlSession>();
private SqlSessionManager(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
// 这个proxy是重点
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{SqlSession.class},
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
public static SqlSessionManager newInstance(Reader reader) {
return new SqlSessionManager(new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, null, null));
}
public static SqlSessionManager newInstance(Reader reader, String environment) {
return new SqlSessionManager(new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, environment, null));
}
//...
// 设置线程局部变量sqlSession的方法
public void startManagedSession() {
this.localSqlSession.set(openSession());
}
public void startManagedSession(boolean autoCommit) {
this.localSqlSession.set(openSession(autoCommit));
}
//...
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
return sqlSessionProxy.<T> selectOne(statement, parameter);
}
@Override
public <K, V> Map<K, V> selectMap(String statement, String mapKey) {
return sqlSessionProxy.<K, V> selectMap(statement, mapKey);
}
//...变量sqlSessionFactory:相当于DefaultSqlSessionFactory的实例(不是proxy)。
变量sqlSessionProxy:是JDK动态代理出来的proxy(是proxy)。
动态代理的目的,是为了通过拦截器InvocationHandler,增强目标target的方法调用。
target:DefaultSqlSession的实例。
所有的调用sqlSessionProxy代理对象的C、R、U、D及事务方法,都将经过SqlSessionInterceptor拦截器,并最终由目标对象target实际完成数据库操作。
org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionInterceptor.java的源码。
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
public SqlSessionInterceptor() {
// Prevent Synthetic Access
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
final SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionManager.this.localSqlSession.get();
if (sqlSession != null) {
try {
// 1、存在线程局部变量sqlSession(不提交、不回滚、不关闭,可在线程生命周期内,自定义sqlSession的提交、回滚、关闭时机,达到复用sqlSession的效果)
return method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
} else {
// 2、不存在线程局部变量sqlSession,创建一个自动提交、回滚、关闭的SqlSession(提交、回滚、关闭,将sqlSession的生命周期完全限定在方法内部)
final SqlSession autoSqlSession = openSession();
try {
final Object result = method.invoke(autoSqlSession, args);
autoSqlSession.commit();
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
autoSqlSession.rollback();
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
} finally {
autoSqlSession.close();
}
}
}
}注意:SqlSession的生命周期,必须严格限制在方法内部或者request范围(也称之为Thread范围),线程不安全,线程之间不能共享。(官方文档有明确说明)
1、request范围使用SqlSession
sqlSessionManager.startManagedSession();
try {
sqlSessionManager.query1();
sqlSessionManager.query2();
sqlSessionManager.update1();
sqlSessionManager.update2();
//...
}catch (Throwable t) {
sqlSessionManager.rollback();
} finally {
sqlSessionManager.close();
}一次性执行了一系列的方法业务,最后统一异常回滚,统一关闭sqlSession,全程创建1次sqlSession,销毁1次sqlSession。只是个例子,具体如何使用线程本地变量sqlSession,完全取决于你自己。
2、method范围使用SqlSession
SqlSessionManager.query1();
SqlSessionManager.query2();以上伪代码,各自分别开启了一个SqlSession,并销毁了各自的SqlSession。即,创建了2次SqlSession,销毁了2次SqlSession。
注:SqlSessionManager似乎是废弃不使用的了,但是,它并不妨碍我们探究其源码
原文:https://my.oschina.net/zudajun/blog/665956



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号