力扣每日一题 636.函数独占时间
有一个 单线程 CPU 正在运行一个含有 n 道函数的程序。每道函数都有一个位于 0 和 n-1 之间的唯一标识符。
函数调用 存储在一个 调用栈 上 :当一个函数调用开始时,它的标识符将会推入栈中。而当一个函数调用结束时,它的标识符将会从栈中弹出。标识符位于栈顶的函数是 当前正在执行的函数 。每当一个函数开始或者结束时,将会记录一条日志,包括函数标识符、是开始还是结束、以及相应的时间戳。
给你一个由日志组成的列表 logs ,其中 logs[i] 表示第 i 条日志消息,该消息是一个按 "{function_id}:{"start" | "end"}:{timestamp}" 进行格式化的字符串。例如,"0:start:3" 意味着标识符为 0 的函数调用在时间戳 3 的 起始开始执行 ;而 "1:end:2" 意味着标识符为 1 的函数调用在时间戳 2 的 末尾结束执行。注意,函数可以 调用多次,可能存在递归调用 。
函数的 独占时间 定义是在这个函数在程序所有函数调用中执行时间的总和,调用其他函数花费的时间不算该函数的独占时间。例如,如果一个函数被调用两次,一次调用执行 2 单位时间,另一次调用执行 1 单位时间,那么该函数的 独占时间 为 2 + 1 = 3 。
以数组形式返回每个函数的 独占时间 ,其中第 i 个下标对应的值表示标识符 i 的函数的独占时间。
示例 1:

输入:n = 2, logs = ["0:start:0","1:start:2","1:end:5","0:end:6"] 输出:[3,4] 解释: 函数 0 在时间戳 0 的起始开始执行,执行 2 个单位时间,于时间戳 1 的末尾结束执行。 函数 1 在时间戳 2 的起始开始执行,执行 4 个单位时间,于时间戳 5 的末尾结束执行。 函数 0 在时间戳 6 的开始恢复执行,执行 1 个单位时间。 所以函数 0 总共执行 2 + 1 = 3 个单位时间,函数 1 总共执行 4 个单位时间。
示例 2:
输入:n = 1, logs = ["0:start:0","0:start:2","0:end:5","0:start:6","0:end:6","0:end:7"] 输出:[8] 解释: 函数 0 在时间戳 0 的起始开始执行,执行 2 个单位时间,并递归调用它自身。 函数 0(递归调用)在时间戳 2 的起始开始执行,执行 4 个单位时间。 函数 0(初始调用)恢复执行,并立刻再次调用它自身。 函数 0(第二次递归调用)在时间戳 6 的起始开始执行,执行 1 个单位时间。 函数 0(初始调用)在时间戳 7 的起始恢复执行,执行 1 个单位时间。 所以函数 0 总共执行 2 + 4 + 1 + 1 = 8 个单位时间。
示例 3:
输入:n = 2, logs = ["0:start:0","0:start:2","0:end:5","1:start:6","1:end:6","0:end:7"] 输出:[7,1] 解释: 函数 0 在时间戳 0 的起始开始执行,执行 2 个单位时间,并递归调用它自身。 函数 0(递归调用)在时间戳 2 的起始开始执行,执行 4 个单位时间。 函数 0(初始调用)恢复执行,并立刻调用函数 1 。 函数 1在时间戳 6 的起始开始执行,执行 1 个单位时间,于时间戳 6 的末尾结束执行。 函数 0(初始调用)在时间戳 7 的起始恢复执行,执行 1 个单位时间,于时间戳 7 的末尾结束执行。 所以函数 0 总共执行 2 + 4 + 1 = 7 个单位时间,函数 1 总共执行 1 个单位时间。
示例 4:
输入:n = 2, logs = ["0:start:0","0:start:2","0:end:5","1:start:7","1:end:7","0:end:8"] 输出:[8,1]
示例 5:
输入:n = 1, logs = ["0:start:0","0:end:0"] 输出:[1]
提示:
1 <= n <= 1001 <= logs.length <= 5000 <= function_id < n0 <= timestamp <= 109- 两个开始事件不会在同一时间戳发生
- 两个结束事件不会在同一时间戳发生
- 每道函数都有一个对应
"start"日志的"end"日志
Related Topics
这题的思路,自己在做的时候,没有完成,查看官方的题解。在类似的代码上添加了个人理解的注解,菜鸟学习别人的解题思路。
//有一个 单线程 CPU 正在运行一个含有 n 道函数的程序。每道函数都有一个位于 0 和 n-1 之间的唯一标识符。
import java.util.*;
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
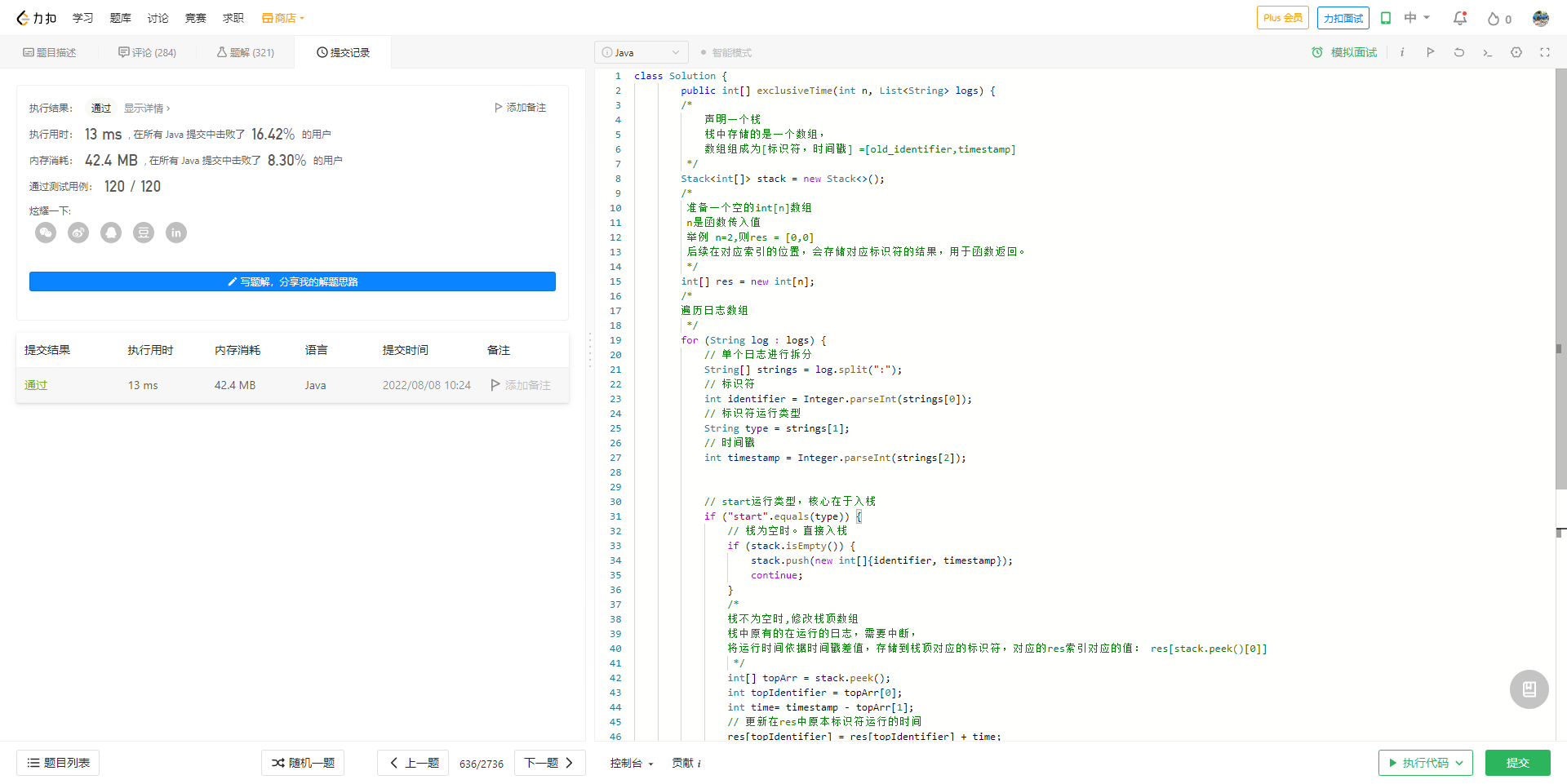
class Q636 {
public int[] exclusiveTime(int n, List<String> logs) {
/*
声明一个栈
栈中存储的是一个数组,
数组组成为[标识符,时间戳] =[identifier,timestamp]
*/
Stack<int[]> stack = new Stack<>();
/*
准备一个空的int[n]数组
n是函数传入值
举例 n=2,则res = [0,0]
后续在对应索引的位置,会存储对应标识符的结果,用于函数返回。
*/
int[] res = new int[n];
/*
遍历日志数组
*/
for (String log : logs) {
// 单个日志进行拆分
String[] strings = log.split(":");
// 标识符
int identifier = Integer.parseInt(strings[0]);
// 标识符运行类型
String type = strings[1];
// 时间戳
int timestamp = Integer.parseInt(strings[2]);
// start运行类型,核心在于入栈
if ("start".equals(type)) {
// 栈为空时。直接入栈
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.push(new int[]{identifier, timestamp});
continue;
}
/*
栈不为空时,修改栈顶数组
栈中原有的在运行的日志,需要中断,
将运行时间依据时间戳差值,存储到栈顶对应的标识符,对应的res索引对应的值: res[stack.peek()[0]]
*/
int[] topArr = stack.peek();
int topIdentifier = topArr[0];
int time= timestamp - topArr[1];
// 更新在res中原本标识符运行的时间
res[topIdentifier] = res[topIdentifier] + time;
// 更新在栈顶中原本标识符运行的时间
stack.peek()[1] = timestamp;
// 新的[标识符,时间戳] 数组成为栈顶
stack.push(new int[]{identifier, timestamp});
}
else {
/*
当是end标志符时,栈顶出栈
*/
int[] topArr = stack.pop();
int topIdentifier = topArr[0];
int startTimestamp = topArr[1];
// +1 的操作是为了对齐题目的时间格式
int time = timestamp - startTimestamp+1;
// 更新在res中出栈标识符运行的时间
res[topIdentifier] = res[topIdentifier]+time;
// 栈顶出栈后,新的栈顶的时间戳值+1。
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.peek()[1] = timestamp + 1;
}
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Q636 q636 = new Q636();
List<String> logs = new ArrayList<>();
logs.add("0:start:0");
logs.add("1:start:2");
logs.add("1:end:5");
logs.add("0:end:6");
int[] res = q636.exclusiveTime(2, logs);
for (int i : res) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
//leetcode submit region end(Prohibit modification and deletion)
等我先恰个🍎


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号