Music in Car
Sasha reaches the work by car. It takes exactly k minutes. On his way he listens to music. All songs in his playlist go one by one, after listening to the i-th song Sasha gets a pleasure which equals ai. The i-th song lasts for ti minutes.
Before the beginning of his way Sasha turns on some song x and then he listens to the songs one by one: at first, the song x, then the song (x + 1), then the song number (x + 2), and so on. He listens to songs until he reaches the work or until he listens to the last song in his playlist.
Sasha can listen to each song to the end or partly.
In the second case he listens to the song for integer number of minutes, at least half of the song's length. Formally, if the length of the song equals d minutes, Sasha listens to it for no less than 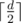 minutes, then he immediately switches it to the next song (if there is such). For example, if the length of the song which Sasha wants to partly listen to, equals 5 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 3 minutes, if the length of the song equals 8 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 4 minutes.
minutes, then he immediately switches it to the next song (if there is such). For example, if the length of the song which Sasha wants to partly listen to, equals 5 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 3 minutes, if the length of the song equals 8 minutes, then he should listen to it for at least 4 minutes.
It takes no time to switch a song.
Sasha wants to listen partly no more than w songs. If the last listened song plays for less than half of its length, then Sasha doesn't get pleasure from it and that song is not included to the list of partly listened songs. It is not allowed to skip songs. A pleasure from a song does not depend on the listening mode, for the i-th song this value equals ai.
Help Sasha to choose such x and no more than w songs for partial listening to get the maximum pleasure. Write a program to find the maximum pleasure Sasha can get from the listening to the songs on his way to the work.
The first line contains three integers n, w and k (1 ≤ w ≤ n ≤ 2·105, 1 ≤ k ≤ 2·109) — the number of songs in the playlist, the number of songs Sasha can listen to partly and time in minutes which Sasha needs to reach work.
The second line contains n positive integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 104), where ai equals the pleasure Sasha gets after listening to thei-th song.
The third line contains n positive integers t1, t2, ..., tn (2 ≤ ti ≤ 104), where ti equals the length of the i-th song in minutes.
Print the maximum pleasure Sasha can get after listening to the songs on the way to work.
7 2 11
3 4 3 5 1 4 6
7 7 3 6 5 3 9
12
8 4 20
5 6 4 3 7 5 4 1
10 12 5 12 14 8 5 8
19
1 1 5
6
9
6
1 1 3
4
7
0
In the first example Sasha needs to start listening from the song number 2. He should listen to it partly (for 4 minutes), then listen to the song number 3 to the end (for 3 minutes) and then partly listen to the song number 4 (for 3 minutes). After listening to these songs Sasha will get pleasure which equals 4 + 3 + 5 = 12. Sasha will not have time to listen to the song number 5 because he will spend4 + 3 + 3 = 10 minutes listening to songs number 2, 3 and 4 and only 1 minute is left after that.
分析:two pointer+ two sets;
一个set维护听part的歌曲,一个维护full;
右指针向右时,优先考虑能否part,若不能,考虑full或将part里替换出一个来;
左指针向右delete后,考虑能否将full的加到part里;
代码:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <climits> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <set> #include <bitset> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <list> #define rep(i,m,n) for(i=m;i<=n;i++) #define mod 1000000007 #define inf 0x3f3f3f3f #define vi vector<int> #define pb push_back #define mp make_pair #define fi first #define se second #define ll long long #define pi acos(-1.0) #define pii pair<int,int> #define Lson L, mid, ls[rt] #define Rson mid+1, R, rs[rt] #define sys system("pause") const int maxn=2e5+10; using namespace std; ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==0?p:gcd(q,p%q);} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=1;while(q){if(q&1)f=f*p%mod;p=p*p%mod;q>>=1;}return f;} inline void umax(int &p,int q){if(p<q)p=q;} inline void umin(int &p,int q){if(p>q)p=q;} inline ll read() { ll x=0;int f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int n,m,k,w,a[maxn],t[maxn],ma,now; set<pii>full,half; int main() { int i,j; scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&k,&w); rep(i,1,n)a[i]=read(); rep(i,1,n)t[i]=read(); int l,r; l=r=1; while(r<=n) { //right pointer; while(r<=n) { if(k) { if(w>=(t[r]+1)/2) { w-=(t[r]+1)/2; umax(ma,now+=a[r]); half.insert(mp(t[r],r)); r++; k--; } else break; } else { int tmp=half.begin()->fi; if(tmp<=t[r]&&w>=(t[r]+1)/2-(tmp+1)/2+tmp) { w-=(t[r]+1)/2-(tmp+1)/2+tmp; umax(ma,now+=a[r]); auto p=half.begin(); full.insert(*p); half.erase(p); half.insert(mp(t[r],r)); r++; } else if(tmp>t[r]&&w>=t[r]) { w-=t[r]; umax(ma,now+=a[r]); full.insert(mp(t[r],r)); r++; } else break; } } //left pointer; if(l<r) { if(full.find(mp(t[l],l))!=full.end()) { w+=t[l]; now-=a[l]; full.erase(mp(t[l],l)); } else { w+=(t[l]+1)/2; now-=a[l]; half.erase(mp(t[l],l)); k++; if(!full.empty()) { auto p=--full.end(); w+=p->fi-(p->fi+1)/2; half.insert(*p); k--; full.erase(p); } } l++; } else l++,r++; } printf("%d\n",ma); return 0; }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号