TensorFlow笔记三:从Minist数据集出发 三种经典训练方法
Minist数据集:MNIST_data 包含四个数据文件

一、方法一:经典方法 tf.matmul(X,w)+b
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import input_data import time #define paramaters learning_rate=0.01 batch_size=128 n_epochs=900 # 1.read from data file #using TF learn built in function to load MNIST data to the folder data mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data/',one_hot=True) # 2.creat placeholders for features and label # each img in mnist data is 28*28 ,therefor need a 1*784 tensor # 10 classes corresponding to 0-9 X=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[batch_size,784],name='X_placeholder') Y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[batch_size,10 ],name='Y_placeholder') # 3.creat weight and bias ,w init to random variables with mean of 0 ; # b init to 0 ,shape of b depends on Y ,shape of w depends on the dimension of X and Y_placeholder w=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[784,10],stddev=0.01),name='weights') b=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10]),name="bias") # 4.build model to predict # the model that returns the logits ,the logits will later passed through softmax layer logits=tf.matmul(X,w)+b # 5.define lose function # use cross entropy of softmax of logits as the loss function entropy=tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=Y,name='loss') loss=tf.reduce_mean(entropy) # 6.define training open # using gradient descent with learning rate of 0.01 to minimize loss optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss) with tf.Session() as sess: writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('./my_graph/logistic_reg',sess.graph) start_time= time.time() sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) n_batches=int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size) for i in range(n_epochs) : #train n_epochs times total_loss=0 for _ in range(n_batches): X_batch,Y_batch=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) _,loss_batch=sess.run([optimizer,loss],feed_dict={X:X_batch,Y:Y_batch}) total_loss +=loss_batch if i%100==0: print('Average loss epoch {0} : {1}'.format(i,total_loss/n_batches)) print('Total time: {0} seconds'.format(time.time()-start_time)) print('Optimization Finished!') # 7.test the model n_batches=int(mnist.test.num_examples/batch_size) total_correct_preds=0 for i in range(n_batches): X_batch,Y_batch=mnist.test.next_batch(batch_size) _,loss_batch,logits_batch=sess.run([optimizer,loss,logits],feed_dict={X:X_batch,Y:Y_batch}) preds=tf.nn.softmax(logits_batch) correct_preds=tf.equal(tf.argmax(preds,1),tf.argmax(Y_batch,1)) accuracy=tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct_preds,tf.float32)) total_correct_preds+=sess.run(accuracy) print('Accuracy {0}'.format(total_correct_preds/mnist.test.num_examples)) writer.close()
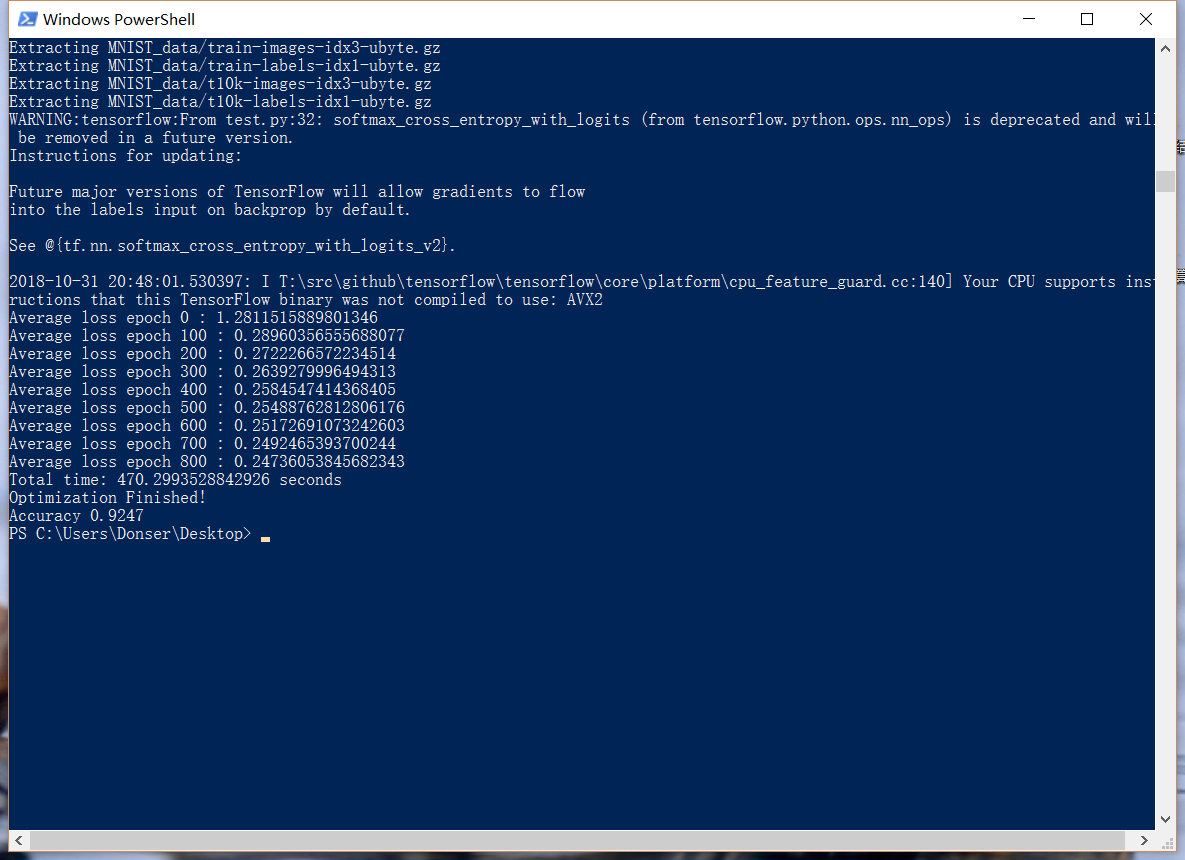
准确率大约是92%,TFboard:
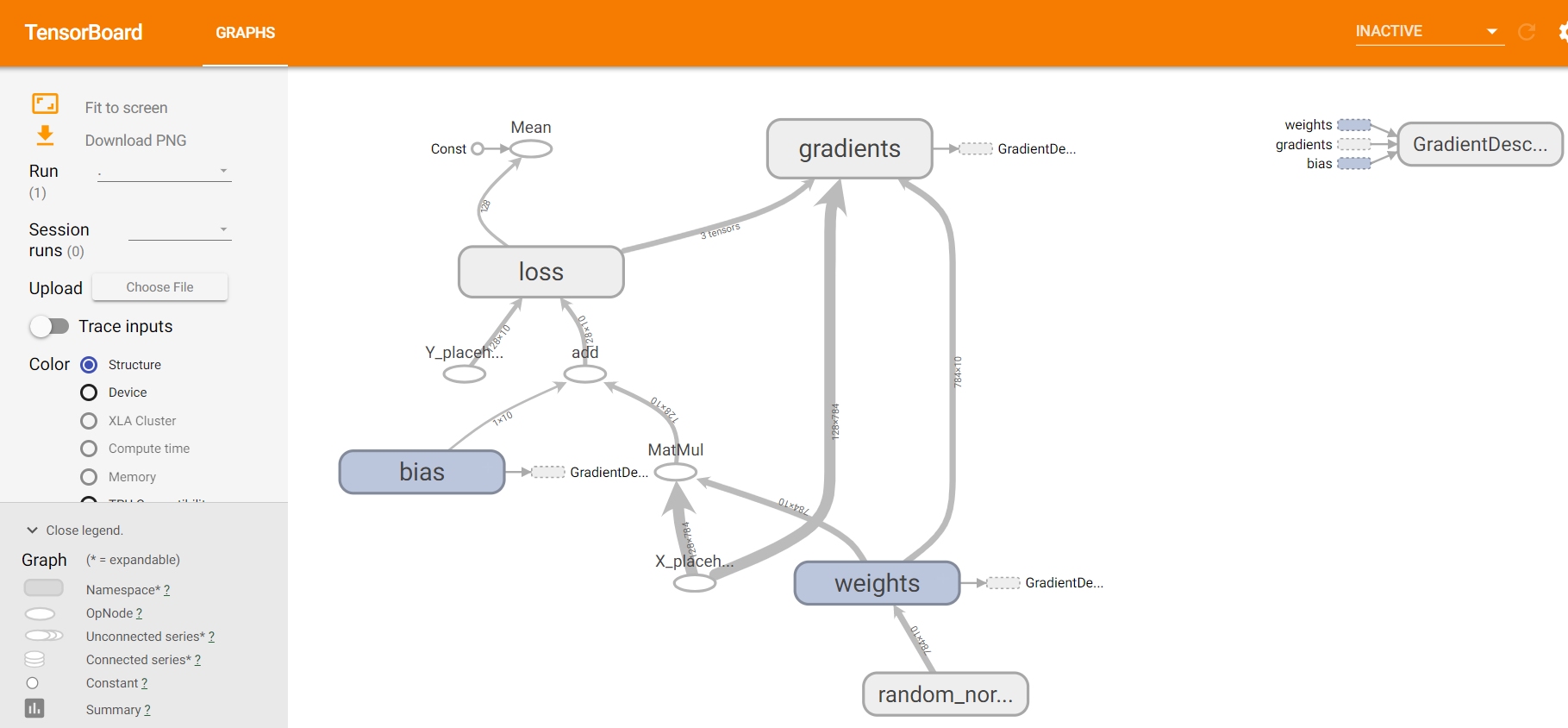
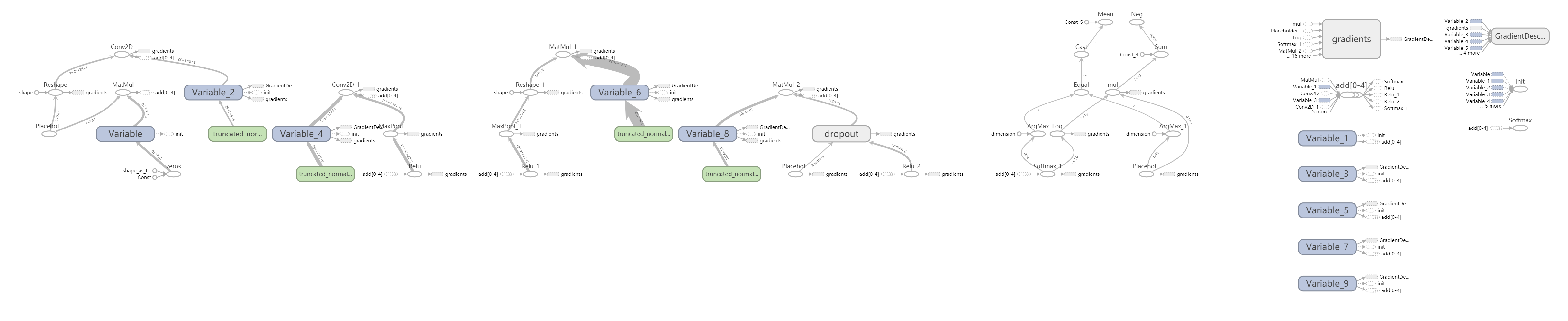
二、方法二:deep learning 卷积神经网络
# load MNIST data import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot=True) # start tensorflow interactiveSession import tensorflow as tf sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # weight initialization def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) def bias_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape = shape) return tf.Variable(initial) # convolution def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') # pooling def max_pool_2x2(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') # Create the model # placeholder x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 784]) y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 10]) # variables W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10])) b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W) + b) print (y) # first convolutinal layer w_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32]) b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) print (x) x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) print (x_image) h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, w_conv1) + b_conv1) h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) print (h_conv1) print (h_pool1) # second convolutional layer w_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64]) b_conv2 = bias_variable([64]) h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, w_conv2) + b_conv2) h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) print (h_conv2) print (h_pool2) # densely connected layer w_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64, 1024]) b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024]) h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1) print (h_fc1) # dropout keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float") h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob) print (h_fc1_drop) # readout layer w_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10]) b_fc2 = bias_variable([10]) y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, w_fc2) + b_fc2) # train and evaluate the model cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv)) train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-3).minimize(cross_entropy) #train_step = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('./my_graph/mnist_deep',sess.graph) # Train tf.initialize_all_variables().run() for i in range(1000): batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100) #print (batch_xs.shape,batch_ys) if i % 100 == 0: train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys, keep_prob:0.5}) print (("step %d, train accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))) train_step.run({x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys, keep_prob:0.5}) #print(accuracy.eval({x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels})) # Test trained model print( ("python_base accuracy %g" % accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images[0:500], y_:mnist.test.labels[0:500], keep_prob:0.5}))) writer.close()
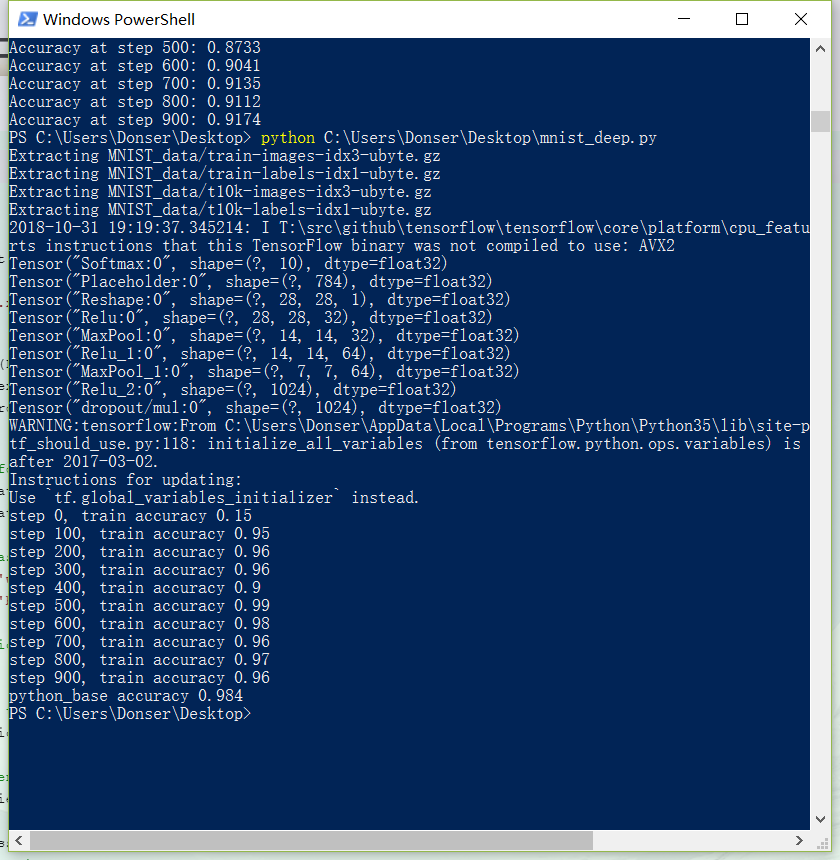
准确率达到98%,Board:
三、第三种 使用minist数据集做图像去噪
from keras.datasets import mnist from keras.layers import Input, Dense from keras.models import Model from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, UpSampling2D import numpy as np from keras.callbacks import TensorBoard import matplotlib.pyplot as plt (x_train, _), (x_test, _) = mnist.load_data() x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255. x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255. x_train = np.reshape(x_train, (len(x_train), 28, 28, 1)) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format x_test = np.reshape(x_test, (len(x_test), 28, 28, 1)) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format noise_factor = 0.5 x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_factor * np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=x_train.shape) x_test_noisy = x_test + noise_factor * np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=x_test.shape) x_train_noisy = np.clip(x_train_noisy, 0., 1.) x_test_noisy = np.clip(x_test_noisy, 0., 1.) x_train_noisy = x_train_noisy.astype(np.float) x_test_noisy = x_test_noisy.astype(np.float) input_img = Input(shape=(28, 28, 1)) # adapt this if using `channels_first` image data format x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(input_img) x = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) encoded = MaxPooling2D((2, 2), padding='same')(x) # at this point the representation is (7, 7, 32) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(encoded) x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x) x = Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) x = UpSampling2D((2, 2))(x) decoded = Conv2D(1, (3, 3), activation='sigmoid', padding='same')(x) autoencoder = Model(input_img, decoded) autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adadelta', loss='binary_crossentropy') autoencoder.fit(x_train_noisy, x_train, epochs=100, batch_size=128, shuffle=True, validation_data=(x_test_noisy, x_test), callbacks=[TensorBoard(log_dir='/tmp/tb', histogram_freq=0, write_graph=True)]) n = 10 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4)) for i in range(n): #noisy data ax = plt.subplot(3, n, i+1) plt.imshow(x_test_noisy[i].reshape(28, 28)) plt.gray() ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) #predict ax = plt.subplot(3, n, i+1+n) decoded_img = autoencoder.predict(x_test_noisy) plt.imshow(decoded_img[i].reshape(28, 28)) plt.gray() ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) #original ax = plt.subplot(3, n, i+1+2*n) plt.imshow(x_test[i].reshape(28, 28)) plt.gray() ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) plt.show()
使用了keras,见官网 https://blog.keras.io/building-autoencoders-in-keras.html
第一行是加了噪声的图,第二行是去噪以后的图,第三行是原图,回复效果较好

125s跑一个epoch,100组三个半小时搞定
tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tb


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号