Java Queue 队列
队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,队列中插入元素和删除元素分别位于队列的两端。
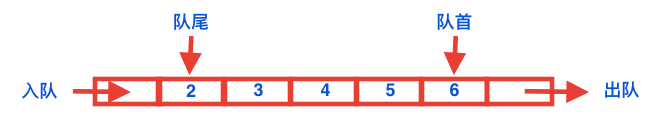
在Java中 队列实现类众多,本文不再赘述。本文探讨的是如何自定义队列实现类:
基于数组方式实现队列:
注意点:
当出队时队首为空,如果不移动队列元素那么会使得队尾在插入元素过程中越界,因队首为空,数组实际使用空间小于数组的大小,所有要移动队列的元素。
而且每次出队都要移动,使得耗费大量的时间。
import java.util.Arrays; public class ArrayQueue<E> { Object[] queue; int size; public ArrayQueue() { queue = new Object[10]; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } //入队 public void offer(E data) { ensureCapacity(size+1); queue[size++] = data; } //出队 public E poll() { if (isEmpty()) return null; E data = (E) queue[0]; System.arraycopy(queue, 1, queue, 0, size-1); //填满空位 size--; return data; } //扩容 private void ensureCapacity(int size) { if (size > queue.length) { int len = queue.length + 10; queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, len); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { queue.offer(i); } for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("出队元素:"+queue.poll()); } } }
基于链表实现的队列
由于链表的地址是不连续的的所以无须扩容。出队和入队都非常快。
class ListNode<E> { ListNode<E> next = null; E data; public ListNode(E data) { this.data = data; } } public class ListQueue<E> { private ListNode<E> head = null; //队首 private ListNode<E> end = null; //队尾 public boolean isEmpty() { return head == null; } //入队 public void offer(E e) { ListNode<E> node = new ListNode<E>(e); if (isEmpty()) { head = node; end = node; return; } end.next = node; end = node; } //出队 public E poll() { if (isEmpty()) return null; E data = head.data; head = head.next; return data; } public static void main(String[] args) { ListQueue<String> queue = new ListQueue<>(); System.out.println("入队"); queue.offer("first"); queue.offer("second"); System.out.println("出队"+queue.poll()); System.out.println("出队"+queue.poll()); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号