网络编程之Reactor 模式
基本的架构是 epoll+线程池。
这篇博文主要从以下几个方面进行阐述:
(1)reactor模式的一个介绍:(只要是我的理解)
(2)关于线程池的说明。
(3)如何将epoll + 池结合起来实现一个群聊
一. reactor 模式:
从我个人的理解角度,所谓的reactor模式类似于:
场景:银行, 和三个业务工作人员 ,一个接待,有很多人在等待。
当你进去的时候,银行的接待会给你一个编号,这就是你第几个才会被业务工作人员接待。
这个时候,你就进入了等待的状态。直到轮流到你了,三个业务工作人员中的一个就会帮助你处理你的问题。
类比到计算机就是:作为接待只是给你发了一个编号,她并不关心你要处理什么业务,之后又去给后续进来的人发送编号。她就不在乎什么时候你的业务才会被处理到,至于你的业务被处理的时候,就属于业务处理人员。当然业务处理人员也不会关心给进来的人发编号,他只关心你当前要处理的业务是什么。
这种模式的优点在于:主线程只监听当前套接字是否可读或者可写,至于你要处理什么事情,就交给工作线程了。
估计现在本来清晰的你,已经被我弄糊涂了,那就用图说明:
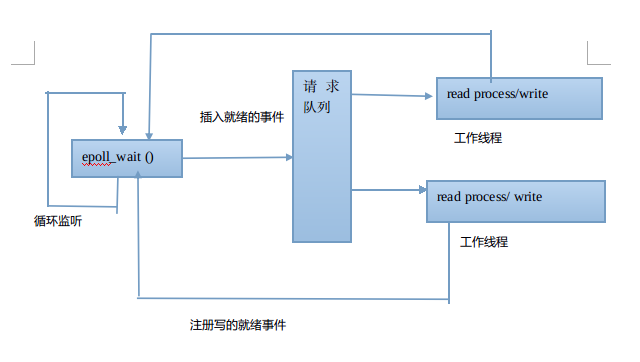
IO模型实现reactor 模式的工作流程:
(1)主线程向epoll内核事件表内注册socket上的可读就绪事件。
(2)主线程调用epoll_wait()等待socket上有数据可读
(3)当socket上有数据可读,epoll_wait 通知主线程。主线程从socket可读事件放入请求队列。
(4)睡眠在请求队列上的某个可读工作线程被唤醒,从socket上读取数据,处理客户的请求。
然后向 epoll内核事件表里注册写的就绪事件
(5)主线程调用epoll_wait()等待数据可写 。
以上就是关于Reactor模式的一个说明,下面就来看线程池的说明。
(二)线程池:
之所以会出现池这个概念就是:单个任务处理事件比较短,需要处理的任务有比较多。使用线程池可以减少在创建和撤销线程上花费的时间以及系统资源的开销。如果不使用线程池有可能创建大量的线程而消耗完系统资源以及过度的切换。
线程池的概念是从一个很简单的模型开始的,那就是生产者和消费者思想,这个模型我相信很多学过操作系统的人,都知道。主线程就相当于是生产者,而我们自己创建的大量的线程就相当于消费者(工作线程),生产者将自己需要处理的业务放到一个任务队列中,而工作线程从任务队列中取出任务,然后又加以处理。我们创建的大量线程通过一个池的东西维护起来,这个池里面包含我们创建的线程,还有那个工作的队列,互斥锁,条件变量等等很多的东西。
(三)epoll + 池的结合
#include <arpa/inet.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <assert.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <sys/epoll.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <assert.h> #include <errno.h> #include <netinet/in.h> #include "thread_pool.h" #include "thread_pool.c" #define MAX_EVENT_NUMBER 1000 #define SIZE 1024 #define MAX 10 //从主线程向工作线程数据结构 struct fd { int epollfd; int sockfd ; }; //用户说明 struct user { int sockfd ; //文件描述符 char client_buf [SIZE]; //数据的缓冲区 }; struct user user_client[MAX]; //定义一个全局的客户数据表 //由于epoll设置的EPOLLONESHOT模式,当出现errno =EAGAIN,就需要重新设置文件描述符(可读) void reset_oneshot (int epollfd , int fd) { struct epoll_event event ; event.data.fd = fd ; event.events = EPOLLIN|EPOLLET|EPOLLONESHOT ; epoll_ctl (epollfd , EPOLL_CTL_MOD, fd , &event); } //向epoll内核事件表里面添加可写的事件 int addreadfd (int epollfd , int fd , int oneshot) { struct epoll_event event ; event.data.fd = fd ; event.events |= ~ EPOLLIN ; event.events |= EPOLLOUT ; event.events |= EPOLLET; if (oneshot) { event.events |= EPOLLONESHOT ; //设置EPOLLONESHOT } epoll_ctl (epollfd , EPOLL_CTL_MOD ,fd , &event); } //群聊函数 int groupchat (int epollfd , int sockfd , char *buf) { int i = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < MAX ; i++) { if (user_client[i].sockfd == sockfd) { continue ; } strncpy (user_client[i].client_buf ,buf , strlen (buf)) ; addreadfd (epollfd , user_client[i].sockfd , 1); } } //接受数据的函数,也就是线程的回调函数 int funcation (void *args) { int sockfd = ((struct fd*)args)->sockfd ; int epollfd =((struct fd*)args)->epollfd; char buf[SIZE]; memset (buf , '\0', SIZE); printf ("start new thread to receive data on fd :%d\n", sockfd); //由于我将epoll的工作模式设置为ET模式,所以就要用一个循环来读取数据,防止数据没有读完,而丢失。 while (1) { int ret = recv (sockfd ,buf , SIZE-1 , 0); if (ret == 0) { close (sockfd); break; } else if (ret < 0) { if (errno == EAGAIN) { reset_oneshot (epollfd, sockfd); //重新设置(上面已经解释了) break; } } else { printf (" read data is %s\n", buf); sleep (5); groupchat (epollfd , sockfd, buf ); } } printf ("end thread receive data on fd : %d\n", sockfd); } //这是重新注册,将文件描述符从可写变成可读 int addagainfd (int epollfd , int fd) { struct epoll_event event; event.data.fd = fd ; event.events |= ~EPOLLOUT ; event.events = EPOLLIN|EPOLLET|EPOLLONESHOT; epoll_ctl (epollfd , EPOLL_CTL_MOD , fd , &event); } //与前面的解释一样 int reset_read_oneshot (int epollfd , int sockfd) { struct epoll_event event; event.data.fd = sockfd ; event.events = EPOLLOUT |EPOLLET |EPOLLONESHOT ; epoll_ctl (epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD , sockfd , &event); return 0 ; } //发送读的数据 int readfun (void *args) { int sockfd = ((struct fd *)args)->sockfd ; int epollfd= ((struct fd*)args)->epollfd ; int ret = send (sockfd, user_client[sockfd].client_buf , strlen (user_client[sockfd].client_buf), 0); //发送数据 if (ret == 0 ) { close (sockfd); printf ("发送数据失败\n"); return -1 ; } else if (ret == EAGAIN) { reset_read_oneshot (epollfd , sockfd); printf("send later\n"); return -1; } memset (&user_client[sockfd].client_buf , '\0', sizeof (user_client[sockfd].client_buf)); addagainfd (epollfd , sockfd);//重新设置文件描述符 } //套接字设置为非阻塞 int setnoblocking (int fd) { int old_option = fcntl (fd, F_GETFL); int new_option = old_option|O_NONBLOCK; fcntl (fd , F_SETFL , new_option); return old_option ; } int addfd (int epollfd , int fd , int oneshot) { struct epoll_event event; event.data.fd = fd ; event.events = EPOLLIN|EPOLLET ; if (oneshot) { event.events |= EPOLLONESHOT ; } epoll_ctl (epollfd , EPOLL_CTL_ADD ,fd , &event); setnoblocking (fd); return 0 ; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { struct sockaddr_in address ; const char *ip = "127.0.0.1"; int port = 8086 ; memset (&address , 0 , sizeof (address)); address.sin_family = AF_INET ; inet_pton (AF_INET ,ip , &address.sin_addr); address.sin_port =htons( port) ; int listenfd = socket (AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); assert (listen >=0); int reuse = 1; setsockopt (listenfd , SOL_SOCKET , SO_REUSEADDR , &reuse , sizeof (reuse)); //端口重用,因为出现过端口无法绑定的错误 int ret = bind (listenfd, (struct sockaddr*)&address , sizeof (address)); assert (ret >=0 ); ret = listen (listenfd , 5); assert (ret >=0); struct epoll_event events[MAX_EVENT_NUMBER]; int epollfd = epoll_create (5); //创建内核事件描述符表 assert (epollfd != -1); addfd (epollfd , listenfd, 0); thpool_t *thpool ; //线程池 thpool = thpool_init (5) ; //线程池的一个初始化 while (1) { int ret = epoll_wait (epollfd, events, MAX_EVENT_NUMBER , -1);//等待就绪的文件描述符,这个函数会将就绪的复制到events的结构体数组中。 if (ret < 0) { printf ("poll failure\n"); break ; } int i =0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < ret ; i++ ) { int sockfd = events[i].data.fd ; if (sockfd == listenfd) { struct sockaddr_in client_address ; socklen_t client_length = sizeof (client_address); int connfd = accept (listenfd , (struct sockaddr*)&client_address,&client_length); user_client[connfd].sockfd = connfd ; memset (&user_client[connfd].client_buf , '\0', sizeof (user_client[connfd].client_buf)); addfd (epollfd , connfd , 1);//将新的套接字加入到内核事件表里面。 } else if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) { struct fd fds_for_new_worker ; fds_for_new_worker.epollfd = epollfd ; fds_for_new_worker.sockfd = sockfd ; thpool_add_work (thpool, (void*)funcation ,&fds_for_new_worker);//将任务添加到工作队列中 }else if (events[i].events & EPOLLOUT) { struct fd fds_for_new_worker ; fds_for_new_worker.epollfd = epollfd ; fds_for_new_worker.sockfd = sockfd ; thpool_add_work (thpool, (void*)readfun , &fds_for_new_worker );//将任务添加到工作队列中 } } } thpool_destory (thpool); close (listenfd); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
线程池的代码在这里:
#include <unistd.h> #include <assert.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <errno.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <semaphore.h> #include "thread_pool.h" static int thpool_keepalive = 1 ; //线程池保持存活 pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER ; //静态赋值法初始化互斥锁 thpool_t * thpool_init (int threadsN){ thpool_t *tp_p ; if (!threadsN || threadsN < 1){ threadsN = 1 ; } tp_p = (thpool_t *)malloc (sizeof (thpool_t)) ; if (tp_p == NULL){ fprintf (stderr ,"thpool_init (): could not allocate memory for thread pool\n"); return NULL ; } tp_p->threads = (pthread_t *)malloc (threadsN * sizeof (pthread_t)); if (tp_p->threads == NULL){ fprintf( stderr , "could not allocation memory for thread id\n"); return NULL; } tp_p->threadsN = threadsN ; if (thpool_jobqueue_init (tp_p) == -1){ fprintf (stderr ,"could not allocate memory for job queue\n"); return NULL; } /*初始化信号*/ tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem = (sem_t *)malloc (sizeof (sem_t)); /*定位一个匿名信号量,第二个参数是1表示。这个信号量将在进程内的线程是共享的,第三个参数是信号量的初始值*/ sem_init (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem, 0 , 0 ); int t ; for (t = 0 ; t < threadsN ; t++){ printf ("Create thread %d in pool\n", t); //第四个参数是传递给函数指针的一个参数,这个函数指针就是我们所说的线程指针 if (pthread_create (&(tp_p->threads[t]) , NULL , (void *) thpool_thread_do , (void *)tp_p)){ free (tp_p->threads); free (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem); free (tp_p->jobqueue); free (tp_p); } } return tp_p ; } /* * 初始化完线程应该处理的事情 * 这里存在两个信号量, */ void thpool_thread_do (thpool_t *tp_p){ while (thpool_keepalive) { if (sem_wait (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem)) //如果工作队列中没有工作,那么所有的线程都将在这里阻塞,当他调用成功的时候,信号量-1 { fprintf(stderr , "Waiting for semaphore\n"); exit (1); } if (thpool_keepalive) { void *(*func_buff) (void *arg); void *arg_buff; thpool_job_t *job_p; pthread_mutex_lock (&mutex); job_p = thpool_jobqueue_peek (tp_p); func_buff = job_p->function ; arg_buff= job_p->arg ; thpool_jobqueue_removelast (tp_p); pthread_mutex_unlock (&mutex); func_buff (arg_buff); free (job_p); } else { return ; } } return ; } int thpool_add_work (thpool_t *tp_p ,void * (*function_p )(void *), void *arg_p){ thpool_job_t *newjob ; newjob = (thpool_job_t *)malloc (sizeof (thpool_job_t)); if (newjob == NULL) { fprintf (stderr,"couldnot allocate memory for new job\n"); exit (1); } newjob->function = function_p ; newjob->arg = arg_p ; pthread_mutex_lock (&mutex); thpool_jobqueue_add (tp_p ,newjob); pthread_mutex_unlock (&mutex); return 0 ; } void thpool_destory (thpool_t *tp_p){ int t ; thpool_keepalive = 0 ; //让所有的线程运行的线程都退出循环 for (t = 0 ; t < (tp_p->threadsN) ; t++ ){ //sem_post 会使在这个线程上阻塞的线程,不再阻塞 if (sem_post (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem) ){ fprintf (stderr,"thpool_destory () : could not bypass sem_wait ()\n"); } } if (sem_destroy (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem)!= 0){ fprintf (stderr, "thpool_destory () : could not destroy semaphore\n"); } for (t = 0 ; t< (tp_p->threadsN) ; t++) { pthread_join (tp_p->threads[t], NULL); } thpool_jobqueue_empty (tp_p); free (tp_p->threads); free (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem); free (tp_p->jobqueue); free (tp_p); } int thpool_jobqueue_init (thpool_t *tp_p) { tp_p->jobqueue = (thpool_jobqueue *)malloc (sizeof (thpool_jobqueue)); if (tp_p->jobqueue == NULL) { fprintf (stderr ,"thpool_jobqueue malloc is error\n"); return -1 ; } tp_p->jobqueue->tail = NULL ; tp_p->jobqueue->head = NULL ; tp_p->jobqueue->jobsN = 0 ; return 0 ; } void thpool_jobqueue_add (thpool_t *tp_p , thpool_job_t *newjob_p){ newjob_p->next = NULL ; newjob_p->prev = NULL ; thpool_job_t *oldfirstjob ; oldfirstjob = tp_p->jobqueue->head; switch (tp_p->jobqueue->jobsN) { case 0 : tp_p->jobqueue->tail = newjob_p; tp_p->jobqueue->head = newjob_p; break; default : oldfirstjob->prev= newjob_p ; newjob_p->next = oldfirstjob ; tp_p->jobqueue->head= newjob_p; break; } (tp_p->jobqueue->jobsN)++ ; sem_post (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem); //原子操作,信号量增加1 ,保证线程安全 int sval ; sem_getvalue (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem , &sval); //sval表示当前正在阻塞的线程数量 } int thpool_jobqueue_removelast (thpool_t *tp_p){ thpool_job_t *oldlastjob , *tmp; oldlastjob = tp_p->jobqueue->tail ; switch (tp_p->jobqueue->jobsN) { case 0 : return -1 ; break; case 1 : tp_p->jobqueue->head = NULL ; tp_p->jobqueue->tail = NULL ; break; default : tmp = oldlastjob->prev ; tmp->next = NULL ; tp_p->jobqueue->tail = oldlastjob->prev; } (tp_p->jobqueue->jobsN) -- ; int sval ; sem_getvalue (tp_p->jobqueue->queueSem, &sval); return 0 ; } thpool_job_t * thpool_jobqueue_peek (thpool_t *tp_p){ return tp_p->jobqueue->tail ; } void thpool_jobqueue_empty (thpool_t *tp_p) { thpool_job_t *curjob; curjob = tp_p->jobqueue->tail ; while (tp_p->jobqueue->jobsN){ tp_p->jobqueue->tail = curjob->prev ; free (curjob); curjob = tp_p->jobqueue->tail ; tp_p->jobqueue->jobsN -- ; } tp_p->jobqueue->tail = NULL ; tp_p->jobqueue->head = NULL ; }
线程池的.h文件
#ifndef THREAD_POOL_H #define THREAD_POOL_H #include <pthread.h> #include <semaphore.h> /*Individual job*/ typedef struct thpool_job_t { void (*function)(void* arg); //函数指针 void *arg ; //函数的参数 struct tpool_job_t *next ; //指向下一个任务 struct tpool_job_t *prev ; //指向前一个任务 }thpool_job_t ; /*job queue as doubly linked list*/ typedef struct thpool_jobqueue { thpool_job_t *head ; //队列的头指针 thpool_job_t *tail; //对列的尾指针 int jobsN; //队列中工作的个数 sem_t *queueSem; //原子信号量 }thpool_jobqueue; /*thread pool*/ typedef struct thpool_t { pthread_t *threads ; //线程的ID int threadsN ; //线程的数量 thpool_jobqueue *jobqueue; //工作队列的指针 }thpool_t; /*线程池中的线程都需要互斥锁和指向线程池的一个指针*/ typedef struct thread_data{ pthread_mutex_t *mutex_p ; thpool_t *tp_p ; }thread_data; /* * 初始化线程池 * 为线程池, 工作队列, 申请内存空间,信号等申请内存空间 * @param :将被使用的线程ID * @return :成功返回的线程池结构体,错误返回null */ thpool_t *thpool_init (int threadsN); /* * 每个线程要做的事情 * 这是一个无止境循环,当撤销这线程池的时候,这个循环才会被中断 *@param: 线程池 *@return:不做任何的事情 */ void thpool_thread_do (thpool_t *tp_p); /* *向工作队列里面添加任何 *采用来了一个行为和他的参数,添加到线程池的工作对列中去, * 如果你想添加工作函数,需要更多的参数,通过传递一个指向结构体的指针,就可以实现一个接口 * ATTENTION:为了不引起警告,你不得不将函数和参数都带上 * * @param: 添加工作的线程线程池 * @param: 这个工作的处理函数 * @param:函数的参数 * @return : int */ int thpool_t_add_work (thpool_t *tp_p ,void* (*function_p) (void *), void* arg_p ); /* *摧毁线程池 * *这将撤销这个线程池和释放所申请的内存空间,当你在调用这个函数的时候,存在有的线程还在运行中,那么 *停止他们现在所做的工作,然后他们被撤销掉 * @param:你想要撤销的线程池的指针 */ void thpool_destory (thpool_t *tp_p); /*-----------------------Queue specific---------------------------------*/ /* * 初始化队列 * @param: 指向线程池的指针 * @return :成功的时候返回是 0 ,分配内存失败的时候,返回是-1 */ int thpool_jobqueue_init (thpool_t *tp_p); /* *添加任务到队列 *一个新的工作任务将被添加到队列,在使用这个函数或者其他向别的类似这样 *函数 thpool_jobqueue_empty ()之前,这个新的任务要被申请内存空间 * * @param: 指向线程池的指针 * @param:指向一个已经申请内存空间的任务 * @return nothing */ void thpool_jobqueue_add (thpool_t * tp_p , thpool_job_t *newjob_p); /* * 移除对列的最后一个任务 *这个函数将不会被释放申请的内存空间,所以要保证 * *@param :指向线程池的指针 *@return : 成功返回0 ,如果对列是空的,就返回-1 */ int thpool_jobqueue_removelast (thpool_t *tp_p); /* *对列的最后一个任务 *在队列里面得到最后一个任务,即使队列是空的,这个函数依旧可以使用 * *参数:指向线程池结构体的指针 *返回值:得到队列中最后一个任务的指针,或者在对列是空的情况下,返回是空 */ thpool_job_t * thpool_jobqueue_peek (thpool_t *tp_p); /* *移除和撤销这个队列中的所有任务 *这个函数将删除这个队列中的所有任务,将任务对列恢复到初始化状态,因此队列的头和对列的尾都设置为NULL ,此时队列中任务= 0 * *参数:指向线程池结构体的指针 * */ void thpool_jobqueue_empty (thpool_t *tp_p); #endif





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 25岁的心里话