141. Linked List Cycle
Problem:
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Example 1:
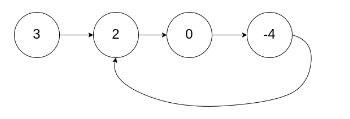
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
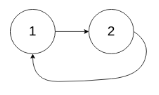
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: true
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: false
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.

思路:
解释一下所给输入中包含pos的意思,因为给的函数里面并没有这个输入。pos存在的意义是为了构造一个有环或无环的链表(从尾节点指向pos指向的节点,为-1则无环),而我们所给的就是头结点head,所以不能用pos来判断是否有环。
1.设置2个指针:fast和slow;
2.fast每次移动2个节点,slow每次移动一个节点;
3.如果fast和slow指向的节点相同,说明有循环,不相同则说明不存在循环。
Solution:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head) return false;
ListNode *fast = head, *slow = head;
while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { //这种方法只能证明环存在,而不能找到环开始的节点位置
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) return true;
}
return false;
}
性能:
Runtime: 12 ms Memory Usage: 9.9 MB
相关链接如下:

知乎:littledy
GitHub主页:https://github.com/littledy
github.io:https://littledy.github.io/
欢迎关注个人微信公众号:小邓杂谈,扫描下方二维码即可

作者:littledy
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



