转载 fhog enhanced HOG features
理论
像素级特征图
使用[−1,0,1],[−1,0,1]T[−1,0,1],[−1,0,1]T计算梯度。
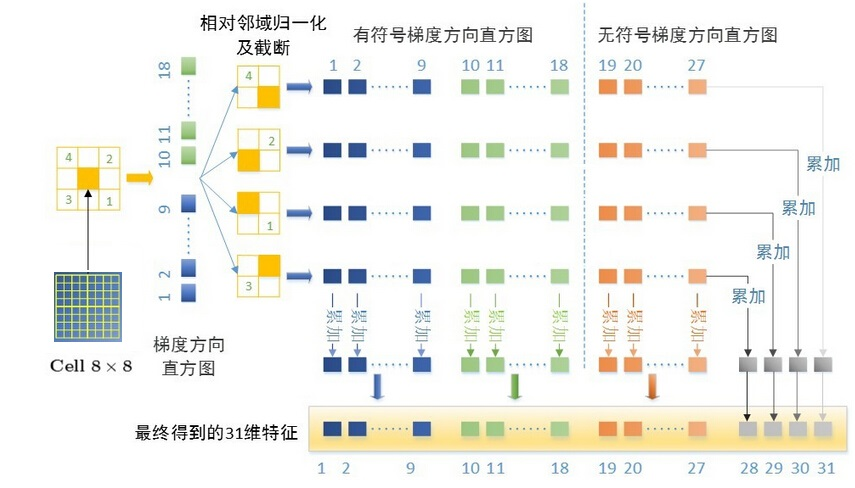
空间聚合
C(i,j),for0≤i≤⌊(w−1)k⌋,0≤j≤⌊(h−1)k⌋
C(i,j),for0≤i≤⌊(w−1)k⌋,0≤j≤⌊(h−1)k⌋
其中ww是图像的宽度,hh是图像的高度,kk就是下面的sbinsbin,注意C(i,j)=C(x,y)C(i,j)=C(x,y)而不是ii为行,jj为列。
标准化和截断
Nδ,γ(i,j)=(||C(i,j)||2+||C(i+δ,j)||2+||C(i,j+γ)||2+||C(i+δ,j+γ)||2)1/2
Nδ,γ(i,j)=(||C(i,j)||2+||C(i+δ,j)||2+||C(i,j+γ)||2+||C(i+δ,j+γ)||2)1/2
其中:
{δ,γ} ∈ {−1,1}
{δ,γ} ∈ {−1,1}
截断,文中αα取0.2:
Tα(C(i,j)/Nδ,γ(i,j))
Tα(C(i,j)/Nδ,γ(i,j))
理论和实现可能有细微的差别,但是实验效果好才是王道。
实现
#include <math.h>
#include "mex.h"
#define round(x) ((x-floor(x))>0.5 ? ceil(x) : floor(x))
// small value, used to avoid division by zero
#define eps 0.0001
// 单位方向向量
// unit vectors used to compute gradient orientation
double uu[9] = {1.0000, //0
0.9397, //20°
0.7660, //40
0.500, //60
0.1736, //80
-0.1736, //100
-0.5000, //120
-0.7660, //140
-0.9397};//160
double vv[9] = {0.0000,
0.3420,
0.6428,
0.8660,
0.9848,
0.9848,
0.8660,
0.6428,
0.3420};
static inline double min(double x, double y) { return (x <= y ? x : y); }
static inline double max(double x, double y) { return (x <= y ? y : x); }
static inline int min(int x, int y) { return (x <= y ? x : y); }
static inline int max(int x, int y) { return (x <= y ? y : x); }
// main function:
// takes a double color image and a bin size
// returns HOG features
// [input]:double color imgae and sbin
// [output]:out[0]*out[1]*32
mxArray *process(const mxArray *mximage, const mxArray *mxsbin) {
double *im = (double *)mxGetPr(mximage);
const int *dims = mxGetDimensions(mximage);//彩色图像,三通道维数
if (mxGetNumberOfDimensions(mximage) != 3 ||
dims[2] != 3 ||
mxGetClassID(mximage) != mxDOUBLE_CLASS)
mexErrMsgTxt("Invalid input");
int sbin = (int)mxGetScalar(mxsbin);
// memory for caching orientation histograms & their norms
int blocks[2];
blocks[0] = (int)round((double)dims[0]/(double)sbin);
blocks[1] = (int)round((double)dims[1]/(double)sbin);
//连续存储的三维数组
double *hist = (double *)mxCalloc(blocks[0]*blocks[1]*18, sizeof(double));
double *norm = (double *)mxCalloc(blocks[0]*blocks[1], sizeof(double));
// memory for HOG features
int out[3];
out[0] = max(blocks[0]-2, 0);
out[1] = max(blocks[1]-2, 0);
out[2] = 27+4+1;//18个方向敏感的,9个方向不敏感的,4个纹理,和1最后没用。
mxArray *mxfeat = mxCreateNumericArray(3, out, mxDOUBLE_CLASS, mxREAL);
double *feat = (double *)mxGetPr(mxfeat);
int visible[2];
visible[0] = blocks[0]*sbin;
visible[1] = blocks[1]*sbin;
for (int x = 1; x < visible[1]-1; x++) {//行
for (int y = 1; y < visible[0]-1; y++) {//列
// first color channel
// min(x,dims[1]-2),防止越出原图像的取值边界
double *s = im + min(x, dims[1]-2)*dims[0] + min(y, dims[0]-2);
//图像坐标轴为:横x,纵y
//图像是按列顺序存储的。
double dy = *(s+1) - *(s-1);
double dx = *(s+dims[0]) - *(s-dims[0]);
double v = dx*dx + dy*dy;
// second color channel
//第二个通道
s += dims[0]*dims[1];
double dy2 = *(s+1) - *(s-1);
double dx2 = *(s+dims[0]) - *(s-dims[0]);
double v2 = dx2*dx2 + dy2*dy2;
// third color channel
s += dims[0]*dims[1];
double dy3 = *(s+1) - *(s-1);
double dx3 = *(s+dims[0]) - *(s-dims[0]);
double v3 = dx3*dx3 + dy3*dy3;
// pick channel with strongest gradient
if (v2 > v) {
v = v2;
dx = dx2;
dy = dy2;
}
if (v3 > v) {
v = v3;
dx = dx3;
dy = dy3;
}
// v,dx,dy 三个通道中最强的梯度,即其方向。
// snap to one of 18 orientations 投影到18个方向
double best_dot = 0;
int best_o = 0;
for (int o = 0; o < 9; o++) {
double dot = uu[o]*dx + vv[o]*dy;//计算与单位方向向量的内积
if (dot > best_dot) {
best_dot = dot;
best_o = o;
} else if (-dot > best_dot) {
best_dot = -dot;
best_o = o+9;
}
}
// add to 4 histograms around pixel using linear interpolation
double xp = ((double)x+0.5)/(double)sbin - 0.5;
double yp = ((double)y+0.5)/(double)sbin - 0.5;
int ixp = (int)floor(xp);
int iyp = (int)floor(yp);
double vx0 = xp-ixp;
double vy0 = yp-iyp;
double vx1 = 1.0-vx0;
double vy1 = 1.0-vy0;
v = sqrt(v);
//点(ixp,iyp)为其所在cell投票
//hist为首地址,ixp*blocks[0]+iyp表示按列存储,其中blocks[0]为图像的高度,或者说成矩阵的行数
if (ixp >= 0 && iyp >= 0) {
*(hist + ixp*blocks[0] + iyp + best_o*blocks[0]*blocks[1]) +=
vx1*vy1*v;
}
//为其右边的cell进行投票
if (ixp+1 < blocks[1] && iyp >= 0) {
*(hist + (ixp+1)*blocks[0] + iyp + best_o*blocks[0]*blocks[1]) +=
vx0*vy1*v;
}
//为其下面的cell进行投票
if (ixp >= 0 && iyp+1 < blocks[0]) {
*(hist + ixp*blocks[0] + (iyp+1) + best_o*blocks[0]*blocks[1]) +=
vx1*vy0*v;
}
//对其右下角的cell进行投票
if (ixp+1 < blocks[1] && iyp+1 < blocks[0]) {
*(hist + (ixp+1)*blocks[0] + (iyp+1) + best_o*blocks[0]*blocks[1]) +=
vx0*vy0*v;
}
}
}
// compute energy in each block by summing over orientations
for (int o = 0; o < 9; o++) {
double *src1 = hist + o*blocks[0]*blocks[1];
double *src2 = hist + (o+9)*blocks[0]*blocks[1];
double *dst = norm;
double *end = norm + blocks[1]*blocks[0];
while (dst < end) {
*(dst++) += (*src1 + *src2) * (*src1 + *src2);
src1++;
src2++;
}
}
// compute features
for (int x = 0; x < out[1]; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < out[0]; y++) {
double *dst = feat + x*out[0] + y;
double *src, *p, n1, n2, n3, n4;
//首先计算blocks[1][1]处的标准化
p = norm + (x+1)*blocks[0] + y+1;
n1 = 1.0 / sqrt(*p + *(p+1) + *(p+blocks[0]) + *(p+blocks[0]+1) + eps);
p = norm + (x+1)*blocks[0] + y;
n2 = 1.0 / sqrt(*p + *(p+1) + *(p+blocks[0]) + *(p+blocks[0]+1) + eps);
p = norm + x*blocks[0] + y+1;
n3 = 1.0 / sqrt(*p + *(p+1) + *(p+blocks[0]) + *(p+blocks[0]+1) + eps);
p = norm + x*blocks[0] + y;
n4 = 1.0 / sqrt(*p + *(p+1) + *(p+blocks[0]) + *(p+blocks[0]+1) + eps);
double t1 = 0;
double t2 = 0;
double t3 = 0;
double t4 = 0;
// contrast-sensitive features
//从块的[1,1]处位置开始标准化
src = hist + (x+1)*blocks[0] + (y+1);
for (int o = 0; o < 18; o++) {
double h1 = min(*src * n1, 0.2);
double h2 = min(*src * n2, 0.2);
double h3 = min(*src * n3, 0.2);
double h4 = min(*src * n4, 0.2);
*dst = 0.5 * (h1 + h2 + h3 + h4);//0.5
t1 += h1;
t2 += h2;
t3 += h3;
t4 += h4;
dst += out[0]*out[1];
src += blocks[0]*blocks[1];
}
// contrast-insensitive features
src = hist + (x+1)*blocks[0] + (y+1);
for (int o = 0; o < 9; o++) {
double sum = *src + *(src + 9*blocks[0]*blocks[1]);
double h1 = min(sum * n1, 0.2);
double h2 = min(sum * n2, 0.2);
double h3 = min(sum * n3, 0.2);
double h4 = min(sum * n4, 0.2);
*dst = 0.5 * (h1 + h2 + h3 + h4);//0.5
dst += out[0]*out[1];
src += blocks[0]*blocks[1];
}
// texture features
*dst = 0.2357 * t1;//0.2357
dst += out[0]*out[1];
*dst = 0.2357 * t2;
dst += out[0]*out[1];
*dst = 0.2357 * t3;
dst += out[0]*out[1];
*dst = 0.2357 * t4;
// 上面的0.5 0.5 0.2357 可能是为了使得各特征的响应均衡
// truncation feature
dst += out[0]*out[1];
*dst = 0;
}
}
mxFree(hist);
mxFree(norm);
return mxfeat;
}
// matlab entry point
// F = features(image, bin)
// image should be color with double values
void mexFunction(int nlhs, mxArray *plhs[], int nrhs, const mxArray *prhs[]) {
if (nrhs != 2)
mexErrMsgTxt("Wrong number of inputs");
if (nlhs != 1)
mexErrMsgTxt("Wrong number of outputs");
plhs[0] = process(prhs[0], prhs[1]);
}
辅助理解图
图像示例
原图像
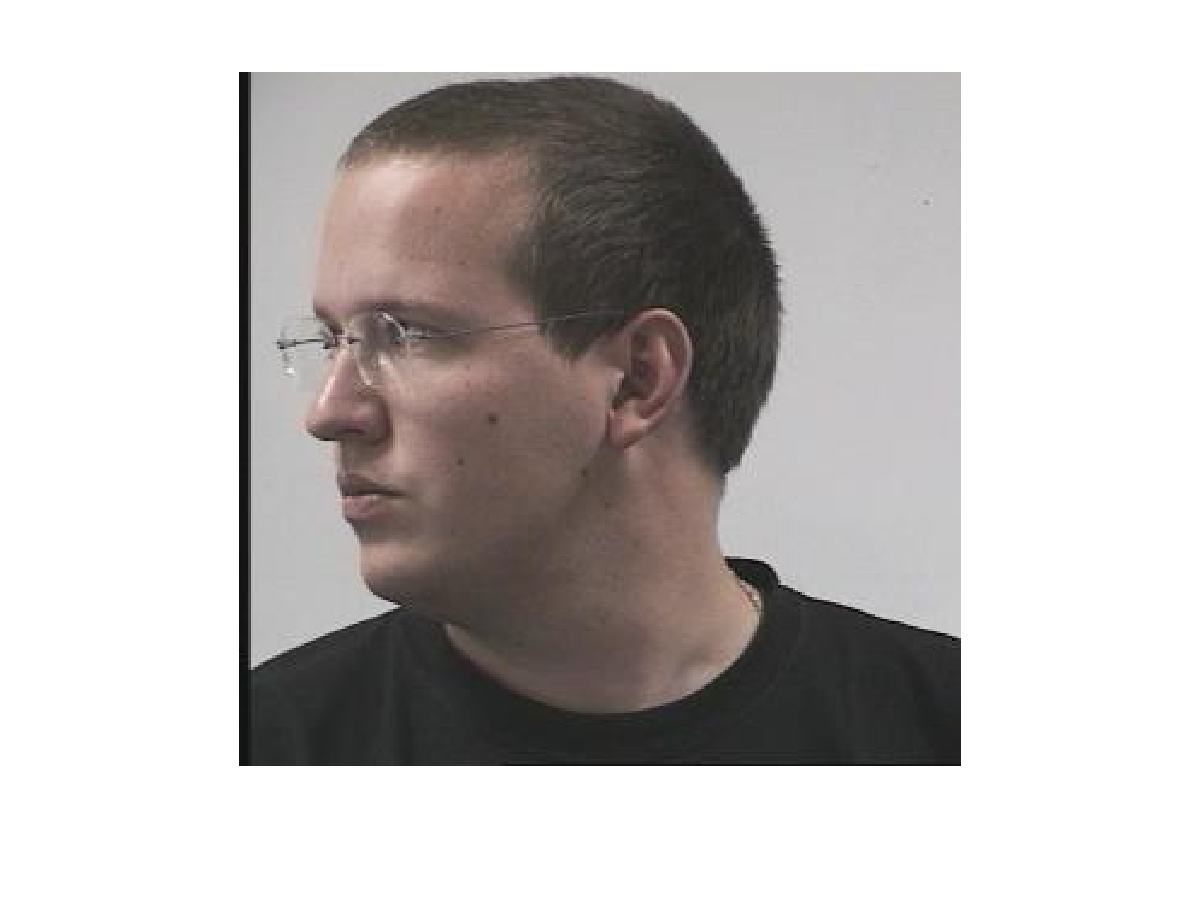

特征图像
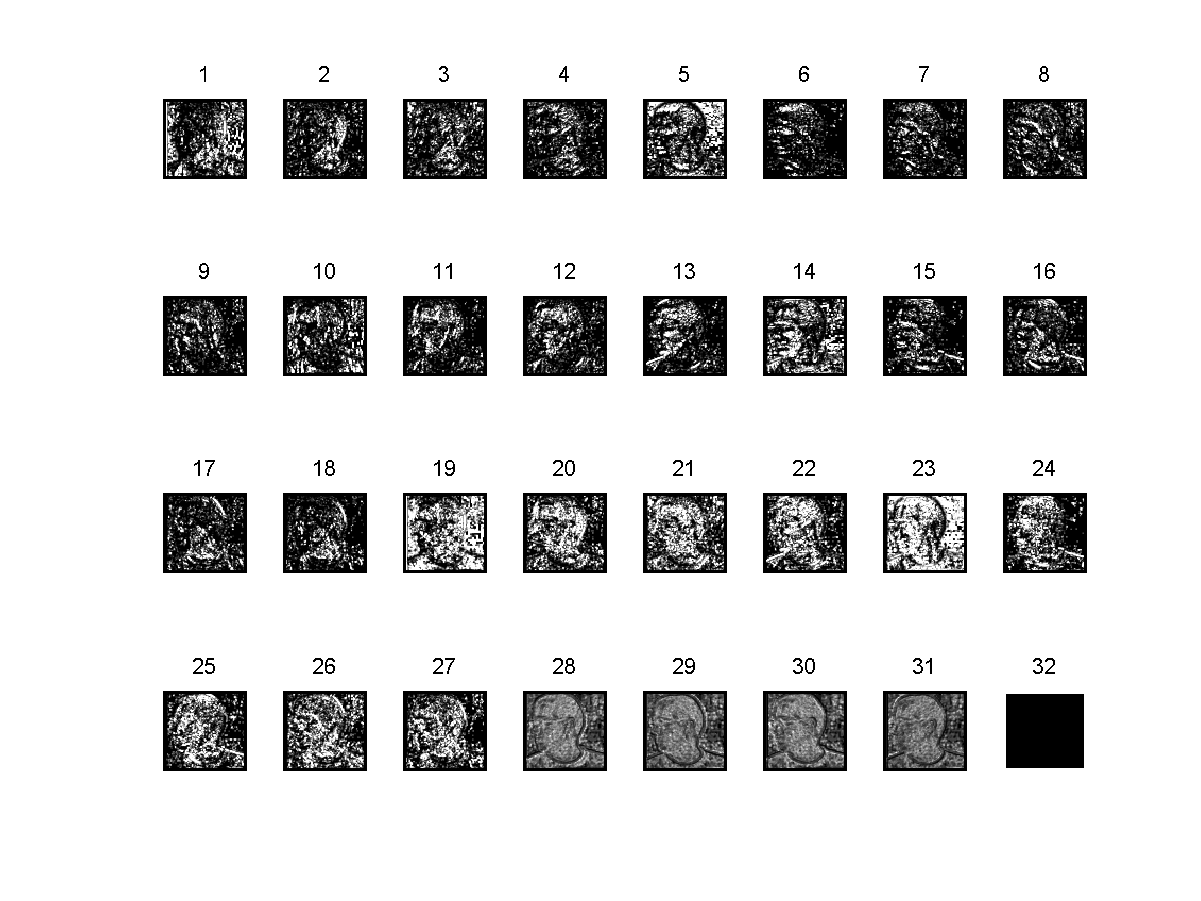
参考文献:
1、From Rigid Templates to GrammarsObject Detection with Structured Models(23-25)
2、Face Detection, Pose Estimation, and Landmark Localization in the Wild。
3、http://blog.csdn.net/ubunfans/article/details/46830833
4、http://apprenticez.github.io/2013/10/08/hog-feature/
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「机器学习的小学生」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/raby_gyl/article/details/51785926






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】