Future 是一个接口,看源码有Future 和 FutreTask 使用Demo
package java.util.concurrent; /** * A <tt>Future</tt> represents the result of an asynchronous * computation. Methods are provided to check if the computation is * complete, to wait for its completion, and to retrieve the result of * the computation. The result can only be retrieved using method * <tt>get</tt> when the computation has completed, blocking if * necessary until it is ready. Cancellation is performed by the * <tt>cancel</tt> method. Additional methods are provided to * determine if the task completed normally or was cancelled. Once a * computation has completed, the computation cannot be cancelled. * If you would like to use a <tt>Future</tt> for the sake * of cancellability but not provide a usable result, you can * declare types of the form {@code Future<?>} and * return <tt>null</tt> as a result of the underlying task. * * <p> * <b>Sample Usage</b> (Note that the following classes are all * made-up.) <p> * <pre> {@code * interface ArchiveSearcher { String search(String target); } * class App { * ExecutorService executor = ... * ArchiveSearcher searcher = ... * void showSearch(final String target) * throws InterruptedException { * Future<String> future * = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() { * public String call() { * return searcher.search(target); * }}); * displayOtherThings(); // do other things while searching * try { * displayText(future.get()); // use future * } catch (ExecutionException ex) { cleanup(); return; } * } * }}</pre> * * The {@link FutureTask} class is an implementation of <tt>Future</tt> that * implements <tt>Runnable</tt>, and so may be executed by an <tt>Executor</tt>. * For example, the above construction with <tt>submit</tt> could be replaced by: * <pre> {@code * FutureTask<String> future = * new FutureTask<String>(new Callable<String>() { * public String call() { * return searcher.search(target); * }}); * executor.execute(future);}</pre> * * <p>Memory consistency effects: Actions taken by the asynchronous computation * <a href="package-summary.html#MemoryVisibility"> <i>happen-before</i></a> * actions following the corresponding {@code Future.get()} in another thread. * * @see FutureTask * @see Executor * @since 1.5 * @author Doug Lea * @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's <tt>get</tt> method */ public interface Future<V> {
1:测试类 App.

package com.future; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; public class App { static ExecutorService executor = null; static ArchiveSearcher searcher = null; public static void main(String[] args) { executor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(); searcher = new ArchiveSearcherImp(); try { showSearch("hello"); //showSearch2("world"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } static void showSearch(final String target) throws InterruptedException { Future<String> future = executor.submit(new Callable<String>() { public String call() { return searcher.search(target); } }); System.out.println("displayOtherThings"); //boolean c = future.cancel(true); // do other things while searching try { System.out.println("displayText(" + future.get() + ")"); } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println("Future Canceled:" + future.isCancelled()); return; } } static void showSearch2(final String target) throws InterruptedException { FutureTask<String> future = new FutureTask<String>( new Callable<String>() { public String call() { return searcher.search(target); } }); executor.execute(future); } }
2:接口类

package com.future; public interface ArchiveSearcher { String search(String target); }
3:接口实现类

package com.future; public class ArchiveSearcherImp implements ArchiveSearcher { public String search(String target) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("ArchiveSearcherImp:" + target); return target + "End "; } }
这样小Demo就跑完了,帮助我们理解,
区别:(应用来自http://blog.csdn.net/naughty610/article/details/38961675)
Future是一个接口,代表可以取消的任务,并可以获得任务的执行结果
FutureTask 是基本的实现了Future和runnable接口
实现runnable接口,说明可以把FutureTask实例传入到Thread中,在一个新的线程中执行。
实现Future接口,说明可以从FutureTask中通过get取到任务的返回结果,也可以取消任务执行(通过interreput中断)
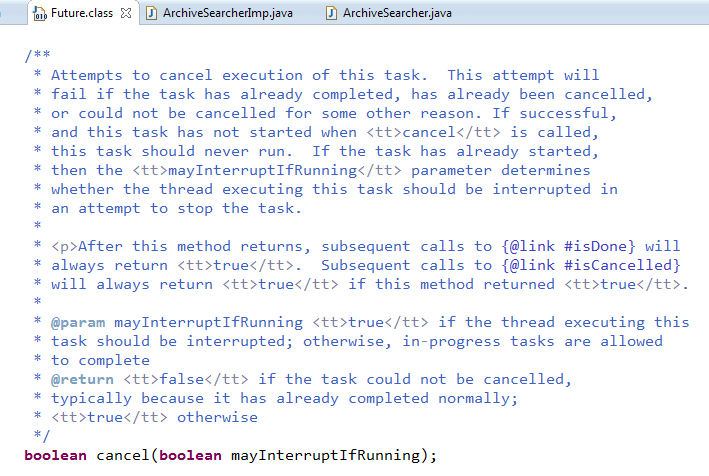
cancel方法用来取消任务,如果取消任务成功则返回true,如果取消任务失败则返回false . 参数mayInterruptIfRunning 表示是否允许取消正在执行却没有执行完毕的任务, 如果设置true,则表示可以取消正在执行过程中的任务。 如果任务已经完成,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,此方法肯定返回false,即如果取消已经完成的任务会返回false; 如果任务正在执行,若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为true,则返回true, 若mayInterruptIfRunning设置为false,则返回false;如果任务还没有执行,则无论mayInterruptIfRunning为true还是false,肯定返回true。
isDone
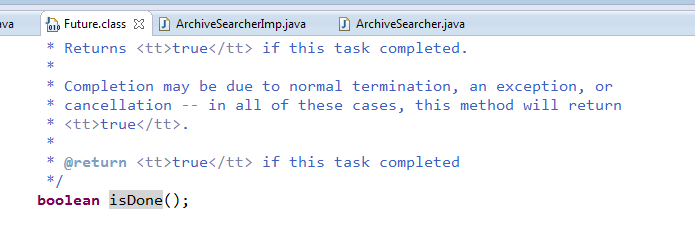
isDone方法表示任务是否已经完成,若任务完成,则返回true;




