14.Android开发笔记:碎片(Fragment)
1.什么是碎片(Fragment)
碎片(Fragment)是一种可以嵌入在活动当中的UI片段,它能让程序更加合理和充分地利用大屏幕的空间,因而在平板上应用得非常广泛。
它和活动一样都能包含布局,同样都有自己的生命周期。你甚至可以将碎片理解成一个迷你型的活动,虽然这个迷你型的活动有可能和普通的活动是一样大的。
2.使用碎片(Fragment)
- 创建Fragment:
LeftFragment.java
public class LeftFragment extends Fragment {
private View view;
public LeftFragment() {
// Required empty public constructor
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_left, container, false);
}
}
布局文件LeftFragment.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".LeftFragment">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_add_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="动态切换Fragment" />
</FrameLayout>
-
同理,创建另外两个Fragmetnt:
RightFragmentOtherRightFragment
-
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/left_fragment"
android:name="com.arzirtime.fragmentdemo.LeftFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<!-- <fragment
android:id="@+id/right_fragment"
android:name="com.arzirtime.fragmentdemo.RightFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>-->
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/right_framelayout"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
replaceFragment(new RightFragment());
Button button = findViewById(R.id.btn_add_fragment);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
replaceFragment(new OtherRightFragment());
}
});
}
private void replaceFragment(Fragment fragment){
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction =fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.right_framelayout, fragment);
transaction.commit();
}
}
-
要点解析:
- 使用
添加Fragment,
其中,使用android:name指定那个自定义的Fragment
- 使用
<fragment
android:id="@+id/left_fragment"
android:name="com.arzirtime.fragmentdemo.LeftFragment"
- 动态创建或者替换Fragment:
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction =fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.right_framelayout, fragment);
transaction.commit();
其中,这里使用了布局控件FrameLayout Fragment 的容器,
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/right_framelayout"
3.在碎片中模拟返回栈
private void replaceFragment(Fragment fragment){
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction =fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.right_framelayout, fragment);
transaction.addToBackStack(null);//模拟返回堆栈的效果,按回车键返回上一个Fragment
transaction.commit();
}
先后调用
replaceFragment(new RightFragment());
replaceFragment(new OtherRightFragment());
按下回车键,显示:RightFragment, 再按下回车键,才退出程序
4.碎片和活动间进行通信
- 在Activity中获取Fragment:
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
Fragment left_fragment = fragmentManager.findFragmentById(R.id.left_fragment);
- 在Fragment中获取Activity:
MainActivity activity =(MainActivity) getActivity();//获取跟Fragment相关的Activity
当Frament是一个可复用,设计成Activity去调用Frament,参见
https://www.imooc.com/video/19294
5.碎片的生命周期
5.1Fragment生命周期
每个活动在其生命周期内可能会有哪几种状态吗?没错,一共有运行状态、暂停状态、停止状态和销毁状态这4种。
类似地,每个碎片在其生命周期内也可能会经历这几种状态,只不过在一些细小的地方会有部分区别。
- 运行状态
当一个碎片是可见的,并且它所关联的活动正处于运行状态时,该碎片也处于运行状态。 - 暂停状态
当一个活动进入暂停状态时(由于另一个未占满屏幕的活动被添加到了栈顶),与它相关联的可见碎片就会进入到暂停状态。 - 停止状态
当一个活动进入停止状态时,与它相关联的碎片就会进入到停止状态,或者通过调用FragmentTransaction的remove()、replace()方法将碎片从活动中移除,但如果在 事务提交之前调用addToBackStack()方法,这时的碎片也会进入到停止状态。总的来说,进入停止状态的碎片对用户来说是完全不可见的,有可能会被系统回收。 - 销毁状态
碎片总是依附于活动而存在的,因此当活动被销毁时,与它相关联的碎片就会进入到销毁状态。或者通过调用FragmentTransaction的remove()
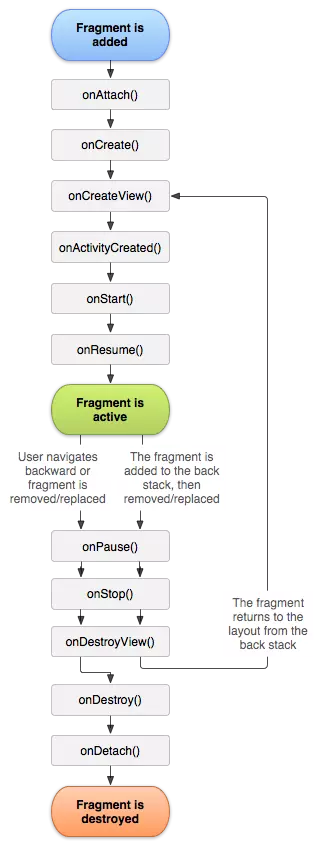
5.2Fragment回调方法
Fragment类中也提供了一系列的回调方法,以覆盖碎片生命周期的每个环节。
其中,活动中有的回调方法,碎片中几乎都有,不过碎片还提供了一些附加的回调方法,
-
onAttach()。当碎片和活动建立关联的时候调用。当fragment被加入到activity时调用(在这个方法中可以获得所在的activity -
onCreateView()。为碎片创建视图(加载布局)时调用。当activity要得到fragment的layout时,调用此方法,fragment在其中创建自己的layout(界面)。 -
onActivityCreated()。确保与碎片相关联的活动一定已经创建完毕的时候调用。当activity的onCreated()方法返回后调用此方法 -
onDestroyView()。当与碎片关联的视图被移除的时候调用。当fragment中的视图被移除的时候,调用这个方法。 -
onDetach()。当碎片和活动解除关联的时候调用。 当fragment和activity分离的时候,调用这个方法 -
1、通过 add hide show 方式来切换 Fragment
当以这种方式进行 Fragment 1 与 Fragment 2 的切换时,Fragment 隐藏的时候并不走 onDestroyView,所有的显示也不会走 onCreateView 方法,所有的 view 都会保存在内存。 -
2、使用 replace 的方法进行切换时
通过 replace 方法进行替换的时,Fragment 都是进行了销毁,重建的过程,相当于走了一整套的生命周期。 -
3、使用 ViewPager 进行切换时
ViewPager 会进行预加载;
但是切换的时候不会销毁,除非达到了 ViewPager 的缓存限制(可以通过setOffscreenPageLimit(int limit) 设置)




