Heaps
Heap Definition
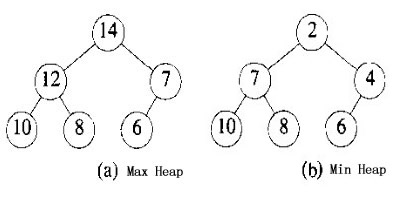
A max tree(min tree) is a tree in which the value in each node is greater(less) than or equal to those in its children(if any)
![]()
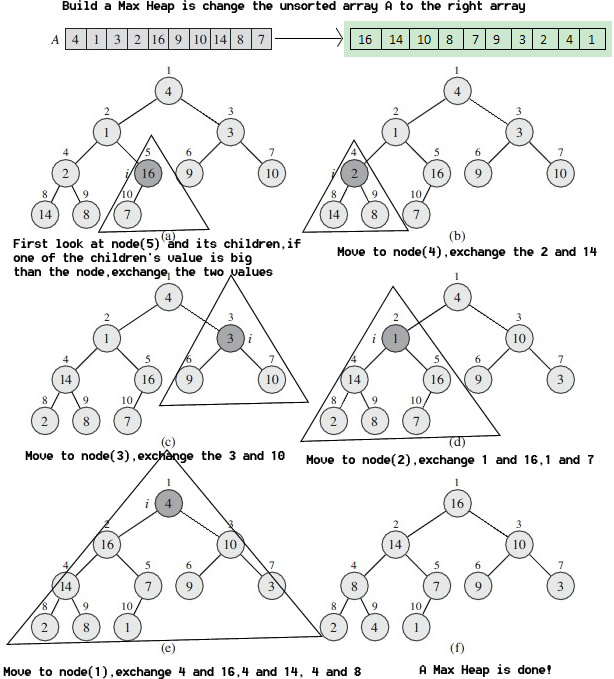
Building a max heap
Look at below figure, we adjust elements in a array, swap some elements, at last we have a max heap.
The progress begin from the last smallest heap. If it is a illegal max heap, we swap elements to let it became a legal max heap. Look at (b) in the figure. Three elements 2, 14, 8 is not a max heap. We adjust the tree by swaping 2 and 14, then it is a max heap, looking at (c) in the figure.
![]()
int a[10]={4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7};
for(int i = 4; i >= 0; i--){
int leftIndex = i * 2 + 1; // i is the node index, so the node's left child's index is i * 2 + 1
// notice: in an array , 0 is the first index.
while(leftIndex < n){ // if we do not have the left child, quit the loop
int left = a[leftIndex];
//---------------find the max element in the three element, and exchange the two elements. begin----------------------
int maxIndex = i; // In a 3 elements heap, we assume the node is the max element.
if(left > a[i]){ // If node's left child value is big than node
maxIndex = leftIndex; // we change the maxIndex value to left child's index
}
if(leftIndex + 1 < n && a[leftIndex + 1] > a[maxIndex]){ //if we have the right child, and right child's value is big
// than the max value of the two(node and its left child)
maxIndex = leftIndex + 1; // we change the maxIndex value to right child's index
}
if(maxIndex != i){ // if some child of the node is big than the node's value
swap(a[i], a[maxIndex]); // we exchange the two elements
}else{
break;
}
//---------------find the max element in the three element, and exchange the two elements. end ----------------------
i = maxIndex; // Because we exchange some value,so we will look down from the element we had changed,
// So we change the node index to the max value's index,change the left index
leftIndex = 2 * i + 1;
}
}
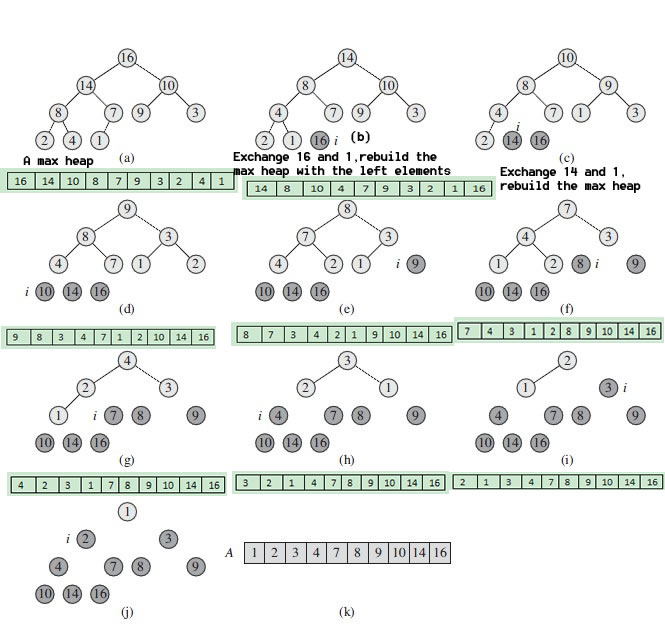
HeapSort From a max heap
First, we swap the first element and last element, and rebuild the max heap of the elments except the last element. To do such thing in the new max heap until there is only one element.
![]()
int a[10]={4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7};
BuildMaxHeap(a, 10);// build max heap
// heap sort
for(int i = 9; i >= 1;i--){
swap(a[0],a[i]);
MaxHeapify(a, 0, i); // rebuild max heap
}
Whole Code:
// HeapSort.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//A easy version, but it is not the best one.
/*
template <class T>
void MaxHeapify(T a[], int i, int n){
int leftIndex = i * 2 + 1; // i is the node index, so the node's left child's index is i * 2 + 1
// notice: in an array , 0 is the first index.
while(leftIndex < n){ // if we do not have the left child, quit the loop
int left = a[leftIndex];
//---------------find the max element in the three element, and exchange the two elements. begin----------------------
int maxIndex = i; // In a 3 elements heap, we assume the node is the max element.
if(left > a[i]){ // If node's left child value is big than node
maxIndex = leftIndex; // we change the maxIndex value to left child's index
}
if(leftIndex + 1 < n && a[leftIndex + 1] > a[maxIndex]){ //if we have the right child, and right child's value is big
// than the max value of the two(node and its left child)
maxIndex = leftIndex + 1; // we change the maxIndex value to right child's index
}
if(maxIndex != i){ // if some child of the node is big than the node's value
swap(a[i], a[maxIndex]); // we exchange the two elements
}else{
break;
}
//---------------find the max element in the three element, and exchange the two elements. end ----------------------
i = maxIndex; // Because we exchange some value,so we will look down from the element we had changed,
// So we change the node index to the max value's index,change the left index
leftIndex = 2 * i + 1;
}
}*/
//The best one.
template <class T>
//adjust elements from i to n.
void MaxHeapify(T a[], int i, int n)
{
int leftIndex, node;
node = a[i];
leftIndex = 2 * i + 1;
while (leftIndex < n)
{
//---------- finding a max element in left child and right child--------------
if (leftIndex + 1 < n && a[leftIndex + 1] > a[leftIndex])
leftIndex++;
//---------- finding a max element in left child and right child--------------
if (a[leftIndex] <= node)
break;
a[i] = a[leftIndex];
i = leftIndex;
leftIndex = 2 * i + 1;
}
a[i] = node;
}
template <class T>
void BuildMaxHeap(T a[], int n){
for(int i = n/2 - 1; i >= 0; i--){
MaxHeapify(a, i ,n);
}
}
template <class T>
void HeapSort(T a[], int n){
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1;i--){
swap(a[0],a[i]);
MaxHeapify(a, 0, i); // rebuild max heap
}
}
template <class T>
void PrintfNum(T a[], int n);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
const int NUM = 10;
int a[NUM]={4,1,3,2,16,9,10,14,8,7};
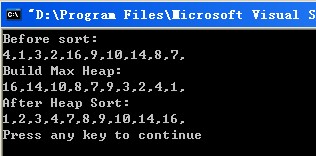
cout << "Before sort:" << endl;
int flag;
PrintfNum(a, NUM);
cout << "Build Max Heap:" << endl;
BuildMaxHeap(a, NUM);// building a max heap
PrintfNum(a, NUM);
cout << "After Heap Sort:" << endl;
HeapSort(a, NUM);
PrintfNum(a, NUM);
return 0;
}
template <class T>
void PrintfNum(T a[], int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout << a[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
}
![]() http://www.easycpp.com/?p=15
http://www.easycpp.com/?p=15
 http://www.easycpp.com/?p=15
http://www.easycpp.com/?p=15


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号