cs61a 2021 fall cats
网址 https://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61a/fa21/proj/cats/
在github上面有一个写的更好的
https://github.com/y1cunhui/cs61A-2021Fall/blob/main/proj02-cats/cats.py
写这个pro的时候可以多注意题目给的函数,大部分都用的上
problem1:
这个小题意思就是从paragraphs中挑选符合select函数的字符,然后输出第k个。
部分测试:
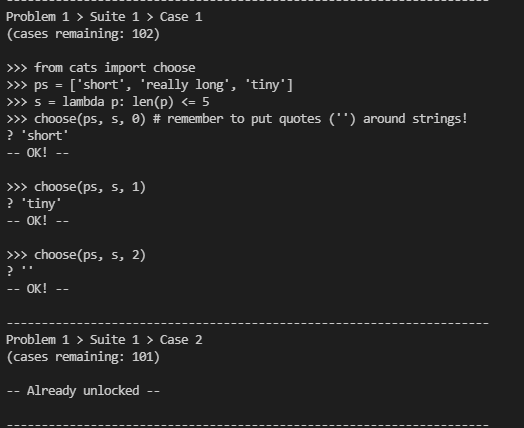
代码:
def choose(paragraphs, select, k):
"""Return the Kth paragraph from PARAGRAPHS for which SELECT called on the
paragraph returns True. If there are fewer than K such paragraphs, return
the empty string.
Arguments:
paragraphs: a list of strings
select: a function that returns True for paragraphs that can be selected
k: an integer
>>> ps = ['hi', 'how are you', 'fine']
>>> s = lambda p: len(p) <= 4
>>> choose(ps, s, 0)
'hi'
>>> choose(ps, s, 1)
'fine'
>>> choose(ps, s, 2)
''
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 1
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
num = 0
for i in paragraphs:
if select(i):
if num == k:
return i
else :
num += 1
return ''
# END PROBLEM 1
problem2:
这个小题意思是从传进来一句(paragraph),然后本身这个函数有一个list(a list of words related to a subject),如果这个paragraph中含有list中的单词就返回True,否则返回False
部分测试
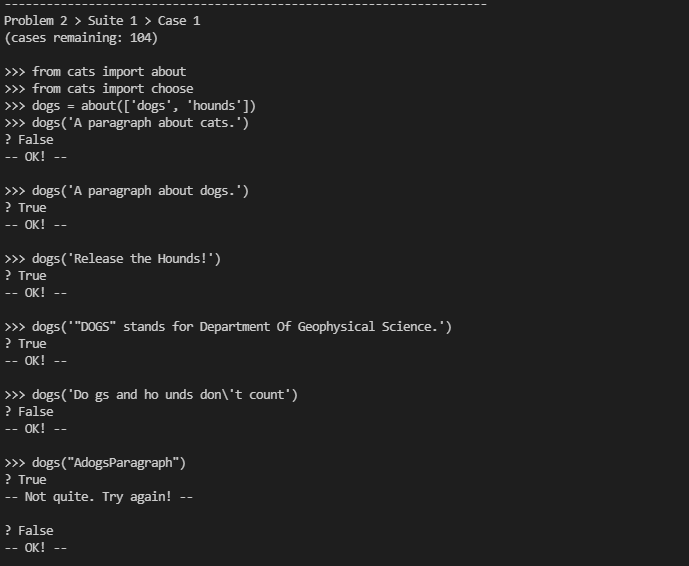
代码:
def about(topic):
"""Return a select function that returns whether
a paragraph contains one of the words in TOPIC.
Arguments:
topic: a list of words related to a subject
>>> about_dogs = about(['dog', 'dogs', 'pup', 'puppy'])
>>> choose(['Cute Dog!', 'That is a cat.', 'Nice pup!'], about_dogs, 0)
'Cute Dog!'
>>> choose(['Cute Dog!', 'That is a cat.', 'Nice pup.'], about_dogs, 1)
'Nice pup.'
"""
assert all([lower(x) == x for x in topic]), 'topics should be lowercase.'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 2
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
def func(para):
para = split(lower(remove_punctuation(para)))#remove_punctuatuion的作用是去掉标点符号
for i in para:
if i in topic:
return True
return False
return func
remove_punctuatuion函数的代码:
def remove_punctuation(s):
"""Return a string with the same contents as s, but with punctuation removed.
>>> remove_punctuation("It's a lovely day, don't you think?")
'Its a lovely day dont you think'
>>> remove_punctuation("Its a lovely day dont you think")
'Its a lovely day dont you think'
"""
punctuation_remover = str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation)
return s.strip().translate(punctuation_remover)
problem3:
这个题目意思就是给定两个字符列表一个type,一个reference,都为空就返回100,其中某一个为零就是返回0,
然后按照一一对应的方式,看type和reference中相等的个数有多少,然后用这个数字取比type的个数,输出百分比。(标点也算,转义符不算)
部分测试:
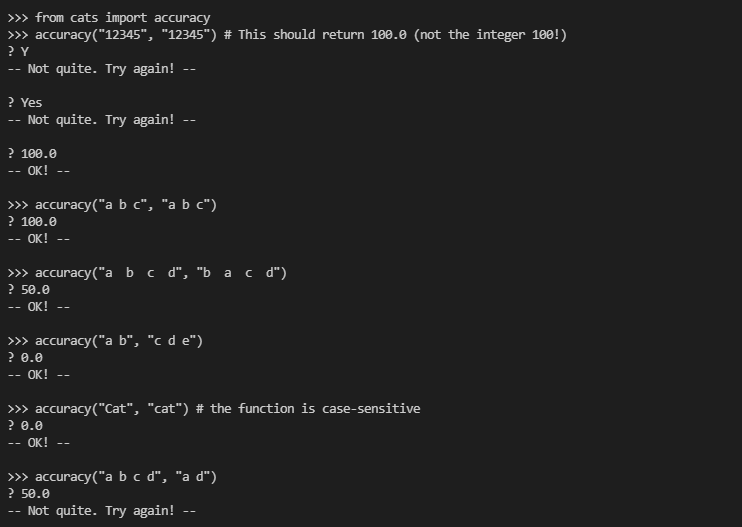
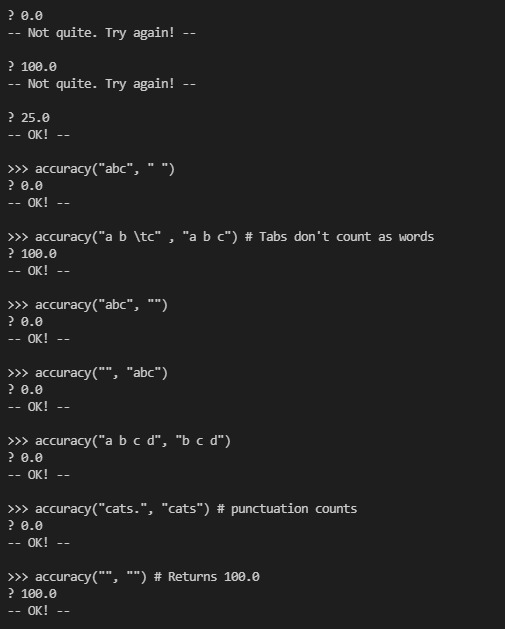
代码
def accuracy(typed, reference):
"""Return the accuracy (percentage of words typed correctly) of TYPED
when compared to the prefix of REFERENCE that was typed.
Arguments:
typed: a string that may contain typos
reference: a string without errors
>>> accuracy('Cute Dog!', 'Cute Dog.')
50.0
>>> accuracy('A Cute Dog!', 'Cute Dog.')
0.0
>>> accuracy('cute Dog.', 'Cute Dog.')
50.0
>>> accuracy('Cute Dog. I say!', 'Cute Dog.')
50.0
>>> accuracy('Cute', 'Cute Dog.')
100.0
>>> accuracy('', 'Cute Dog.')
0.0
>>> accuracy('', '')
100.0
"""
typed_words = split(typed)
reference_words = split(reference)
# BEGIN PROBLEM 3
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if len(reference_words) == 0 and len(typed_words) == 0:
return 100.0
if len(reference_words) == 0 or len(typed_words) == 0:
return 0.0
num = 0
ans = 0
for i in reference_words:
if i == typed_words[num]:
ans += 1
num += 1
if num == len(typed_words) :
break
return round(ans / len(typed_words) * 100, 10)#round函数不会保留最后面的零
# END PROBLEM 3
problem4:
这个题目意思就是输一个字符串,计算他的字符个数(算空格)然后以每五个字符算一个单词,第二个参数是耗时(秒),计算每分钟可以打多少单词
部分测试:
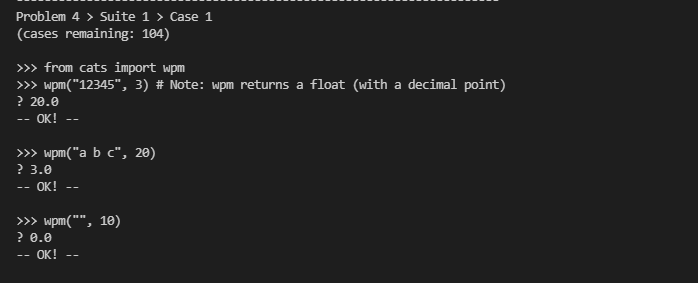
代码:
def wpm(typed, elapsed):
"""Return the words-per-minute (WPM) of the TYPED string.
Arguments:
typed: an entered string
elapsed: an amount of time in seconds
>>> wpm('hello friend hello buddy hello', 15)
24.0
>>> wpm('0123456789',60)
2.0
"""
assert elapsed > 0, 'Elapsed time must be positive'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 4
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
return round(len(typed) * 12 / elapsed, 10)
# END PROBLEM 4
problem5:
这个题目意思就是给定一个输入字符t和一个判断字符列表v,如果t在v里面就返回t如果不在,就用一个判断函数判断t与v里面每一个字符,差距返回一个数字,如果数字小于给定的limit就返回那个和
t判断字符,如果多个字符判断数字相等就返回第一个出现在列表里面的,如果都大于limit则返回t本身。
部分测试:
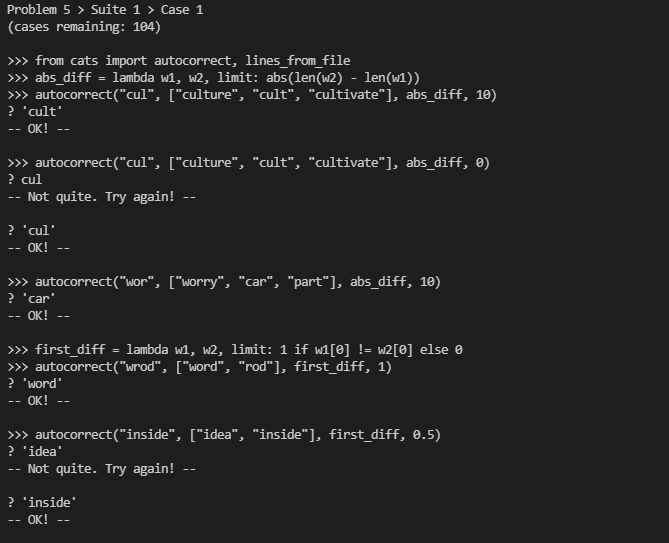
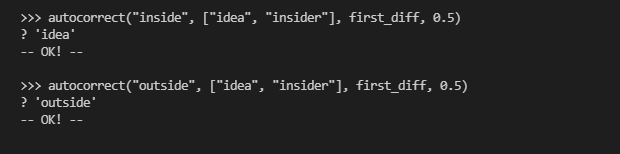
代码:
def autocorrect(typed_word, valid_words, diff_function, limit):
"""Returns the element of VALID_WORDS that has the smallest difference
from TYPED_WORD. Instead returns TYPED_WORD if that difference is greater
than LIMIT.
Arguments:
typed_word: a string representing a word that may contain typos
valid_words: a list of strings representing valid words
diff_function: a function quantifying the difference between two words
limit: a number
>>> ten_diff = lambda w1, w2, limit: 10 # Always returns 10
>>> autocorrect("hwllo", ["butter", "hello", "potato"], ten_diff, 20)
'butter'
>>> first_diff = lambda w1, w2, limit: (1 if w1[0] != w2[0] else 0) # Checks for matching first char
>>> autocorrect("tosting", ["testing", "asking", "fasting"], first_diff, 10)
'testing'
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 5
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
ans = float('inf')
lastans = ''
for i in valid_words:
if i == typed_word:
return typed_word
temp = diff_function(typed_word, i, limit)
if temp > limit:
continue
if ans > temp:
ans = temp
lastans = i
if lastans == '':
return typed_word
else :
return lastans
problem6:
这个题目的意思就是比较两个字符的差距,不同就修改,长短不一就加一个,这两个步骤都算一步,最后计算需要的步数,如果需要的步数大于limit,则需要立马结束递归。
部分测试:
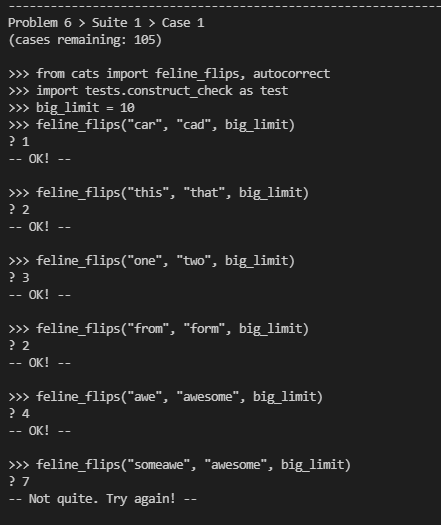
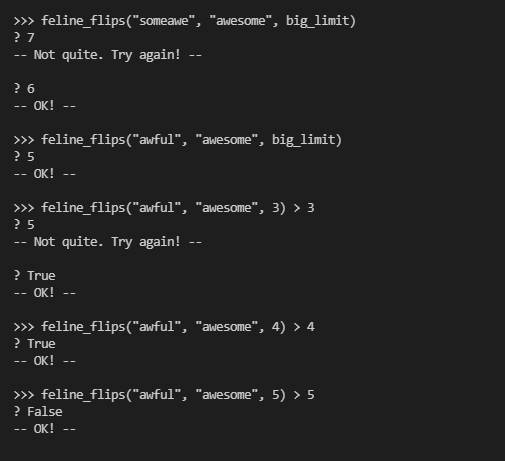
代码:
def feline_flips(start, goal, limit):
"""A diff function for autocorrect that determines how many letters
in START need to be substituted to create GOAL, then adds the difference in
their lengths and returns the result.
Arguments:
start: a starting word
goal: a string representing a desired goal word
limit: a number representing an upper bound on the number of chars that must change
>>> big_limit = 10
>>> feline_flips("nice", "rice", big_limit) # Substitute: n -> r
1
>>> feline_flips("range", "rungs", big_limit) # Substitute: a -> u, e -> s
2
>>> feline_flips("pill", "pillage", big_limit) # Don't substitute anything, length difference of 3.
3
>>> feline_flips("roses", "arose", big_limit) # Substitute: r -> a, o -> r, s -> o, e -> s, s -> e
5
>>> feline_flips("rose", "hello", big_limit) # Substitute: r->h, o->e, s->l, e->l, length difference of 1.
5
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 6
def myfunc(temp, temp_goal, ans):
if ans > limit:
return ans + 1
if temp == '':
return len(temp_goal) + ans
elif temp_goal == '':
return len(temp) + ans
elif temp[0] == temp_goal[0]:
return myfunc(temp[1:], temp_goal[1:], ans)
else:
return myfunc(temp[1:], temp_goal[1:], ans + 1)
if start[0] == goal[0]:
return myfunc(start[1:], goal[1:], 0)
else:
return myfunc(start[1:], goal[1:], 1)
# END PROBLEM 6
problem7:
这与第六题差不多,只不过他需要更加细致的更改,从三个选择,替换,删除,添加,选一种,以达到最后的修改次数最少,这里同样是用递归实现
部分测试:
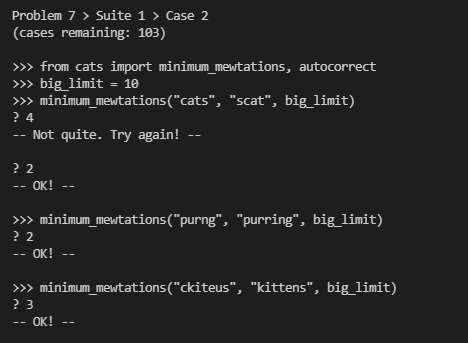
代码:
def minimum_mewtations(start, goal, limit):
"""A diff function that computes the edit distance from START to GOAL.
This function takes in a string START, a string GOAL, and a number LIMIT.
Arguments:
start: a starting word
goal: a goal word
limit: a number representing an upper bound on the number of editss
>>> big_limit = 10
>>> minimum_mewtations("cats", "scat", big_limit) # cats -> scats -> scat
2
>>> minimum_mewtations("purng", "purring", big_limit) # purng -> purrng -> purring
2
>>> minimum_mewtations("ckiteus", "kittens", big_limit) # ckiteus -> kiteus -> kitteus -> kittens
3
"""
def myfunc(s, g, ans):
if ans > limit:
return ans + 1
if s == '':
return ans + len(g)
if g == '':
return ans + len(s)
if s[0] == g[0]:
return myfunc(s[1:], g[1:], ans)
else:
return min(myfunc(s[1:], g, ans + 1), myfunc(g[0] + s[0:], g, ans + 1), myfunc(s[1:], g[1:], ans + 1))
return myfunc(start, goal, 0)
problem8:
这个题目意思就是,需要计算输入的字符和需要输入的字符的一个比值,然后打印出打字员的编号和完成度
部分测试:

代码:
def report_progress(sofar, prompt, user_id, upload):
"""Upload a report of your id and progress so far to the multiplayer server.
Returns the progress so far.
Arguments:
sofar: a list of the words input so far
prompt: a list of the words in the typing prompt
user_id: a number representing the id of the current user
upload: a function used to upload progress to the multiplayer server
>>> print_progress = lambda d: print('ID:', d['id'], 'Progress:', d['progress'])
>>> # The above function displays progress in the format ID: __, Progress: __
>>> print_progress({'id': 1, 'progress': 0.6})
ID: 1 Progress: 0.6
>>> sofar = ['how', 'are', 'you']
>>> prompt = ['how', 'are', 'you', 'doing', 'today']
>>> report_progress(sofar, prompt, 2, print_progress)
ID: 2 Progress: 0.6
0.6
>>> report_progress(['how', 'aree'], prompt, 3, print_progress)
ID: 3 Progress: 0.2
0.2
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 8
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
num = 0
for i in sofar:
if i == prompt[num]:
num += 1
else:
break
ans = num / len(prompt)
upload({'id': user_id, 'progress': round(ans,100)})
return round(ans,100)
# END PROBLEM 8
problem9:
部分测试:
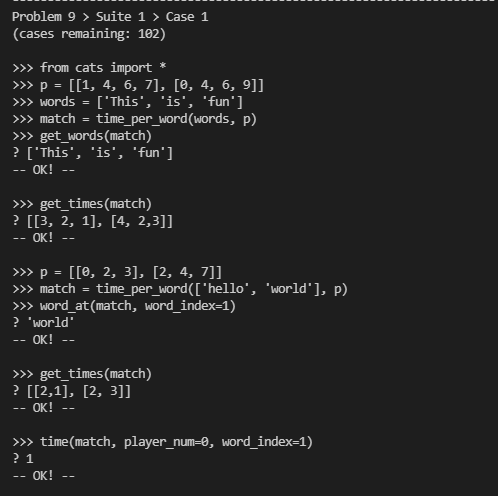
代码:
def time_per_word(words, times_per_player):
"""Given timing data, return a match data abstraction, which contains a
list of words and the amount of time each player took to type each word.
Arguments:
words: a list of words, in the order they are typed.
times_per_player: A list of lists of timestamps including the time
the player started typing, followed by the time
the player finished typing each word.
>>> p = [[75, 81, 84, 90, 92], [19, 29, 35, 36, 38]]
>>> match = time_per_word(['collar', 'plush', 'blush', 'repute'], p)
>>> get_words(match)
['collar', 'plush', 'blush', 'repute']
>>> get_times(match)
[[6, 3, 6, 2], [10, 6, 1, 2]]
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 9
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
match = []
match.append(words)
temp = []
for j in range(len(times_per_player)):
temp.append([])
for i in range(len(times_per_player[j])):
if i == len(times_per_player[j]) - 1:
break
temp[j].append(times_per_player[j][i + 1] - times_per_player[j][i])
match.append(temp)
return match
# END PROBLEM 9
problem10:
这个题目的意思就是给两个玩家的时间,输出这些单词中那些单词哪一个玩家输出的更快(如果一样就输出第一个出现的玩家)
部分测试:
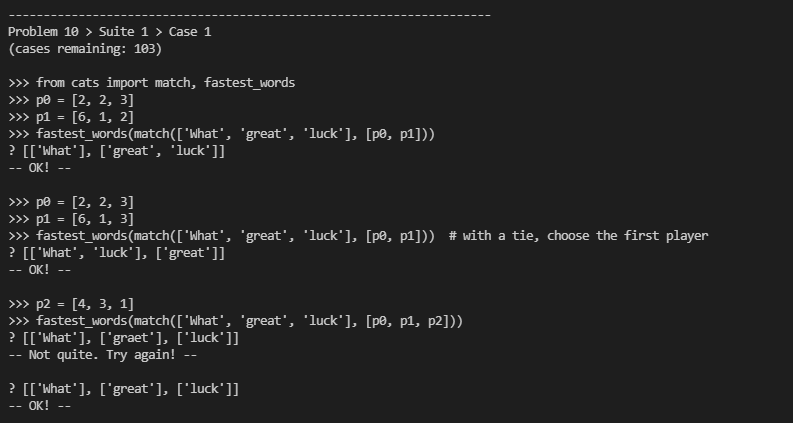
代码:
def fastest_words(match):
"""Return a list of lists of which words each player typed fastest.
Arguments:
match: a match data abstraction as returned by time_per_word.
>>> p0 = [5, 1, 3]
>>> p1 = [4, 1, 6]
>>> fastest_words(match(['Just', 'have', 'fun'], [p0, p1]))
[['have', 'fun'], ['Just']]
>>> p0 # input lists should not be mutated
[5, 1, 3]
>>> p1
[4, 1, 6]
"""
player_indices = range(len(get_times(match))) # contains an *index* for each player
word_indices = range(len(get_words(match))) # contains an *index* for each word
# BEGIN PROBLEM 10
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
ans_list = [[] for k in player_indices]
for i in word_indices:
times = [time(match, j, i) for j in player_indices]
# print("DEBUG: times:", times)
# print("DEBUG: index:",times.index(min(times)))
ans_list[times.index(min(times))].append(word_at(match, i))
# print("DEBUG: ", ans_list)
return ans_list
# END PROBLEM 10
全部代码:
"""Typing test implementation"""
from utils import lower, split, remove_punctuation, lines_from_file
from ucb import main, interact, trace
from datetime import datetime
###########
# Phase 1 #
###########
def choose(paragraphs, select, k):
"""Return the Kth paragraph from PARAGRAPHS for which SELECT called on the
paragraph returns True. If there are fewer than K such paragraphs, return
the empty string.
Arguments:
paragraphs: a list of strings
select: a function that returns True for paragraphs that can be selected
k: an integer
>>> ps = ['hi', 'how are you', 'fine']
>>> s = lambda p: len(p) <= 4
>>> choose(ps, s, 0)
'hi'
>>> choose(ps, s, 1)
'fine'
>>> choose(ps, s, 2)
''
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 1
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
num = 0
for i in paragraphs:
if select(i):
if num == k:
return i
else :
num += 1
return ''
# END PROBLEM 1
def about(topic):
"""Return a select function that returns whether
a paragraph contains one of the words in TOPIC.
Arguments:
topic: a list of words related to a subject
>>> about_dogs = about(['dog', 'dogs', 'pup', 'puppy'])
>>> choose(['Cute Dog!', 'That is a cat.', 'Nice pup!'], about_dogs, 0)
'Cute Dog!'
>>> choose(['Cute Dog!', 'That is a cat.', 'Nice pup.'], about_dogs, 1)
'Nice pup.'
"""
assert all([lower(x) == x for x in topic]), 'topics should be lowercase.'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 2
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
def func(para):
para = split(lower(remove_punctuation(para)))
for i in para:
if i in topic:
return True
return False
return func
# END PROBLEM 2
def accuracy(typed, reference):
"""Return the accuracy (percentage of words typed correctly) of TYPED
when compared to the prefix of REFERENCE that was typed.
Arguments:
typed: a string that may contain typos
reference: a string without errors
>>> accuracy('Cute Dog!', 'Cute Dog.')
50.0
>>> accuracy('A Cute Dog!', 'Cute Dog.')
0.0
>>> accuracy('cute Dog.', 'Cute Dog.')
50.0
>>> accuracy('Cute Dog. I say!', 'Cute Dog.')
50.0
>>> accuracy('Cute', 'Cute Dog.')
100.0
>>> accuracy('', 'Cute Dog.')
0.0
>>> accuracy('', '')
100.0
"""
typed_words = split(typed)
reference_words = split(reference)
# BEGIN PROBLEM 3
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
if len(reference_words) == 0 and len(typed_words) == 0:
return 100.0
if len(reference_words) == 0 or len(typed_words) == 0:
return 0.0
num = 0
ans = 0
for i in reference_words:
if i == typed_words[num]:
ans += 1
num += 1
if num == len(typed_words) :
break
return round(ans / len(typed_words) * 100, 10)#round函数不会保留最后面的零
# END PROBLEM 3
def wpm(typed, elapsed):
"""Return the words-per-minute (WPM) of the TYPED string.
Arguments:
typed: an entered string
elapsed: an amount of time in seconds
>>> wpm('hello friend hello buddy hello', 15)
24.0
>>> wpm('0123456789',60)
2.0
"""
assert elapsed > 0, 'Elapsed time must be positive'
# BEGIN PROBLEM 4
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
return round(len(typed) * 12 / elapsed, 10)
# END PROBLEM 4
###########
# Phase 2 #
###########
def autocorrect(typed_word, valid_words, diff_function, limit):
"""Returns the element of VALID_WORDS that has the smallest difference
from TYPED_WORD. Instead returns TYPED_WORD if that difference is greater
than LIMIT.
Arguments:
typed_word: a string representing a word that may contain typos
valid_words: a list of strings representing valid words
diff_function: a function quantifying the difference between two words
limit: a number
>>> ten_diff = lambda w1, w2, limit: 10 # Always returns 10
>>> autocorrect("hwllo", ["butter", "hello", "potato"], ten_diff, 20)
'butter'
>>> first_diff = lambda w1, w2, limit: (1 if w1[0] != w2[0] else 0) # Checks for matching first char
>>> autocorrect("tosting", ["testing", "asking", "fasting"], first_diff, 10)
'testing'
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 5
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
ans = float('inf')
lastans = ''
for i in valid_words:
if i == typed_word:
return typed_word
temp = diff_function(typed_word, i, limit)
if temp > limit:
continue
if ans > temp:
ans = temp
lastans = i
if lastans == '':
return typed_word
else :
return lastans
# END PROBLEM 5
def feline_flips(start, goal, limit):
"""A diff function for autocorrect that determines how many letters
in START need to be substituted to create GOAL, then adds the difference in
their lengths and returns the result.
Arguments:
start: a starting word
goal: a string representing a desired goal word
limit: a number representing an upper bound on the number of chars that must change
>>> big_limit = 10
>>> feline_flips("nice", "rice", big_limit) # Substitute: n -> r
1
>>> feline_flips("range", "rungs", big_limit) # Substitute: a -> u, e -> s
2
>>> feline_flips("pill", "pillage", big_limit) # Don't substitute anything, length difference of 3.
3
>>> feline_flips("roses", "arose", big_limit) # Substitute: r -> a, o -> r, s -> o, e -> s, s -> e
5
>>> feline_flips("rose", "hello", big_limit) # Substitute: r->h, o->e, s->l, e->l, length difference of 1.
5
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 6
def myfunc(temp, temp_goal, ans):
if ans > limit:
return ans + 1
if temp == '':
return len(temp_goal) + ans
elif temp_goal == '':
return len(temp) + ans
elif temp[0] == temp_goal[0]:
return myfunc(temp[1:], temp_goal[1:], ans)
else:
return myfunc(temp[1:], temp_goal[1:], ans + 1)
if start[0] == goal[0]:
return myfunc(start[1:], goal[1:], 0)
else:
return myfunc(start[1:], goal[1:], 1)
# END PROBLEM 6
def minimum_mewtations(start, goal, limit):
"""A diff function that computes the edit distance from START to GOAL.
This function takes in a string START, a string GOAL, and a number LIMIT.
Arguments:
start: a starting word
goal: a goal word
limit: a number representing an upper bound on the number of editss
>>> big_limit = 10
>>> minimum_mewtations("cats", "scat", big_limit) # cats -> scats -> scat
2
>>> minimum_mewtations("purng", "purring", big_limit) # purng -> purrng -> purring
2
>>> minimum_mewtations("ckiteus", "kittens", big_limit) # ckiteus -> kiteus -> kitteus -> kittens
3
"""
def myfunc(s, g, ans):
if ans > limit:
return ans + 1
if s == '':
return ans + len(g)
if g == '':
return ans + len(s)
if s[0] == g[0]:
return myfunc(s[1:], g[1:], ans)
else:
return min(myfunc(s[1:], g, ans + 1), myfunc(g[0] + s[0:], g, ans + 1), myfunc(s[1:], g[1:], ans + 1))
return myfunc(start, goal, 0)
def final_diff(start, goal, limit):
"""A diff function that takes in a string START, a string GOAL, and a number LIMIT.
If you implement this function, it will be used."""
assert False, 'Remove this line to use your final_diff function.'
FINAL_DIFF_LIMIT = 6 # REPLACE THIS WITH YOUR LIMIT
###########
# Phase 3 #
###########
def report_progress(sofar, prompt, user_id, upload):
"""Upload a report of your id and progress so far to the multiplayer server.
Returns the progress so far.
Arguments:
sofar: a list of the words input so far
prompt: a list of the words in the typing prompt
user_id: a number representing the id of the current user
upload: a function used to upload progress to the multiplayer server
>>> print_progress = lambda d: print('ID:', d['id'], 'Progress:', d['progress'])
>>> # The above function displays progress in the format ID: __, Progress: __
>>> print_progress({'id': 1, 'progress': 0.6})
ID: 1 Progress: 0.6
>>> sofar = ['how', 'are', 'you']
>>> prompt = ['how', 'are', 'you', 'doing', 'today']
>>> report_progress(sofar, prompt, 2, print_progress)
ID: 2 Progress: 0.6
0.6
>>> report_progress(['how', 'aree'], prompt, 3, print_progress)
ID: 3 Progress: 0.2
0.2
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 8
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
num = 0
for i in sofar:
if i == prompt[num]:
num += 1
else:
break
ans = num / len(prompt)
upload({'id': user_id, 'progress': round(ans,100)})
return round(ans,100)
# END PROBLEM 8
def time_per_word(words, times_per_player):
"""Given timing data, return a match data abstraction, which contains a
list of words and the amount of time each player took to type each word.
Arguments:
words: a list of words, in the order they are typed.
times_per_player: A list of lists of timestamps including the time
the player started typing, followed by the time
the player finished typing each word.
>>> p = [[75, 81, 84, 90, 92], [19, 29, 35, 36, 38]]
>>> match = time_per_word(['collar', 'plush', 'blush', 'repute'], p)
>>> get_words(match)
['collar', 'plush', 'blush', 'repute']
>>> get_times(match)
[[6, 3, 6, 2], [10, 6, 1, 2]]
"""
# BEGIN PROBLEM 9
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
match = []
match.append(words)
temp = []
for j in range(len(times_per_player)):
temp.append([])
for i in range(len(times_per_player[j])):
if i == len(times_per_player[j]) - 1:
break
temp[j].append(times_per_player[j][i + 1] - times_per_player[j][i])
match.append(temp)
return match
# END PROBLEM 9
def fastest_words(match):
"""Return a list of lists of which words each player typed fastest.
Arguments:
match: a match data abstraction as returned by time_per_word.
>>> p0 = [5, 1, 3]
>>> p1 = [4, 1, 6]
>>> fastest_words(match(['Just', 'have', 'fun'], [p0, p1]))
[['have', 'fun'], ['Just']]
>>> p0 # input lists should not be mutated
[5, 1, 3]
>>> p1
[4, 1, 6]
"""
player_indices = range(len(get_times(match))) # contains an *index* for each player
word_indices = range(len(get_words(match))) # contains an *index* for each word
# BEGIN PROBLEM 10
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
ans_list = [[] for k in player_indices]
for i in word_indices:
times = [time(match, j, i) for j in player_indices]
# print("DEBUG: times:", times)
# print("DEBUG: index:",times.index(min(times)))
ans_list[times.index(min(times))].append(word_at(match, i))
# print("DEBUG: ", ans_list)
return ans_list
# END PROBLEM 10
def match(words, times):
"""A data abstraction containing all words typed and their times.
Arguments:
words: A list of strings, each string representing a word typed.
times: A list of lists for how long it took for each player to type
each word.
times[i][j] = time it took for player i to type words[j].
Example input:
words: ['Hello', 'world']
times: [[5, 1], [4, 2]]
"""
assert all([type(w) == str for w in words]), 'words should be a list of strings'
assert all([type(t) == list for t in times]), 'times should be a list of lists'
assert all([isinstance(i, (int, float)) for t in times for i in t]), 'times lists should contain numbers'
assert all([len(t) == len(words) for t in times]), 'There should be one word per time.'
return [words, times]
def word_at(match, word_index):
"""A selector function that gets the word with index word_index"""
assert 0 <= word_index < len(match[0]), "word_index out of range of words"
return match[0][word_index]
''
def get_words(match):
"""A selector function for all the words in the match"""
return match[0]
def get_times(match):
"""A selector function for all typing times for all players"""
return match[1]
def time(match, player_num, word_index):
"""A selector function for the time it took player_num to type the word at word_index"""
assert word_index < len(match[0]), "word_index out of range of words"
assert player_num < len(match[1]), "player_num out of range of players"
return match[1][player_num][word_index]
def match_string(match):
"""A helper function that takes in a match object and returns a string representation of it"""
return "match(%s, %s)" % (match[0], match[1])
enable_multiplayer = False # Change to True when you're ready to race.
##########################
# Command Line Interface #
##########################
def run_typing_test(topics):
"""Measure typing speed and accuracy on the command line."""
paragraphs = lines_from_file('data/sample_paragraphs.txt')
select = lambda p: True
if topics:
select = about(topics)
i = 0
while True:
reference = choose(paragraphs, select, i)
if not reference:
print('No more paragraphs about', topics, 'are available.')
return
print('Type the following paragraph and then press enter/return.')
print('If you only type part of it, you will be scored only on that part.\n')
print(reference)
print()
start = datetime.now()
typed = input()
if not typed:
print('Goodbye.')
return
print()
elapsed = (datetime.now() - start).total_seconds()
print("Nice work!")
print('Words per minute:', wpm(typed, elapsed))
print('Accuracy: ', accuracy(typed, reference))
print('\nPress enter/return for the next paragraph or type q to quit.')
if input().strip() == 'q':
return
i += 1
@main
def run(*args):
"""Read in the command-line argument and calls corresponding functions."""
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Typing Test")
parser.add_argument('topic', help="Topic word", nargs='*')
parser.add_argument('-t', help="Run typing test", action='store_true')
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.t:
run_typing_test(args.topic)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号