WinSocket编程笔记(三)
二.Kerberos协议的实现
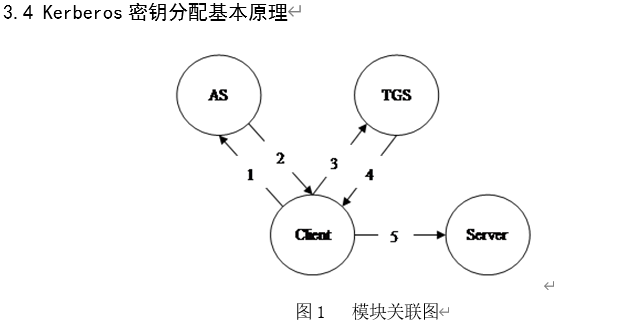
现有Alice、AS、TGS、Bob,实现Alice和Bob的安全密钥交换
这里只实现Alice和AS之间的通信
我把各个部分的代码拆开来写:
1.随机会话密钥生成
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> using namespace std; int main() { srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); int key=(rand()%9000+1000); cout << key << endl; return 0; }
2.加密算法
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> using namespace std; int main() { string plain="ada54ff89m"; string cipher=""; int key=89696; int offset = key % 26; for(int i = 0; i < plain.length(); i++) { char c = plain[i]; if(isalpha(c)) { if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') { c = 'a' + ((c - 'a' + offset) % 26); cipher += c; } else { c = 'A' + ((c - 'A' + offset) % 26); cipher += c; }} else if(isdigit(c)) { c = '0' + ((c - '0' + offset) % 10); cipher += c; } else { cipher += c; } } cout<<cipher<<endl; }
3.解密算法
#include <iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; int main() { int key=89659; string plain =""; string cipher="wsw0lmm"; int offset = key % 26; for(int i = 0; i < cipher.length(); i++) { char c = cipher[i]; if(isalpha(c)) { if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') { c = 'z' - (('z' - c + offset) % 26); plain += c; } else { c = 'Z' - (('Z' - c + offset) % 26); plain += c; } } else if(isdigit(c)) { c = '9' - (('9' - c + offset) % 10); plain += c; } else { plain += c; } } cout<<plain<<endl; }
4.map属性读取内容(对应主密钥)//后来实际操作的时候还是定义了map<string,string>,省去了int转string
#include <fstream> #include <string> #include <iostream> #include<map> using namespace std; int main() { map<string,int> userHash; userHash["ALICE"]=12345; userHash["BOB"]=23456; userHash["AS"]=34567; userHash["TGS"]=45678; int TGSkey = userHash.find("TGS")->second; cout<<TGSkey<<endl; return 0; }
然后就是结合之前的服务器代码,修改合并,之间好几次又要做到类型转换,否则会出错
服务器端主要代码:
if(*a==*secret)//存储空间位置不同,不能直接比较,验证ALICE主密钥是否和发来的密钥相同 { cout<<"验证成功"<<endl; //AS主密钥加密ALICE用户名和随机会话密钥 //int转string,KSkey -> KKSkey char t[256]; string KKSkey; sprintf(t, "%d", KSkey); KKSkey = t; cout<<"KSkey:"<<KKSkey<<endl; string plain=name+KKSkey; cout<<"明文:"<<plain<<endl; string cipher=""; int offset = 34567 % 26; for(int i = 0; i < plain.length(); i++) { char c = plain[i]; if(isalpha(c)) { if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') { c = 'a' + ((c - 'a' + offset) % 26); cipher += c; } else { c = 'A' + ((c - 'A' + offset) % 26); cipher += c; }} else if(isdigit(c)) { c = '0' + ((c - '0' + offset) % 10); cipher += c; } else { cipher += c; } } //string转char,cipher -> p char p[100]; int i; for( i=0;i<cipher.length();i++) { p[i] = cipher[i]; } p[i] = '\0'; cout<<"密文TGT:"<<p<<endl; //ALICE主密钥加密随机会话密钥 string plain2=KKSkey; string cipherr=""; int offset2 = 12345 % 26; for(int i = 0; i < plain2.length(); i++) { char c2 = plain2[i]; if(isalpha(c2)) { if(c2 >= 'a' && c2 <= 'z') { c2 = 'a' + ((c2 - 'a' + offset2) % 26); cipherr += c2; } else { c2 = 'A' + ((c2 - 'A' + offset2) % 26); cipherr += c2; }} else if(isdigit(c2)) { c2 = '0' + ((c2 - '0' + offset2) % 10); cipherr += c2; } else { cipherr += c2; } } //string转char,cipherr -> p2 char p2[100]; int i2; for( i2=0;i2<cipherr.length();i2++) { p2[i2] = cipherr[i2]; } p2[i2] = '\0'; cout<<"ALICE主密钥加密的KSkey:"<<p2<<endl; //ALICE主密钥加密TGT string plain3=cipher; string cipherrr=""; int offset3 = 12345 % 26; for(int i3 = 0; i3 < plain3.length(); i3++) { char c3 = plain3[i3]; if(isalpha(c3)) { if(c3 >= 'a' && c3 <= 'z') { c3 = 'a' + ((c3 - 'a' + offset3) % 26); cipherrr += c3; } else { c3 = 'A' + ((c3 - 'A' + offset3) % 26); cipherrr += c3; }} else if(isdigit(c3)) { c3 = '0' + ((c3 - '0' + offset3) % 10); cipherrr += c3; } else { cipherrr += c3; } } //string转char,cipherrr -> p3 char p3[100]; int i4; for( i4=0;i4<cipherrr.length();i4++) { p3[i4] = cipherrr[i4]; } p3[i4] = '\0'; cout<<"ALICE主密钥加密以后的TGT:"<<p3<<endl; }
客户端代码基本上没有变化,这里就不贴上了
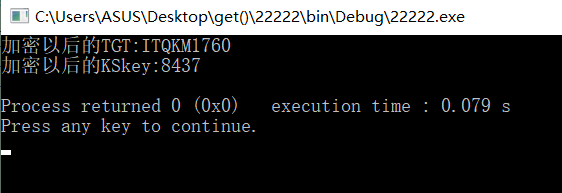
运行结果(因为不是同一次运行截图,所以结果不一样):
服务器端:

客户端:
收到信息:
(待续)
[Sign]做不出ctf题的时候很痛苦,你只能眼睁睁看着其他人领先你


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号