一 原理解析
从下图一中可以看出,该算法的原理也是先检测出来啸叫,然后通过陷波器来进行啸叫抑制的,和笔者以前分析的所用方法基本耦合。
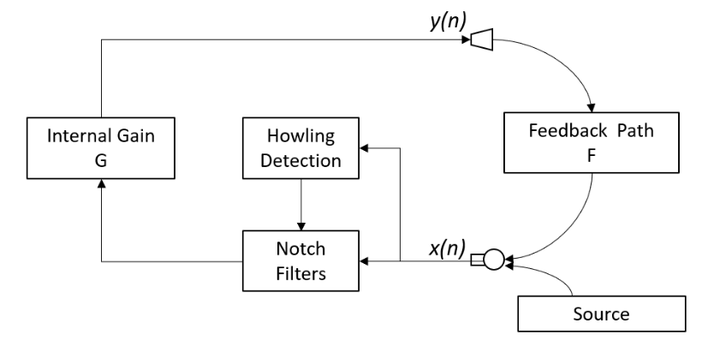
二 源码分析
函数PAPR:计算峰值功率和平均功率的比值
def papr(frame, threshold): """Peak-to-Avarage Power Ratio (PAPR) Returns all frequency indices where power is greater than avarage power + threshold, which are possible candidates where howling occurs.
函数PTPR:计算峰值功率和阈值功率的比值,这里的阈值功率是系统可以产生啸叫的功率阈值,根实际环境有关系。
def ptpr(frame, threshold): """Peak-to-Threshold Power Ratio (PTPR)
函数PNPR:计算峰值功率和相邻频段功率的比值
def pnpr(frame, threshold): """Peak-to-Neighboring Power Ratio (PNPR) Returns all frequency indices of power peaks, which are greater than neighboring frequency bins by a threshold.
函数howling_detect该函数是检测出啸叫频点,是最重要的部分,啸叫抑制的难点就是怎么检出啸叫抑制的频点:这里通过三个维度来筛选,找出共同的频点,认为共同的频点就是啸叫的频点。
def howling_detect(frame, win, nFFT, Slen, candidates, frame_id): insign = win * frame spec = np.fft.fft(insign, nFFT, axis=0) #========== Howling Detection Stage =====================# ptpr_idx = pyHowling.ptpr(spec[:Slen], 10) papr_idx, papr = pyHowling.papr(spec[:Slen], 10) pnpr_idx = pyHowling.pnpr(spec[:Slen], 15) intersec_idx = np.intersect1d(ptpr_idx, np.intersect1d(papr_idx,pnpr_idx)) #print("papr:",papr_idx) #print("pnpr:",pnpr_idx) #print("intersection:", intersec_idx) for idx in intersec_idx: candidates[idx][frame_id] = 1 ipmp = pyHowling.ipmp(candidates, frame_id) #print("ipmp:",ipmp) result = pyHowling.screening(spec, ipmp) #print("result:", result) return result
三 总结
该算法从 效果来看,效果还是比较不错的,但是有一个维度难以把握,就是阈值的设置,这个是和实际环境有关系的,需要根据实际环境调试,这个也决定了算法的准确度。
|
作者:虚生 出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/dylancao/ 以音频和传感器算法为核心的智能可穿戴产品解决方案提供商 ,提供可穿戴智能软硬件解决方案的设计,开发和咨询服务。 勾搭热线:邮箱:1173496664@qq.com weixin:18019245820 市场技术对接群:347609188 |

|






【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 微软正式发布.NET 10 Preview 1:开启下一代开发框架新篇章
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· PowerShell开发游戏 · 打蜜蜂
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验
· WPF到Web的无缝过渡:英雄联盟客户端的OpenSilver迁移实战
2021-04-08 2.4G无线音频传输方案市场调研分析
2019-04-08 gcc链接,去掉不用的函数和data